
05110244
.pdfProduction. Attitudinal research7 should affect the product to be produced, so production is inevitably based on marketing Intelligence study8. Marketing investigates stages before, during and after production and also the stage following sales.
Sales. Sales are always involved with customers service of all kinds. Markets for consumer products9 are segmented on the basis of demographic and psychographic data research.
Communications and advertising. The communications mix10 comprises advertising, public relations, direct mail and special events such as product shows, conferences and exhibitions. Advertising is an important means of promoting the goods that have been produced already, as well as new lines in business. Nowadays there are special departments and agencies dealing with advertising. Different kinds of mass media – TV, radio, newspapers, cinema, magazines, posters – are used for advertising aims. Special leaflets, booklets and other printed matters with the information about goods may be published for the same purpose. The choice of media for advertising depends on the kind of goods and on the local conditions and people's habits.
____________________
1market research – изучение конъюнктуры рынка, маркетинговое исследование
2market potential – емкость рынка
3promotion of sales – мероприятия по содействию сбыта
4post-sales servicing – гарантийное обслуживание
5communications – зд. организация контактов с потребите-
лями
6competitors' interests and claims – интересы и претензии конкурентов
7consumer products – потребительские товары
8the communications mix – мероприятия по организации контактов с потребителями
9printed matter – печатные материалы
TASKS
I. Translate the following words and learn their pronuncia-
tion:
preferences; exhibitions; polls; magazines; leaflets; fee; choice; assortment; promotion; potential; mass media; advertising; experiment; strategy; originally; locally; competitive; attitudinal; environmental; uncontrollable; demographic; psychographic; preliminary.
II. Explain the meaning of the following words and phrases in English:
embassy; market research; market potential; seasonal factors; controllable factors; consumer products; the communications mix; overproduction; direct mail; sales promotion, public relations.
III. Give English equivalents for the following Russian words and phrases:
ценовая политика; торговые представители; традиции и обычаи; факторы, связанные с внешней средой; связи с общественностью; избежать перепроизводства; координировать спрос и предложение; проводить выставки и конференции; считаться конкурентоспособным; включать в себя рекламное дело; проводить сегментацию рынка; влиять на выбор продукции.
IV. Answer the following questions:
1)What was the original aim of marketing?
2)What is the main purpose of marketing nowadays?
3)Where can information for market research be obtained?
4)What are the most important parts of any marketing research?
5)How many parts does marketing strategy include?
6)What is meant by planning?
7)Why is production inevitably based on marketing study?
8)What is the aim of advertising?
61 |
62 |
TOPIC 10. ADVERTISING
Before reading the text think of the following points:
1.How do you think advertising is important for producers/customers?
2.What ways of advertising a product/service do you know?
3.What do you like/hate in advertising nowadays?
TEXT
It’s well-known fact that selling an unknown product “is like rowing a boat upstream, movement is mostly backwards”. So, if the company wants to succeed in generating sales, provide an income and stable growth for its business, it should acknowledge the importance of capturing the public’s attention and increasing the level of brand name recognition. Consequently, later or sooner the company will face the problem of choice of types and means of advertising. That is why we find this question to be worth being discussed.
Depending on business objectives a company wants to achieve 3 principal types of advertising should be pointed out:
image-making advertising (or soft selling),
stimulating advertising (or hard selling),
advertising of stability (or reminder advertising).
Image-making advertising (soft selling)
The slogan of image-making ad is the delicate and emotionally
grounded “Like me!” The first aim of this type is to acquaint potential customers with the product, its destination and characteristics, to claim product’s relevance to consumers and its significant difference from competing products. Image-making ad is designed to build strong brand image and create a propitious attitude, recognition and awareness to the company or the product. This is an emotional way of persuasion aimed at subconsciousness through the association of ideas, techniques and renascence of comfortable psychological environment and situation, which the consumer associates himself with and is involved in symbolism, emotions and in-depth motivation are enabled here. Soft selling is appropriate for a new brand launch and farreaching objectives on its support and development. Ads of this type
impact not only upon potential consumers but all sections of the population. That will provide innovations with already created favorable reception by the customers, if the company diversifies its product range. Such kind of advertising will help in many respects to smooth away failures of future advertising campaigns.
The most effective means of image-making advertising are
trailers on TV;
print advertising in popular magazines and newspapers;
participation in charity actions and its covering in mass media;
outdoor advertising which can be subdivided into 7 types.
1.Billboard advertising – the most traditional type of outdoor advertising, is usually exposed on the busiest streets and highways and becomes the most accessible and obvious medium of information for drivers and passengers. A large address program of billboards (series) allows to cover all important vehicular and pedestrian arteries of the city and to produce a cumulative effect of frequency.
2.Consoles advertising. Advertising series of billboards installed on contact-line supports or on detached consoles have become popular because they are widespread and it is possible to place them in the close proximity of advertised objects. Targeted and serial placement of console advertising enables advertiser to score a high information effect.
3.Necessary attribute of any kind of business, signboards are the face of any company, enterprise, shop, drugstore, etc.
4.Roadside Stoppers usually serve for operative advertising information more often and are a widely spread, handy and mobile advertising type, which blends well with urban landscape.
5.Citylights are a widespread type of advertising. Functionality and small sizes of them allow their installation in the central areas of the city – both along the busy motor highways running through the center, and on sidewalks and pedestrian zones. Owing to moderate design and utility, citylights blend easily and organically with any urban environment. Concentration of citylights in the busiest districts and key areas of the city, business and shopping centers increases efficiency of an advertising structure of this format.
63 |
64 |

6.Over-road banners. Advertisements above carriageway have an important advantage: they always remain in view of drivers and passengers.
7.Transport advertising (motor transport and public transport) is very effective, since it covers mass audience, and the complexity of routes produces a feeling of omnipresence of advertising, owing to which it is perfectly suitable whenever it is necessary to introduce a new trade mark to the public or to develop corporate image.
Stimulator advertising (hard selling)
As it goes from the appellation, this type of advertising makes for motivating customers to buy the concrete product of the concrete company as well as sale stimulating and acceleration of commodity circulation. Such kind of ad implies a rational, informative, wellgrounded and substantiated method of persuasion with the direct appeal “Buy Me!” slogan. Unlike soft selling, hard one is a concrete consumer oriented type. It’s the most widespread type of advertising, as a rule, using verbal arguments as to advantageous features of the product, etc. In most cases this type refers to promotion with shortterm objectives – direct influence over the audiences through sell-outs, etc. Meanwhile, stimulator advertising is a component of imagermaker one as some of hard selling ads create a definite image even if not of the whole company but of the business line the firm presents. So, while planning stimulator advertising activities don’t forget of the company image integrity.
The most effective means of hard selling are:
recurrent ads in newspapers and magazines, that are popular among the potential customers;
direct mail;
radio advertising;
participation in exhibitions;TV advertising.
Advertising of stability (reminder advertising)
Even if the company gets sales going and its brand is recognized, it’s necessary to keep product in public eye and from time to time to consolidate the achievements by advertising. Advertising of stability doesn’t rely on any specific type of appeal, its only objective is to keep the brand name in the mind of the consumers by means of
hidden advertising in the form of articles about the company’s activity and products;
participation in exhibitions;
direct mail of prospects (reports) about the annual activity of the company to the constant partners.
Answer the questions:
1.What are the principal types of advertising?
2.What is soft selling meant for? Who does it appeal to?
3.What are the effective means of image-making advertising? Which is most developed in your country/city?
4.Characterise hard selling. Enumerate means it uses.
5.What is special about reminder advertising? Is it widespread in you country/city?
TOPIC 11. WHOLESALING, RETAILING
TEXT 1
Wholesaling
Wholesalers are one of the two major institutions that make up a firm’s marketing channel. They are persons or firm who sell to retailers and other wholesalers or to industrial users but who do not sell in significant amounts to ultimate consumer.
There are two large groups of independent wholesalers: merchant wholesalers and agents and brokers. Merchant wholesalers take title to the good they handle. Selling agent, brokers are classified as agent wholesaling middlemen because they do not take title to goods.
The operating expenses of wholesaling middleman vary considerably, depending on the services provided out and the cost involved. The services include storage facilities in conveniently located warehouses, market coverage by a sales force, financing for retailers and manufacturers, market information for retailer, management services, retail sales training and merchandising assistance and advice.
Although the percentage of wholesale trade by manufacturer owned facilities has increased since 1925 independent wholesaling middlemen continue to account for 90 percent of all wholesale estab-
65 |
66 |
lishments and nearly two-thirds of total wholesale trade. They accomplish this by continuing to provide desired services to manufacturers, retailers, and industrial buyers.
Answer the questions:
1.The term wholesaling – how is it applied?
2.What are the groups of independent wholesalers?
3.What do the operating expenses of wholesaling middleman depend on?
TEXT 2
Retailing
(the description if Harrods department store)
When the door opened at 9 a.m. thousands of people pushed in and run through the store four floors. Many had camped overnight in the street outside. By midmorning the crush was so thick it was impossible to enter or leave the store. There were 6.500 staff workers on duty to deal with the crowds including a beefed-up security force to handle a situation described by store officials as perfect cover for shoplifters. In the china department according to one witness, there seemed to be more breakages than purchases. In the fur department a group of people demonstrating against cruelty to animals was ignored by women sweeping half-price luxury furs off the racks. Security men had to restore order in the electronics department where jostling crowds caused more than $12.ooo worth of damage to stereo equipment and television sets. One customer was dragged out through an emergency exit to end a tussle over a bargain. A fistfight was narrowly avoided in the linen department where satin-look sheets were selling for $2.40 each.
The store where Queen Elizabeth has some of her shoppings done, holds the most popular of the annual New Year’s sales that turn London department stores into battle grounds.
Almost a city in itself , it arranges funerals, caters, weddings, plans vacations, sеlls hоuses and has its own bank. It advertises itself as the store where you can buy “a pound of potatoes or mink coat."
What is Retailing?
Harrods is engaged in retailing activities. Giant stores like Harrods may generate daily sales of several million dollars, while a small shoe store may have annual sales of less than $ 100.000. But both large and small perform the major activity: creating time, place and ownership utility. In a very real sense, retailers are the marketing channel for most consumers, since the typical shopper has little contact with manufacturers and virtually none with wholesaling intermediaries. As a result, the services provided – location, store hours, quality of salespeople, store layout, selection and the returns policy, among others – are often more important than the physical product in developing consumer images of the products and services offered.
Retailing may be defined as all the activities involved in the sale of products and services to the ultimate consumer.
The supermarket is a large-scale departmentalized retail store offering a variety of food products such as meat products, canned goods, and frozen goods in addition to various nonfood items. It operates on a self-service bases and emphasizes low prices and adequate parking facilities.
Supermarket customers typically shop once or twice a week. With a razor-thin profit margin (only about 1 percent of sales af-
ter taxes) supermarkets complete through careful planning of retail displays in order to sell a large amount of merchandise each week and by retaining a low investment in inventory. In an attempt to fight the fast-food threat – the tendency of consumers to eat many of their meals outside the home – supermarkets have begun to feature their own delicatessen. In Florida, the supermarkets sell fried chicken by the bucket. Supermarkets General of New Jersey has even established cafeterias and snack shops in factories.
Supermarkets carry nonfood products such as magazines, records, small kitchen utensils, toiletries and toys for two reasons: consumers have displayed a willingness to buy such items in supermarkets, and supermarket managers like the profit margin on the items, which is higher than that of food products. Nonfood sales account for almost one-fourth of all supermarket sales.
67 |
68 |

Department store is a series of special stores under one roof. It is a large retail firm handling a variety of merchandise: women’s wear and accessories, household linens and dry goods, home furnishings, appliances and furniture.
Department stores are known for offering their customers a wide variety of services, such as charge accounts, delivery, gift wrapping and liberal return privileges. In addition, some 50 % of their employees and 40 % of their floor space are devoted to nonselling activities.
Now Department stores have faced intensified competition in the past thirty years. Their relatively high operating costs make them vulnerable to such new retailing innovations as discount stores, catalog merchandisers, and hypermarkets.
In addition, department stores were typically located in downtown business districts and experienced the problems associated with limited parking, traffic congestion, and urban migration to the suburbs.
They have displayed a willingness to adapt to changing consumer desires. They have added bargain basement and expanded parking facilities in attempts to compete with discount operations and suburban retailers. They have also followed the movement of the population to the suburbs by opening major branches in outlying shopping centers.
Answer the questions:
1.What is retailing?
2.Why do they say retailers are the marketing channel for most consumers?
3.What is a supermarket?
4.What is a department store?
5.What are the problems department stores have faced for the past 30 years?
TOPIC 12. BUDGETING
I. Study the terms:
Budget: the financial operating plan or forecast for an organization for a fixed period. The budget shows what income is anticipated and how the resources will be used during the budget period.
Master budget: the total of separate budgets from different departments within a company that shows in detail how the entire business operates.
Financial Forecast: an estimation of what will probably happen in the future, based on the past and present fiscal records.
Control Device: a standard plan for the performance of a business by which its operations may be measured and regulated.
Retail Trade Business: a business that acquires goods to sell to general public. A wholesale business is a middleman operation that acquires goods from the manufacturer and then sells them in turn to the retailer.
Retail Outlet: a unit of the retail business, usually a store.
Unit Price: in the context of retailing, the price at which a single item is sold to the buyer.
Sales Mix: the inventory of items available for sale. Geographical Breakout: organisation of a business on the basis
of location.
Allowances: special terms of sale granted to specified custom-
ers.
Discount: a reduction in the price of an item for sale. Inflationary period: a period of rising prices in which more
money becomes available in relation to goods.
Recession: a period of reduced general economic activity market by a decline in employment, profits, production and sales.
Inventory: in retailing, tangible property either held for sale or to be consumed in the sale of goods.
Lead Time: the time that elapses between ordering and displaying merchandize.
General and Administrative Expenses: such expenses as employees’ and officers’ salaries, utility bills, payroll, taxes, stationery and office suppliers.
Break-even Point: minimum volume of sales a company needs to enable it to function as a going concern without realization a profit or incurring a loss.
Accrual Basis: the method of keeping accounts that recognizes income when earned and expenses when incurred regardless of when cash is received or disbursed.
69 |
70 |
Obligations Outstanding: unpaid or unmet obligations, usually
debts.
Collectible Receivables: goods sold for which the firm has not been paid, but which it is reasonably sure of collecting.
Cash Flow: the predicted pattern of actual cash to be received by a business.
II. Find the answers in the text:
1.What does budgeting involve? What is its primary objective?
2.What is the accounting period for the budget? When can a budget be reviewed or changed?
3.What is included in the financed forecast? What can a flexible master budget be used for?
4.What kinds of activities are included in a business involved in retail trade. For which of them would budget be prepared?
5.What are the important entries in the budget? What else must be added if the business sells more than one item?
6.What items could be grouped to form a sales department in a furniture store?
7.When do sales figures have to be adjusted?
8.In what way can the purchases budget be considered the ’mirror image’ of the sale budget? What factors are involved in its preparation?
TEXT
Budgeting involves setting financial goals and standards for an enterprise. The primary objective of the budget is to establish a financial framework for the operations of the business. The accounting period for the budget is usually either the calendar year or the fiscal year.
A generally accepted budgeting device is a flexible master budget. This budget foresees that management plans to operate the business at various levels of activity and that all the different activities of the enterprise are included in the financial forecast. Budgets for various sections of the company are gathered together into one overall budget. Then, as the business year progresses management can use the budget as a control device, that permits monitoring of the company operations.
We will talk about retail trade business. This type of enterprise purchases merchandise, sells those goods, pays its employees and its suppliers, and employs an administrative staff.
It may also move into new headquarters or expand into new retail outlets. It must account for each activity. This is generally accomplished by means of separate budgets which can be combined into a master budget.
One of the activity budgets is the sales budget information about unit prices; the price of one item of each kind of merchandise sold, and the expected sales volume are the important entries for this budget.
TOPIC 13. BANKING
Read the text below and write short headings (one or two words) for each paragraph.
TEXT 1
Types of Bank
1 .........................................................
Commercial or retail banks are businesses that trade in money. They receive and hold deposits, pay money according to customers' instructions, lend money, offer investment advice, exchange foreign currencies, and so on. They make a profit from the difference (known as a spread or a margin) between the interest rates they pay to lenders or depositors and those they charge to borrowers. Banks also create credit, because the money they lend, from their deposits, is generally spent (either on goods or services, or to settle debts), and in this way transferred to another bank account – often by way of a bank transfer or a cheque (check) rather than the use of notes or coins – from where it can be lent to another borrower, and so on. When lending money, bankers have to find a balance between yield and risk, and between liquidity and different maturities.
2.........................................................
Merchant banks in Britain raise funds for industry on the various financial markets, finance international trade, issue and underwrite securities, deal with takeovers and mergers, and issue government
71 |
72 |
bonds. They also generally offer stockbroking and portfolio management services to rich corporate and individual clients. Investment banks in the USA are similar, but they can only act as intermediaries offering advisory services, and do not offer loans themselves. Investment banks make their profits from the fees and commissions they charge for their services.
3 .........................................................
In the USA, the Glass-Steagall Act of 1934 enforced a strict separation between commercial banks and investment banks or stockbroking firms. Yet the distinction between commercial and investment banking has become less clear in recent years. In some European countries (notably Germany, Austria and Switzerland) there have always been universal banks combining deposit and loan banking with share and bond dealing and investment services.
4 .........................................................
A country's minimum interest rate is usually fixed by the central bank. This is the discount rate, at which the central bank makes secured loans to commercial banks. Banks lend to blue chip borrowers (very safe large companies) at the base rate or the prime rate; all other borrowers pay more, depending on their credit standing (or credit rating, or creditworthiness): the lender's estimation of their present and future solvency. Borrowers can usually get a lower interest rate if the loan is secured or guaranteed by some kind of asset, known as collateral.
TASKS
I. Which of the following three paragraphs most accurately and concisely summarizes the text, and what is wrong with the others?
First summary:
Commercial banks hold customers' deposits and make loans. Investment banks raise funds for industry. Deregulation in Britain and the US is leading to the creation of financial conglomerates similar to the universal banks that have always existed in German-speaking countries. A country's minimum interest rate is usually fixed; banks charge progressively higher rates to less secure borrowers. Many
banks also do Eurocurrency business – lending foreign currencies, notably dollars, at lower rates than in the currencies' home countries.
Second summary:
Commercial banks receive deposits and make loans. Merchant and investment banks arrange security issues and offer other investment services. Yet the traditional distinction between commercial and investment banks is now breaking down. Domestic interest rates are fixed by central banks. Many banks also have branches abroad that do Eurocurrency business, making loans in other European currencies.
Third summary:
Commercial banks receive deposits, lend money, and provide other services. Merchant and investment banks lend money to industry. British and American banks are now joining together in conglomerates. The interest rates that banks charge depend on the borrowers' creditworthiness. European banks also do a lot of Eurodollar and petrodollar business.
II. Find the words or expressions in the text, which mean the following:
1.to place money in a bank; or money placed in a bank
2.the money used in countries other than one's own
3.how much money a loan pays, expressed as a percentage
4.available cash, and how easily other assets can be turned into
cash
5.the date when a loan becomes repayable
6.to guarantee to buy all the new shares that a company issues, if they cannot be sold to the public
7.when a company buys or acquires another one
8.when a company combines with another one
9.buying and selling stocks or shares for clients
10.taking care of all a client's investments
11.the ending or relaxing of legal restrictions
12.a group of companies, operating in different fields, that have joined together
13.a company considered to be without risk
73 |
74 |
14.ability to pay liabilities when they become due
15.anything that acts as a security or a guarantee for a loan
III. The text contains a number of common verb-noun partnerships (e.g. to lend money, to finance international trade). Match up the verbs (column A) and nouns (column B) below to make common collocations.
A |
B |
charge |
advice |
do |
bonds |
exchange |
business |
issue |
currencies |
make |
deposits |
offer |
funds |
pay |
interest |
raise |
loans |
receive |
profits |
underwrite |
security issues |
TEXT 2
Answer the following comprehension questions based on the
text:
1.What is the bank? What factors determine the success of its operation?
2.What makes the 1980s a turning point in banking?
3.What do bank trust operations encompass?
4.What groups do the bank trust operations fall into?
5.What does the Federal Indenture Act of 1939 envisage?
6.What are the obligations of a bank acting as trustee under in-
denture?
7.What are letters of credit aimed at when they are issued by banks acting as fiduciaries to benefit their corporate customers?
New Services in Banking
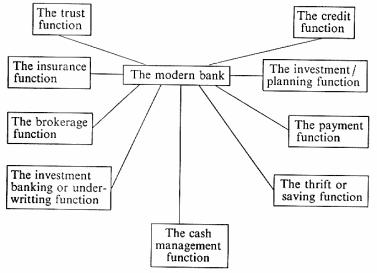
Banks perform the widest range of functions in the economy and consequently any modern full-service banking institution should provide the widest variety of services.
Fig. 6
Banks may be defined as firms producing and selling financial services. Their success or failure hinges on their ability to identify the financial services the public demands, produce those services efficiently, and sell them at a competitive price. The service menu of banks does not remain unchanged as new services are constantly being introduced and developed by commercial banks. Many of them offer a combination of wholesale and retail banking. The former provides large scale services to the corporate sector. The latter mainly provides smaller scale services to the general public.
The 1980s ushered in an explosion of new service options. Many of the new services have simply been variations of traditional deposit and loan product. Other innovative services, however, have broken new ground and exposed bankers to all the uncertainty and risk associated with new product development.
75 |
76 |
Trust services are one of the most important and rapidly growing bank service areas today. Bank trust operations encompass the management of property and other assets owned by a bank customer and the administration of a customer's security holdings and borrowings. In offering trust services the bank places itself as authorized agent between the marketplace and the customer, making investment and management decisions on the customer's behalf and dispensing funds when needed to cover the customer's obligations. A bank's trust operations are usually divided into three broad areas: (1) personal trust services, (2) business trust services, and (3) trust services for charities and nonprofit organizations. Each involves a fiduciary relationship between bank and customer – that is, a trust department acts to benefit its customers within those areas defined by contract (the trust agreement) between the bank (trustee) and the customer (trustor) covering a specified period of time.
Banks provide a wide range of trust services for individuals and families in the form of estate settlement, trust administration and agency services. Bank trust divisions act as agents for corporations and other businesses in a host of different ways. This may involve issuing securities on the business customer's behalf, paying dividends or interest owed on any securities issued, reinvesting the dividends for securities holders who request that service, and retiring the securities at maturity. Under the terms of the Federal Trust Indenture Act of 1939, any foreign or domestic corporation that issue securities to the general public in the United States must designate a trustee for that security issue to act as a fiduciary, representing the investors purchasing those securities. Trust departments also handle transfers of ownership of corporate stock, stock splits, and conversions of stock into debt, and they issue proxies and count votes in connection with annual stockholder meetings.
Today, banks frequently serve as trustees under indenture, holding legal title to property securing a bond issue, with the power to foreclose on and liquidate that property if the issuer defaults. The bank as trustee must make sure all bond covenants agreed to by the issuing corporation are adhered to and that all required liens against the company's property are duly filed and recorded. The trust department will set up and manage a sinking fund, investing all monies that the bond
issuer contributes to that fund periodically with the intent of eventually redeeming the bond issue.
The fiduciary activities of banks make a critical contribution to the functioning of the commercial paper market, where the unsecured, short-term notes of large corporations (both foreign and domestic) are traded. Bank trust departments keep records on which investors purchase commercial paper, see that any notes purchased are actually delivered to the investors involved, and pay off the holders of those notes on the maturity date. Even more important, banks issue letters of credit backstopping issuers of commercial paper in order to reassure investors that the bank will pay off a note issue if the borrowing corporation cannot do so. A bank's trust department will receive and hold any credit letters issued by other lending institutions and check to see that all the terms of those credit letters are being adhered to by borrowing companies. If necessary, the trust department will file: for payment under the terms of a credit letter and dispense the collected funds to note holders.
Many banks today would like to offer real estate brokerage services to their customers, selling a home or commercial structure and then financing the sale. For generations banks have made loans to finance the construction of business facilities and private houses. While preferring to stick predominantly to short-term construction financing, banks have also taken on a limited volume of long-term , commercial and residential real estate mortgages in which the mortgaged property being a home or a commercial structure. Mortgage loans are among the riskiest forms of bank credit, though they can be sold quite readily in the secondary market. Sometimes banks acquire realty companies in order to be able to offer a larger menu of financial services.
____________________
1. to issue a proxy – выдать полномочие на право голосова-
ния
2.to foreclose – лишать права пользования
3.a sinking fund – фонд погашения задолженности, выкуп-
ной
77 |
78 |

TASKS
I. Match the words with the correct definition from the list be-
low.
Fiduciary, relationship, trustee, real estate, mortgage, estate, trust department, trustor, service, a letter of credit.
1.One's collective assets and liabilities.
2.An agreement between a bank and its customer in which the bank becomes responsible for the management of the customer's funds.
3.One who holds legal title to property in trust for the benefit of another person, and who is required to carry out specific duties with regard to the property.
4.One who creates a trust.
5.Debt instrument by which the borrower gives the lender a lien on property as security for the repayment of a loan.
6.Part of a bank engaged in settling estates, administering trusts and guardianships, and performing agency services.
7.Type of business that sells assistance and expertise rather than a tangible product.
8.Immovable property such as land held on a freehold.
9.A document issued by a bank by which credit facilities up to a stated maximum amount are extended to a customer.
II. Look through the excerpt and then fill the spaces with words from the box. Translate the text into Russian.
For many years banks have offered ... (1) the financial affairs and property of individuals and business firms in return for ... (2) that is often based on the value of properties or funds under ... (3). This property management function is known as ... (3). Most banks offer both personal trust services to individuals and families and ... (4) to corporations and other businesses. In their commercial ... (5), banks manage ... (6) portfolios and pension funds for business firms and ...
(7) as agents for corporations issuing stocks and bonds. This requires
... (9) departments to pay interest or dividends on the corporation's
securities at the proper times and ... (10) maturing securities by paying off the investors who hold those securities.
Retire, mortgage, to manage, trust, real estate, fee, act, management, security, trust services, trust departments, commercial trust services.
TOPIC 14. MARKET PLACE
Read the text and find the answers to the questions:
1.What role does the stock market play in the economy of any
country?
2.What does the “stock market” mean?
3.What does AMEX date back to? How was it known?
4.How is the Exchange regulated?
5.Who can become an Exchange member?
6.How is over the counter trading accomplished?
7.What does NASD supervise?
8.What companies was OTC organized for?
TEXT 1
The stock market. To some it is а puzzle. To others it is a source of profit and endless fascination. The stock market is the financial nerve center of any country. It reflects any change in the economy. It is sensitive to interest rates, inflation and political events. In a very real sense, it has its fingers on the pulse of the entire world.
Taken in its broadest sense, the stock market is also a control center. It is the market place where businesses and governments come to raise money so that they can continue and expend their operations. It is the market place where giant businesses and institutions come to make and change their financial commitments. The stock market is also a place of individual opportunity.
The phrase “the stock market” means many things. In the narrowest sense, a stock market is a place where stocks are traded – that is bought and sold. The phrase “the stock market” is often used to refer to the biggest and most important stock market in the world, the New York Stock Exchange, which is as well the oldest in the US. It was
79 |
80 |
