- •I. Read and translate the text. Sociology
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •VIII. Answer: What are the sociologists concerned with? Use the words in brackets.
- •IX. Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Unit II
- •I. Read and translate the text: Social Barometer
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •Word study
- •IV. Complete the following sentences:
- •Unit III
- •I. Read and translate the text: The Origins of Sociology
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •III. Complete the following sentences:
- •IV. Divide the text into logical parts and make up an outline of the text.
- •V. Speak on:
- •VI. Read the text and entitle it:
- •Word study
- •Unit IV
- •I. Read and translate the text: Sociological Theory
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •III. Agree or disagree with the following:
- •IV. Divide the text into logical parts and make up a plan of the text.
- •VI. Contradict the following statements:
- •VII. Translate the text in writing: Social Change and the Development of Sociology
- •Word study
- •I. Find in the text «Sociological Theory» English equivalents for:
- •II. Find in the text antonyms for:
- •III. Fill in the blanks with the words given below in the brackets:
- •IV. Read and translate the following sentences taking into account different meanings of the word 'experience':
- •V. Role-play.
- •I. Read the text and answer the following questions:
- •Theoretical Paradigms
- •II. Be ready to speak on:
- •III. You have just heard three reports. What paper do you think to be the best one? Give your arguments. Use the following:
- •IV. Read and translate the text: The Methods of Sociological Research
- •Experiments.
- •Survey Research
- •Questionnaires and Interviews
- •V. Enumerate all methods of sociological research. What method do you consider to be the most productive? Give your reasons.
- •VI. Answer the following questions:
- •Word study
- •III. Translate the following sentences into Russian with:
- •V. Develop the following situations:
- •Unit VI
- •I. Read and translate the text: The Structure of Social Interaction
- •Social Structure and Individuality
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •Summary
- •Word study
- •I. Find in the text “The Structure of Social Interactions” English equivalents for:
- •II. Arrange the following words into pairs of antonyms:
- •III. Make up sentences choosing an appropriate variant from 1) – 7):
- •IV. Make up dialogues according to the following situations:
- •Unit VII
- •I. Look through the text and find the definitions of:
- •II. Read and translate the text. Role
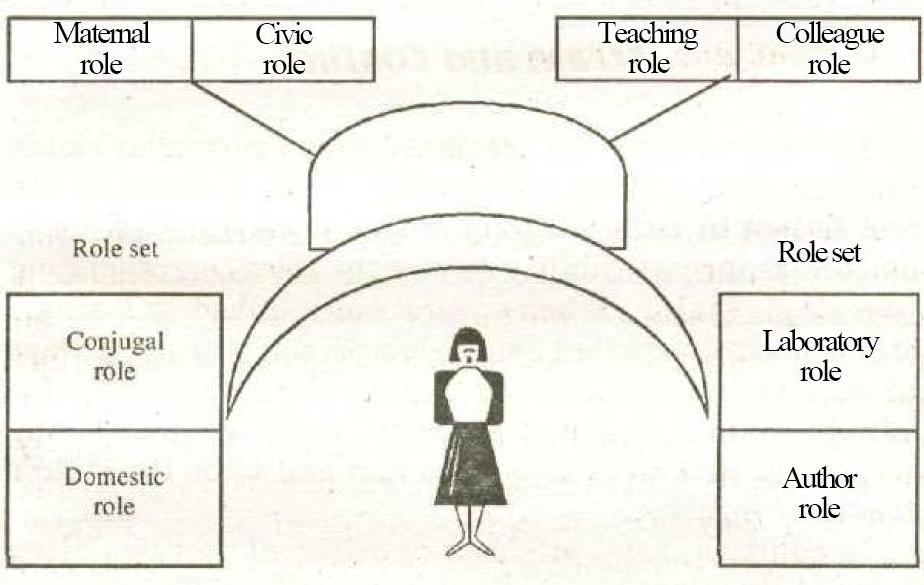
- •Figure 1. Status Set and Role Set
- •Strain and Conflict
- •Dramaturgical Analysis: “The Presentation of Self”
- •IX. Answer the questions:
- •Word study
- •I. Find in the texts English equivalents for:
- •III. Read and translate the following sentences:
- •IV. Make up questions and ask your friend on:
- •V. Complete the following sentences:
- •Unit VIII
- •Kinds of Groups
- •IV. Find the facts to prove that:
- •V. Divide the text into three logical parts.
- •VII. Discuss in the group the following problems:
- •The Nature of Group Cohesiveness
- •XIV. Read and translate the text. Primary and Secondary Groups
- •XV. Answer the following questions.
- •XVI. Contradict the following statements. Start your sentence with: “Quite on the contrary...”
- •XVII. Ask your friend:
- •Divide the text into logical parts and give a heading to each part.
- •Find a leading sentence in each paragraph of the text.
- •Primary Groups and Secondary Groups
- •Give examples of primary and secondary groups.
- •Characterize in brief:
- •XXIV. Read the text and say what new information is contained in it. Networks
- •Word study
- •I. Find in the text “Primary and Secondary Groups” English equivalents for:
- •II. Make up word-combinations and translate them into Russian.
- •IV. Make up your own sentences with — “to be of importance, to be of value” - and ask your partner to translate them.
- •Unit IX
- •I. Read and translate the text. Group Dynamics
- •Group Leadership
- •The Importance of Group Size
- •Figure 3. Group Size and Relationships
- •VII. Read the text again and note the difference between in-groups and out-groups.
- •VIII. Prepare a report on “Group Dynamics and Society.” unit X
- •I. Read and translate the text.
- •Deviance
- •Biological Explanations of Deviance
- •VII. Speak on:
- •VIII. Translate the text in writing. Deviance is a Product of Society?
Word study
I. Find in the text “The Structure of Social Interactions” English equivalents for:
В конце концов; социальные модели; нормы поведения; в обществе; во главе; конечно; отчасти; несмотря на; во многом такие же; другими словами; окружение (среда); с готовностью; например; напротив; ограничить свободу; кроме того.
II. Arrange the following words into pairs of antonyms:
Disorganized Limited
Chaos Familiar
Infinite Quietly
In the presence Difference
Lose Emerge
Unfamiliar Organized
Leave In the absence
Finish Enter
Noisily Arrival
Departure In other words
Ordinary Uncomfortable
Similarity System
In the same way Find
Seldom Begin
Disappear Unique
Comfortable Often
Strong Weak
III. Make up sentences choosing an appropriate variant from 1) – 7):
1.The scientist was guided by ...
2.The room was filled with ...
3.His theory is built on ...
4.Human behaviour is defined by ...
5.Social interaction is patterned ...
6.His activity is encouraged by ...
7.He is in charge of ...
1) Cultural values and norms.
2) The working team.
3) The latest scientific discoveries.
4) The Sociology Research Institute.
5) Unfamiliar faces.
6) Empirical investigation.
7) As society is an organized system.
IV. Make up dialogues according to the following situations:
1) An odd person comes to you. He says you were friends years ago. You have never met him before and you suspect his motives.
2) Your friend is acting very strangely. You feel he has a secret worry. Find out what is wrong with him.
3) Ask your friend to prove that the quality of personality is not inborn. It is a social phenomenon. Ask him whether we can predict a man's behaviour in a certain situation and what measurements of personality exist, what they are called.
4) You are an introvert by nature, you are unable to overcome uncertainty in taking decisions and often experience troubles in life. You are asked to organize a conference, but you are afraid to accept such an offer. Your friend tries to persuade you to agree.
Note: The following word-combinations may be helpful:
To be concerned with, to be interested in, to be guided by, to be encouraged by, to be in charge of, to be filled with, to be prone to, to make use of.
Unit VII
I. Look through the text and find the definitions of:
Role; 2. Role set; 3. Role strain; 4. Role conflict.
II. Read and translate the text. Role
A second major component of social interaction is role, which refers to patterns of behaviour corresponding to a particular status. Ralph Linton described a role as the dynamic expression of a status. A student has a role that involves patterned interaction with professors and other students, and responding to academic demands made by the college. As Linton explained, while individuals occupy a status, they perform a role. Cultural norms suggest how a person who holds a particular status ought to act, which is often called a role expectation. However, real culture only approximates ideal culture; therefore, actual role performance usually varies from role expectation.
Like status, a role is relational by directing social behaviour toward some other person. The role that corresponds to the status of parent, for example, is ideally defined in terms of responsibilities toward a child. Correspondingly, the role of son or daughter is ideally defined in terms of obligations toward a parent. There are countless other examples of roles paired in this way: the behaviour of wives and husbands is performed in relation to each other, as is the behaviour of physicians and patients, and of professors and students.
Because individuals occupy many statuses at one time - a status set - they perform multiple roles. Yet a person has even more roles than statuses because any one status involves performing several roles in relation to various other people. Robert Merton introduced the term role set to identify a number of roles attached to a single status.