- •Раздел I.
- •Английский алфавит (The English Alphabet)
- •Основные правила чтения гласных букв / буквосочетаний
- •Раздел II.
- •Словообразование (word-building)
- •Артикль (the article)*
- •Употребление артиклей
- •Предложение (the sentence)*
- •4. Имя существительное (the noun)*
- •Исключения
- •Притяжательный падеж имен существительных*
- •What happened … … … …?
- •Местоимение (the pronoun)*
- •Имя прилагательное (the adjective)*
- •Порядок постановки имён прилагательных перед существительными
- •Степени сравнения имен прилагательных
- •Наречие (the adverb)*
- •7.1. Степени сравнения наречий (Degrees of Comparison of Adverbs)
- •8. Имя числительное (the numeral)*
- •Количественные и порядковые числительные
- •А рифметические действия
- •Дробные числа и проценты
- •Глагол (the verb) *
- •Действительный залог. Знаменательные / смысловые глаголы.
- •Глагол to be
- •Оборот there is (are)
- •Система простых / неопределенных времен (Simple / Indefinite Tenses)
- •Система перфектно-продолженных времен (Perfect Continuous Tenses)
- •Неличные формы глагола
- •Образование и использование неличных форм глагола
- •Глаголы / выражения, требующие после себя герундия
- •Предлог (the preposition)*
- •Пространственные предлоги направления / движения / места*.
- •Предлоги времени
- •Составные предлоги
- •Наиболее употребительные выражения с предлогами
- •Наклонение (the mood)*
- •14.Придаточныe предложения (subordinate clauses)*
- •Типы придаточных условных предложений
- •Согласование времен (the sequence of tenses)*
- •Вид согласования времен,
- •Вид согласования времен,
- •Прямая и косвенная речь
- •Mr. Murphy said «The national currency of the uk is the pound.»
- •Mrs. Duncan informs us «The famous British newspaper which is printed
- •Раздел III.
- •Ключи к тестовым заданиям упражнений раздела
- •Бланк ответов
- •Раздел V.
- •Раздел VI.
- •Раздел VII.
Система простых / неопределенных времен (Simple / Indefinite Tenses)
Правила использо-вания Когда?/Как? |
Настоящее простое / неопределенное время (Present Simple / Indefinite Tense) Основная формула V (I / we / you / they) V + s (he / she / it) |
||||||||||||||||||||
для обозначения реального факта действия в настоящем времени
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
+ |
? |
– |
|||||||||||||||||||
I / We / You / They He / She / It |
work.
works. |
Do
Does |
I / we / you / they it / he she |
work? |
I / We / You They / He / She / It |
do not (don’t)* does not (doesn’t)* |
work. |
||||||||||||||
Перевод: Я работаю / мы работаем / ты работаешь / Вы/вы работаете / они работают / он/ она/оно работает и т.д. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Формальные признаки: always всегда often часто usually обычно every day/week/month/year каждый день/неделю/месяц/год и т.д. sometimes иногда |
|||||||||||||||||||||
N.B.! Образование форм в третьем лице единственного числа знаменательных смысловых глаголов в настоящем простом времени происходит по следующим правилам:
e.g. he goes / does oн ходит/делает
e.g. to study учиться – he studies он учится
e.g. to play играть - he plays он играет
[s] после [z] после звонких [iz] после глухих согласных согласных / гласных - s/- ss/- z/- x/- ch/- sh/- tch e.g. she looks [lυks] e.g. she plans [plænz] e.g. he catches[‘kætʃiz] oна смотрит она планирует он ловит e.g. he plays[pleiz] e.g. he passes [‘pa:siz] он играет он переходит |
|||||||||||||||||||||
для обозначения реального факта действия в прошедшем времени |
Прошедшее простое / неопределенное время (Pаst Simple / Indefinite Tense) Основная формула V + ed (правильные глаголы) II форма V (неправильные глаголы)** |
||||||||||||||||||||
+ |
? |
– |
|||||||||||||||||||
I / We / You They / He Sh e / It |
worked/ wrote. |
Did
|
I / we / it you /they he / she |
work / write ? |
I / We /It You / He They/She |
did not (didn’t)* |
work / write. |
||||||||||||||
Перевод: Я работал / мы / они работали / ты работал/ вы / Bы работали / он работал / она работала/оно работало и т.д. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Формальные признаки: yesterday вчера / in 1995 в 1995 / last day / week в прошлый день, неделе и т.д. / two years ago два года назад и т.д. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
N.B! Для правильных глаголов существуют следующие правила чтения и правописания форм простого прошедшего времени:
[t] после [d] после [id] после согласных звонких согласных/гласных глухих согласных -t/-d e.g. looked [lυkt] e.g. planned [plænd] e.g wanted [‘wɒntid] смотрел планировал хотел e.g. finished [‘finiʃt] e.g. played [pleid] e.g. added [‘ædid] окончил играл добавил e.g. watched [‘wɒ:tʃt] e.g. followed [‘fɒləυd] e.g. selected [si‘lektid] следил следовал выбирал
e.g. to like любить – liked любил |
|||||||||||||||||||||
: |
Будущее простое / неопределенное время (Future Simple / Indefinite Tense) Основная формула shall + V (I / we) will + V (he / she / it / you / they) |
||||||||||||||||||||
+ |
? |
– |
|||||||||||||||||||
I / We shall (‘ll)* You / It / He He / She / They will (‘ll)* |
work |
Shall Will |
I / we you it / he she / they |
work ?
|
I / We /
You//It/ He /She They |
shall not (shan’t)* will not (won’t)* |
work. |
||||||||||||||
Перевод: Я буду/мы будем/ты будешь/они будут /он/она/оно будет работать |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Формальные признаки: in 2021 в 2021 next day / week / month / year на следующий день / неделе / месяце, году и т.д. tomorrow завтра |
|||||||||||||||||||||
N.B! Будущее простое время не употребляется в придаточных предложениях условия и времени после союзов: If / Provided / Providing that / On condition that если In case в случае если / Unless если не / When когда В этих предложениях будущее простое время выражается глаголами в настоящем времени, которые переводятся на русский язык глаголами будущего времени: e.g. The tourists will visit the sights of Wales*** tomorrow, if the weather is fine. Туристы осмотрят достопримечательности Уэльса завтра, если погода будет хорошей. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
*Краткие формы глагола характерны для разговорной речи
**См. Раздел VI Приложение 1 «Основные формы неправильных знаменательных смысловых глаголов»
***См.: Раздел V Иллюстрированный глоссарий «Социокультурной портрет Соединенного Королевства Великобритании и Северной Ирландии»
У пражнение 30. Выберите следующие предложения в Past / Future Simple Tenses в соответствии с формальными признаками в скобках:
We (to take part) in the Highland Games*. (last year)
We take part in the Highland Games last year.
We took part in the Highland Games last year.
We shall take part in the Highland Games last year.
I (to go) to the Royal Albert Hall* every Sunday. (next year)
I shall go to the Royal Albert Hall every Sunday next year.
I go to the Royal Albert Hall every Sunday next year.
I went to the Royal Albert Hall every Sunday next year.
This house (to cost) a lot. (two years ago)
This house cost a lot two years ago.
This house will cost a lot two years ago.
This house costs a lot two years ago.
He (to play) the bagpipes regularly. (in his childhood)
He plays the bagpipe regularly in his childhood.
He played the bagpipe regularly in his childhood.
He will play the bagpipe regularly in his childhood.
Every summer Barbara (to go) to the sea-side. (when she was young)
Every summer Barbara goes to the sea-side, when she was young.
Every summer Barbara went to the sea-side, when she was young.
Every summer Barbara goed to the sea-side, when she was young.
He (to be) a student at Cambridge*. (in 1996)
He is a student at Cambridge in 1996.
He was a student at Cambridge in 1996.
He will be a student at Cambridge in 1996.
What this sophomore* (to do) every morning (last week)?
What did this sophomore do every morning last week?
What does this sophomore do every morning last week?
What will this sophomore do every morning last week?
He (do not study) the Irish language. (next academic year)
He doesn’t study the Irish language next academic year.
He didn’t study the Irish language next academic year.
He won’t study the Irish language next academic year.
I (to give) you this book about J. Locke,* when I (to meet) you. (tomorrow)
I shall give you this book about J. Locke, when I meet you tomorrow.
I gave you this book about J. Locke, when I meet you tomorrow.
I shall give you this book about J. Locke, when I shall meet you tomorrow.
The tourists usually (to travel) to Bath, when they (to arrive) to the UK.
The tourists usually travel to Bath, when they arrive to the UK.
The tourists usually travelled to Bath, when they arrived to the UK.
The tourists usually will travel to Bath, when they arrived to the UK.
У пражнение 31. Выберите правильную форму глагола в настоящем времени:

Most journeys in Britain are made by road. Some of these are performed by public transport but most by cars. Many people rely on their car for daily local activities, e.g. getting to job, shops, visiting friends.
P
 eople
living in urban areas 1
underground
buses, trains to get anywhere as the traffic is rather heavy,
especially in the centre. Long-distance travel is also by road. Most
places are linked by motorways or other fast roads, and many people
2
driving
a car at their convenience than using a train; even they may get a
stuck in a traffic jam. As the number of cars will increase by a
third within a few years, the main problem with the road transport
3
in traffic congestion and pollution. The cheapest ways to travel are
to walk or to ride a bicycle. In Oxford and Cambridge* bicycles are
common, and many other cities and towns 4
special bicycle routes or cycle lanes beside the main road. A long
distance bus or coach services
5
usually a cheaper alternative to trains, but may be less comfortable.
The British 6
long
distance travels, especially on business by air.
eople
living in urban areas 1
underground
buses, trains to get anywhere as the traffic is rather heavy,
especially in the centre. Long-distance travel is also by road. Most
places are linked by motorways or other fast roads, and many people
2
driving
a car at their convenience than using a train; even they may get a
stuck in a traffic jam. As the number of cars will increase by a
third within a few years, the main problem with the road transport
3
in traffic congestion and pollution. The cheapest ways to travel are
to walk or to ride a bicycle. In Oxford and Cambridge* bicycles are
common, and many other cities and towns 4
special bicycle routes or cycle lanes beside the main road. A long
distance bus or coach services
5
usually a cheaper alternative to trains, but may be less comfortable.
The British 6
long
distance travels, especially on business by air.
There are regular flights between regional airports as well as between Heathrow and international airports. There is a lot of traffic in the streets of London. Most of London buses are red double-deckers* that 7 two platforms for passengers.
There are also green one-storeyed buses, they 8 from London to country-side. Brown buses belong to the British railways. Be careful when you cross the street of London, because in Britain the traffic keeps to the left and not to the right as in European countries. When you 9 to cross the street, look first to the right and then to the left.
The traffic lights are not like in Europe. The red light 10 «Stop», the green light says «Wait» and the yellow light says «Cross». «Keep left» is the general rule in the UK. People cross the street at the black-and-white crossing, but if they are in a hurry they just run across at any place. Sometimes a policeman stops them. He is called «Bobby» there. He stands at street corners and regulates the traffic.
____________________________________________________________________
* См.: Раздел V Иллюстрированный глоссарий «Социокультурной портрет Соединенного Королевства Великобритании и Северной Ирландии»
T raffic дорожное движение
To rely on полагаться (на)
Daily local activities повседневнaя жизнь
To live in urban area жить загородом
A long-distance travel междугородние рейсы
A motorway (fast road) скоростная трасса
At smb’s convenience для удобства кого-либо
To get a stuck in a traffic jam быть зажатым в уличной пробке
Traffic congestion and pollution перегруженный транспорт и загрязнение окружающей среды
a ) use b) uses c) to use
a) prefers b) preferred c) prefer
a) exists b) exist c) to exist
a) has b) have c) had
a) is b) will be c) are
a) undertakes b) undertake c) to undertake
a) have b) has c) to have
a) run b) ran c) runs
a) will want b) wants c) want
a) says b) say c) to say
Система продолженных времен (Continuous Tenses)
Правила исполь-зования Когда?/ Как? |
Основная формула
to be + Participle I |
||||||||||||||
для обозна-чения реального процесса действия в настоящем времени |
Настоящее продолженное время (Present Continuous Tense) Основная формула to be (am / is / are) + Participle I |
||||||||||||||
+ |
? |
– |
|||||||||||||
I am (’m)* We / You They аre (‘re)* He / She / It is (‘s)* |
working
|
Am Are
Is |
I / we you they
he / she it |
working ? |
I / We / You / They
He / She / It |
am not (ain’t)* are not (aren’t)* is not (isn’t)* |
working |
||||||||
Перевод: Я работаю / мы работаем / ты работаешь / они работают / он/она/оно работает (сейчас, в данный момент, в момент речи и т.д.) |
|||||||||||||||
Формальные признаки: now сейчас at this moment в этот момент / at 5 o’clock в 5 часов / at this time в это время |
|||||||||||||||
для обозна-чения реального процесса дейст-вия в прошед-шем времени |
Прошедшее продолженное время (Pаst Continuous Tense) Основная формула to be (was / were) + Participle I |
||||||||||||||
+ |
? |
– |
|||||||||||||
We / You / They were I / He / It She was |
working |
Were
Was |
we /you they I / he She / it |
working ? |
I / He / She / It was not (wasn’t)* We / You / They were not (weren’t)* |
working. |
|||||||||
Перевод: Мы работали/ты работал /Вы/вы работали /они работали / Я / он работал /она работала / оно работало в тот момент at that moment / в то время, когда…at that time when (в прошлом) |
|||||||||||||||
Формальные признаки: at that moment yesterday в тот момент вчера/at 5 o’clock yesterday в 5 часов вчера/at that time yesterday в то время вчера и т.д. |
|||||||||||||||
для обозна-чения реаль-ного процессса действия в буду-щем времени |
Будущее продолженное время (Future Continuous Tense) Основная формула shall be + Participle I (I / we) will be + Participle I (he / she / it / you / they) |
||||||||||||||
+ |
? |
– |
|||||||||||||
I / We shall (‘ll)* You/ They He / She / It will (‘ll)* |
be working |
Shall
Will |
I / we
you / he they / she it |
be working? |
I / We shall not (shan’t)* He / You / It She / They will not (won’t)* |
be working. |
|||||||||
Перевод: Я буду работать / мы будем работать / ты будешь работать / Вы/вы будете работать / они будут работать / он/она/оно будет работать at that moment tomorrow в тот момент, в то время, когда… (в будущем) |
|||||||||||||||
Формальные признаки: at that moment tomorrow в тот момент завтра at 5 o’clock etc. в 5 часов завтра и т.д. |
|||||||||||||||
N.B.!
чувственного восприятия to hear слышать to see видеть to watch наблюдать умственной деятельности to understand понимать; to remember помнить; to forget забывать чувств to like нравиться to dislike не нравиться to hate ненавидеть to love любить желания to want хотеть to wish желать принадлежности to belong принадлежать to possess обладать to cost стоить to be Значение длительности действия передается формами неопределенных времен: e.g. Do you hear what Mr. Picwick is saying? Вы слышите, что говорит господин Пиквик?
If / Provided / Providing that / On condition that если In case в случае если Unless если не When когда В придаточных предложениях времени и условия будущее продолженное время выражается глаголами в настоящем продолженном времени, которые переводятся на русский язык глаголами будущего продолженного времени: e.g. He will meet you in Kensington Gardens** on Monday next week, in case you are waiting for him from 4 till 5 p.m. Он встретит тебя в Кенсингтонском парке на следующей неделе в понедельник, если ты подождешь его с 4 до 5 часов во второй половине дня. |
|||||||||||||||
*Краткие формы глагола характерны для разговорной речи
** См.: Раздел V Иллюстрированный глоссарий «Социокультурной портрет Соединенного Королевства Великобритании и Северной Ирландии»
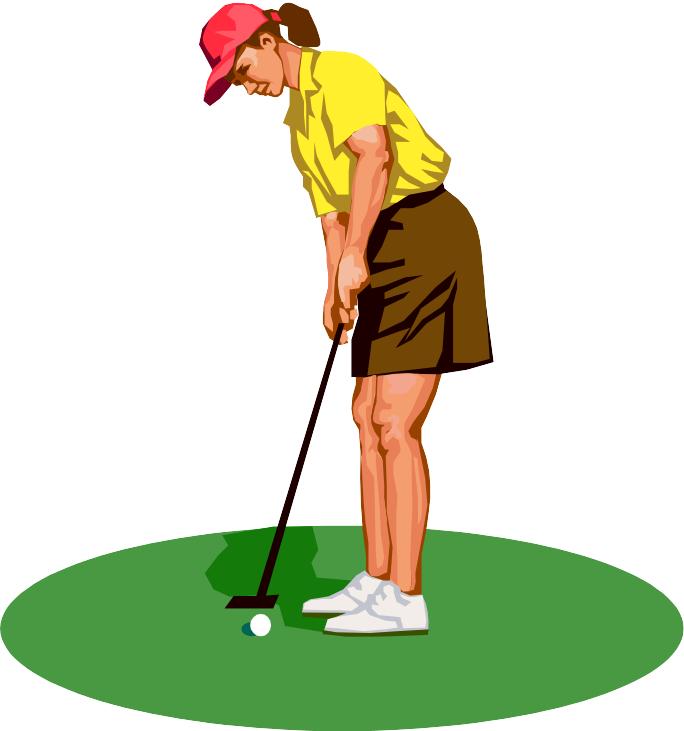
У пражнение 32. Назовите действие, выполняемое в определенный момент на картинках ниже:
1 |
|
Mary (to play) golf on the green. (now) a) Mary will be playing golf on the green. b) Mary was playing golf on the green. c) Mary is playing golf on the green. |
2 |
|
Nick (to play) cricket. (yesterday) a) Nick will be playing cricket. b) Nick is playing cricket. c) Nick was playing cricket. |
3 |
|
Glenda (to prepare) a report on English economics. (next week) a) Glenda prepares a report on English economics. b) Glenda shall be preparing a report on English economics. c) Glenda will be preparing a report on English economics. |
4 |
|
The English students (to discuss) Shakespeare’s play. (at this moment) a) The English students was discussing Shakespeare’s play. b) The English students were discussing Shakespeare’s play. c) The English students are discussing Shakespeare’s play.
|
5 |
|
Winnie-the Pooh*and his friends (to play) together. (last month) a) Winnie-the Pooh and his friends are playing together. b) Winnie-the Pooh and his friends to play together. c) Winnie-the Pooh and his friends were playing together. |
6 |
|
A lot of tourists (to walk) on Trafalgar Square*. (tomorrow at noon) a) A lot of tourists were walking on Trafalgar Square. b) A lot of tourists are walking on Trafalgar Square. c) A lot of tourists will be walking on Trafalgar Square. |
7 |
|
Look! The clouds (to float) above the Big Ben*. a) The clouds are floating above the Big Ben. b) The clouds will be floating the Big Ben. c) The clouds float above the Big Ben. |
8 |
|
The double-decker (to move) near the Royal Albert Hall*.(now) a) The double-decker move near the Royal Albert Hall. b) The double-decker was moving near the Royal Albert Hall. c) The double-decker is moving near the Royal Albert Hall. |
9 |
|
The ship (to go) along the Thames*. (last night)
c) The ship is going along the River Thames. |
10 |
|
Pay attention! The Yeoman Warders* (to take part) in the ceremony! a) TheYeoman Warders are taking part in the ceremony. b) The Yeoman Warders take part in the ceremony. c) The Yeoman Warders will be taking part in the ceremony.
|
*См.: Раздел V Иллюстрированный глоссарий «Социокультурной портрет Соединенного Королевства Великобритании и Северной Ирландии»
**См.: Раздел VI Приложениe 3 «Британские имена «British Names»
У пражнение 33. Выберите правильный вариант предложений:
Doctor Sanford (to travel) along the Irish Sea* at this moment.
Doctor Sanford travelled along the Irish Sea at this moment.
Doctor Sanford travels along the Irish Sea at this moment.
Doctor Sanford is traveling along the Irish Sea at this moment.
I (to wait) for you near the Tate Gallery* from 8 o’clock till 9 o’clock tomorrow.
I wait for you near the Tate Gallery from 8 o’clock till 9 o’clock tomorrow.
I’ll bе waiting for you near the Tate Gallery from 8 o’clock till 9 o’clock tomorrow.
I shall wait for you near the Tate Gallery from 8 o’clock till 9 o’clock tomorrow.
When I came to Henry yesterday, he (to work) in the garden.
When I came to Henry yesterday, he was working in the garden.
When I came to Henry yesterday, he is working in the garden.
When I came to Henry yesterday, he worked in the garden.
I met him every day at 5 o’clock, when I (to go) to the Piccadilly Circus*.
I met him every day at 5 o’clock, when I go to the Piccadilly Circus.
I met him every day at 5 o’clock, when I went to the Piccadilly Circus.
I met him every day at 5 o’clock, when I was going to the Piccadilly Circus.
What Ann (to do) yesterday, when I phoned?
What was Ann doing yesterday, when I phoned?
What did Ann do yesterday, when I phoned?
What does Ann do yesterday, when I phoned?
Look! A double-decker* (to approach) to the bus stop.
Look! A double-decker approaches to the bus stop.
Look! A double-decker is approaching to the bus stop.
Look! A double-decker to approach to the bus stop.
Nick (to prepare) for exams to London University* when I went in.
Nick is preparing for exams to London University when I went in.
Nick prepared for exams to London University when I went in.
Nick was preparing for exams to London University when I went in.
The tourists (to wait) for the guide near Nelson’s Column* for an hour tomorrow.
The tourists will be waiting for the guide near Nelson’s Column for an hour tomorrow.
The tourists shall be waiting for the guide near Nelson’s Column for an hour tomorrow.
The tourists were waiting for the guide near Nelson’s Column for an hour tomorrow.
The foreign guests (to listen) for the guide for a quarter of the hour tomorrow.
The foreign guests will listen for the guide for a quarter of an hour tomorrow.
The foreign guests will be listening for the guide for a quarter of an hour tomorrow.
The foreign guests were listening for the guide for a quarter of an hour tomorrow.
My children (to decorate) Christmas tree* the whole evening yesterday.
My children will be decorating Christmas tree the whole evening yesterday.
My children were decorating Christmas tree the whole evening yesterday.
My children are decorating Christmas tree whole evening yesterday.
____________________________________________________________________
* См.: Раздел VI Иллюстрированный глоссарий «Социокультурной портрет Соединенного Королевства Великобритании и Северной Ирландии»
Система перфектных времен (Perfect Tenses)
Правила использования (Когда / Как?) |
Основная формулa to have + Participle II |
|||||||||||||||
для обозначения реального результата действия в настоящем времени |
Настоящее перфектное время (Present Perfect Tense) Основная формулa have + Participle II (I / we / you / they) has + Participle II (he / she / it) |
|||||||||||||||
+ |
? |
– |
||||||||||||||
I / We / You / They have (‘ve)* He / She / It has (‘s)* |
worked.
|
Have
Has |
I / we you they he / it she |
worked? |
I / We / You They have not (haven’t)* He/ It/She has not (hasn’t)* |
worked.
|
||||||||||
Перевод: Я отработал/мы отработали / ты отработал/Вы/вы/они отработали /он отработал /она отработала/оно отработало (уже к определенному периоду времени в настоящем времени, который еще не закончился) |
||||||||||||||||
Формальные признаки: recently недавно/lately в последнее время / недавно / never никогда / ever когда-нибудь/already уже/yet ещё; (в вопро-сительных предложениях) / today сегодня / this year в этом году / bу 5 o’clock к 5 часам в настоящем времени /с предлогoм since с тех пор, как |
||||||||||||||||
1. для обозна-чения реально-го результата действия в прошедшем времени 2. для обозна-чения прошед-шего действия, завершившего-ся до другого действия в прошлом |
Прошедшее перфектное время (Pаst Perfect Tense) Основная формулa had + Participle II |
|||||||||||||||
+ |
? |
– |
||||||||||||||
I / We You / It They / He She |
had worked. |
Had |
I / we you / she they he / it |
worked? |
I / We / It You / They He / She |
had not (hadn’t)* worked. |
||||||||||
Перевод: Я отработал / мы отработали / ты отработал / Вы/вы/мы отработали / он отработал / она отработала / оно отработало до начала другого действия в прошлом либо к определенному времени в прошлом |
||||||||||||||||
Формальные признаки: by that time к тому времени before I saw him до того, как я его увидел bу 5 o’clock к 5 часам в прошедшем времени |
||||||||||||||||
1.для обозначения реального результата действия в будущем времени 2. для обозначения будущего действия, завершившего-ся до другого действия в будущем |
Будущее перфектное время (Future Perfect Tense) Основная формулa shall have + Participle II (I / we) will have + Participle II (he / she / it / you / they) |
|||||||||||||||
+ |
? |
– |
||||||||||||||
I / We shall (‘ll)* You / They He / She / It will (‘ll)* |
have worked |
Shall
Will |
I / we
you they / he she / it |
have worked?
|
I / We shall not (shan’t)* He / It / She You / They will not (won’t )* |
have worked
|
||||||||||
Перевод: Я (уже) отработаю/мы отработаем / ты отработаешь / Вы/ты отработаете / они отработают он отработает/он/она/оно отраработает к определенному времени либо до начала другого действия в будущем |
||||||||||||||||
Формальные признаки: by that time tomorrow (next week / month / August etc.) к тому времени завтра (следующей неделе / месяцу /августу) |
||||||||||||||||
N.B! Будущее завершенное (перфектное) время не употребляется в придаточных предложениях условия и времени после союзов: When когда / If /Provided / Providing that / On condition that если / In case в случае если В этих предложениях будущее завершенное/перфектное время выражается глаголами в настоящем завершенном/перфектном времени, которые пере-водятся на русский язык глаголами будущего завершенного/перфектного времени. e.g. In case you have worked out the guidebook on the British Museum* by the end of the week, we’ll be able to publish it next year.В том случае, если Вы разработаете путеводитель по Британскому Музею к концу неделе, мы сможем издать его в следующем году. |
||||||||||||||||
*Краткие формы глагола характерны для разговорной речи
** См.: Раздел V Иллюстрированный глоссарий «Социокультурной портрет Соединенного Королевства Великобритании и Северной Ирландии»
У пражнение 34. Подберите к временным формам в колонке А соответствующие значения этих форм из колонки В:
А |
В |
||
1. |
Я читаю эту английскую книгу (всегда). |
a |
I’ll have read this English book. |
2. |
Я прочитала эту английскую книгу (раньше). |
b |
I read [ri:d] this English book. |
3 |
Я читаю эту английскую книгу (сейчас). |
c |
I was reading this English book. |
4. |
Я буду читать эту английскую книгу (в тот момент). |
d |
I had read this English book. |
5. |
Я прочитала эту английскую книгу (уже). |
e. |
I have read this English book. |
6. |
Я читала эту английскую книгу (раньше). |
f |
I’m reading this English book. |
7. |
Я прочитаю эту английскую книгу (завершу действие). |
g |
I’ll be reading this English book. |
8. |
Я читала эту английскую книгу (в тот момент). |
h |
I read [red] this English book. |
9. |
Я прочитаю эту английскую книгу (в будущем). |
i |
I’ll read this English book. |
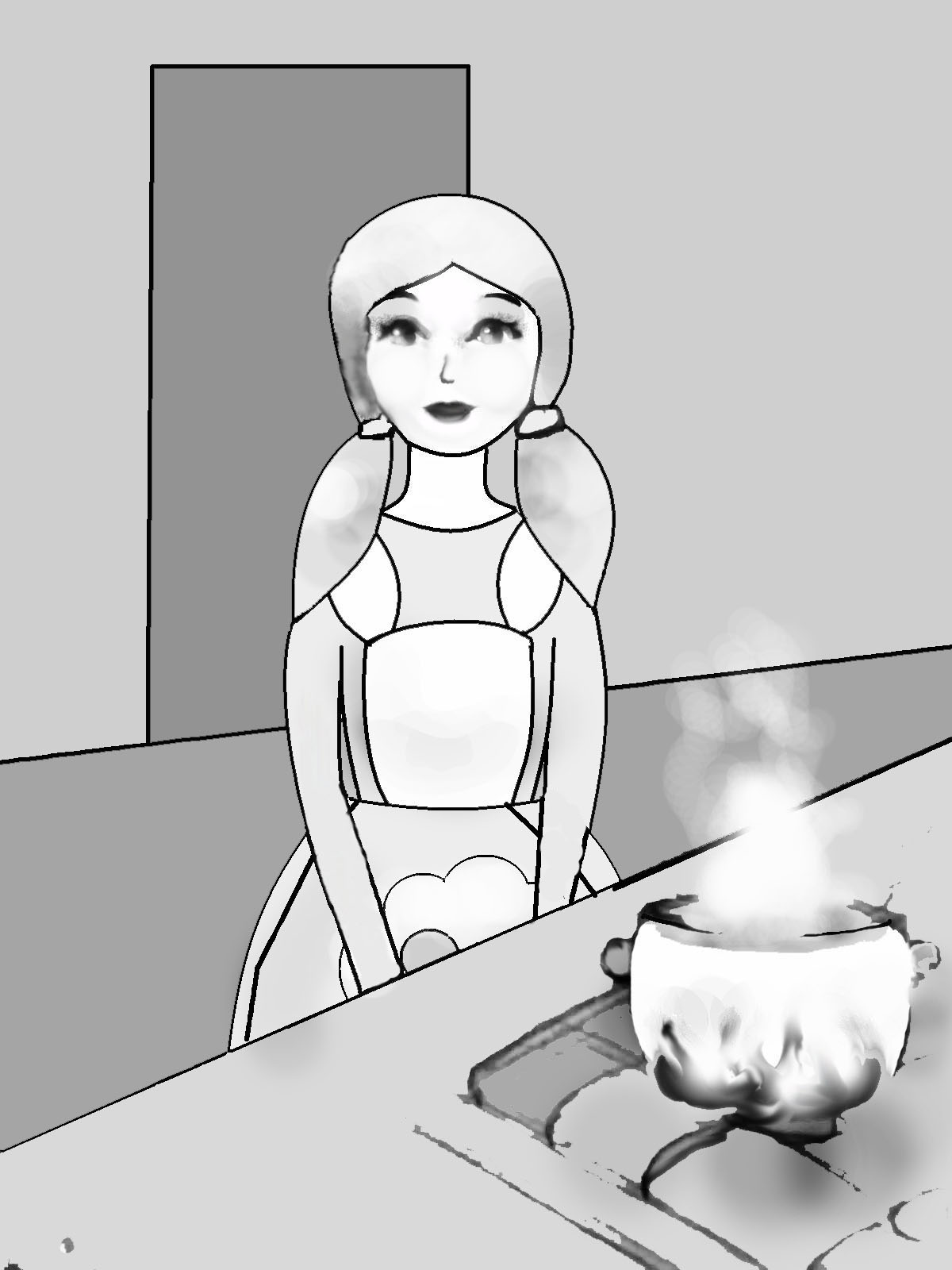
У прaжнение 35. Распределите следующие предложения по смыслу под картинками на рис. 14:
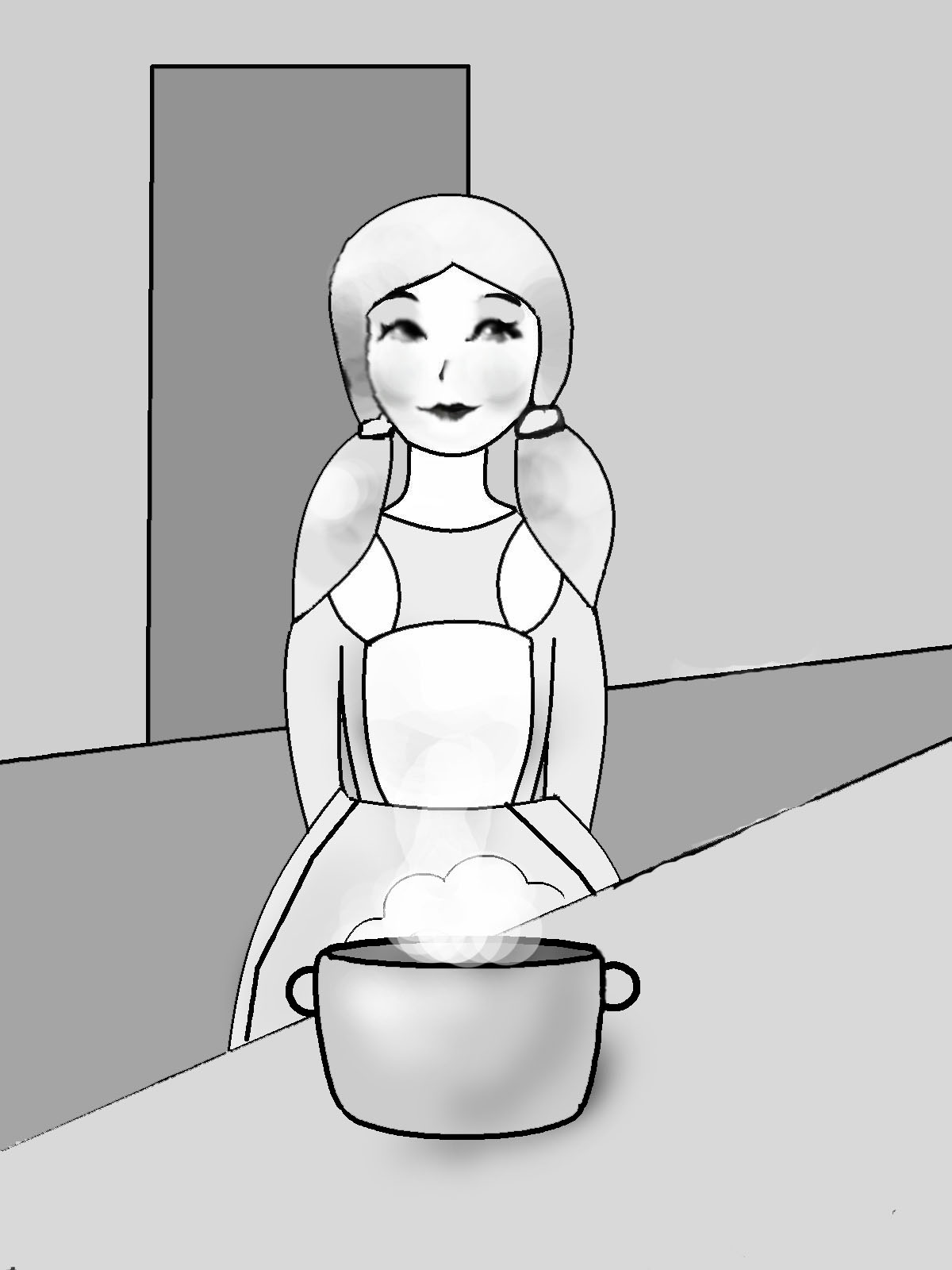
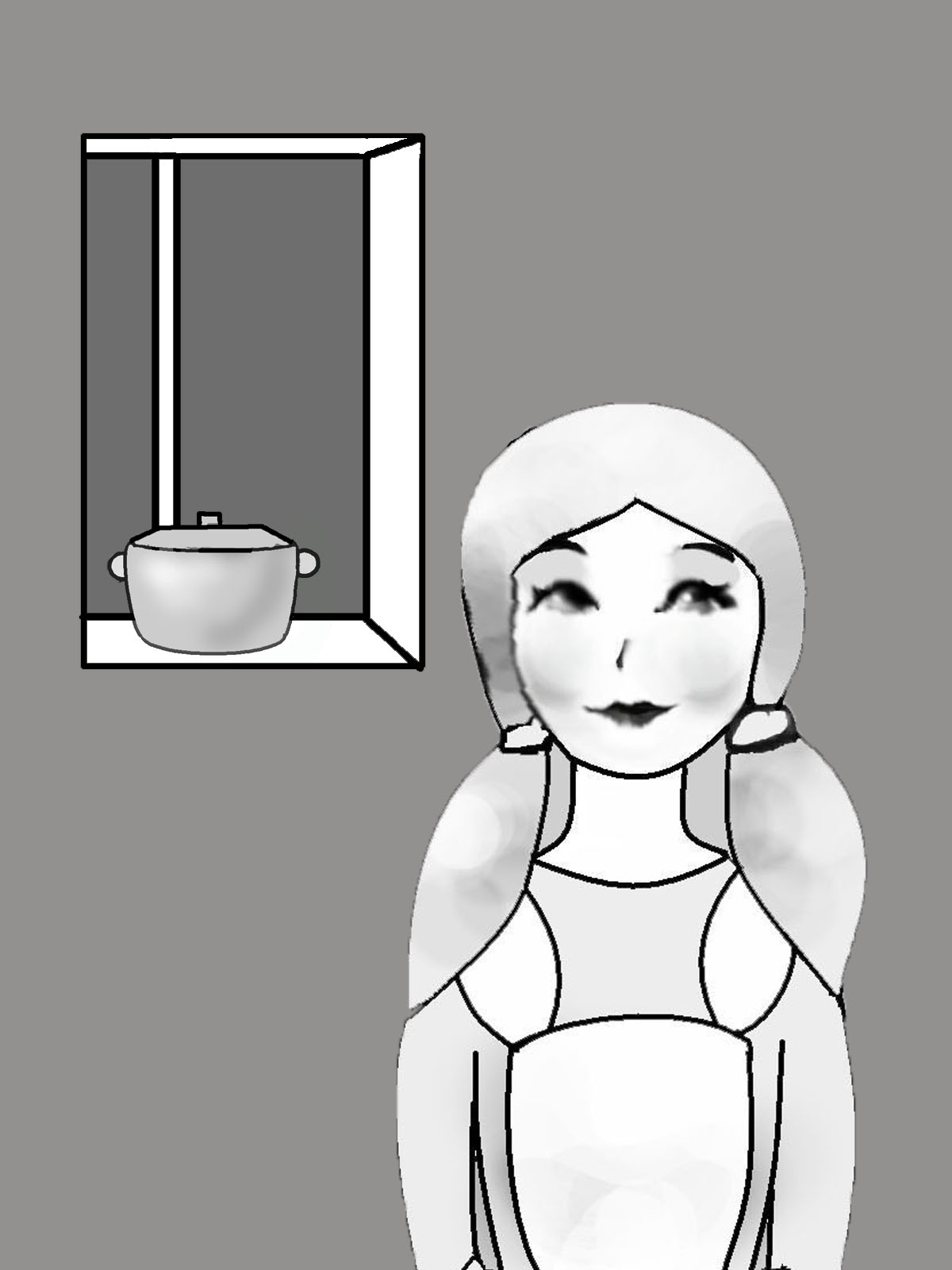
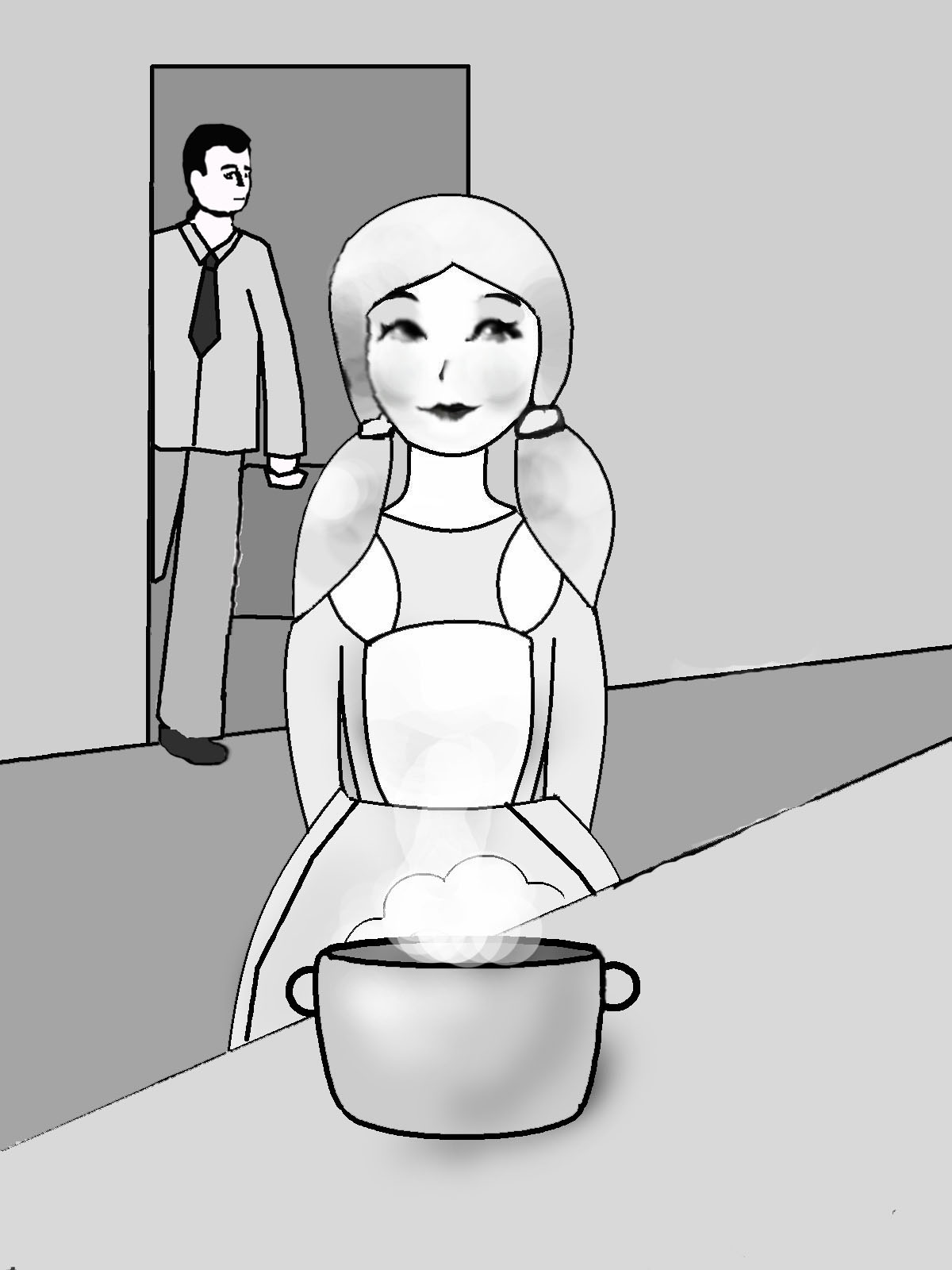
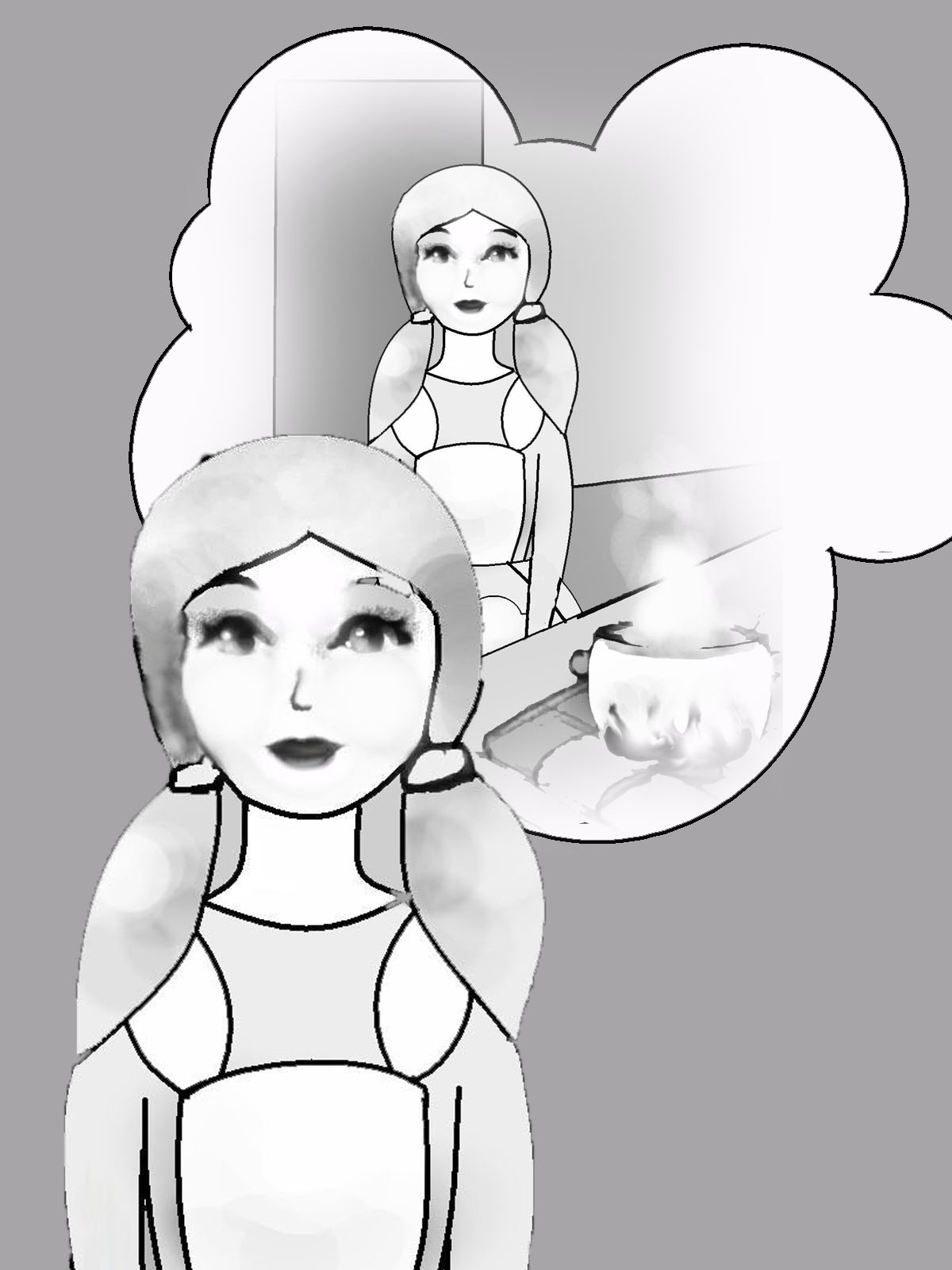
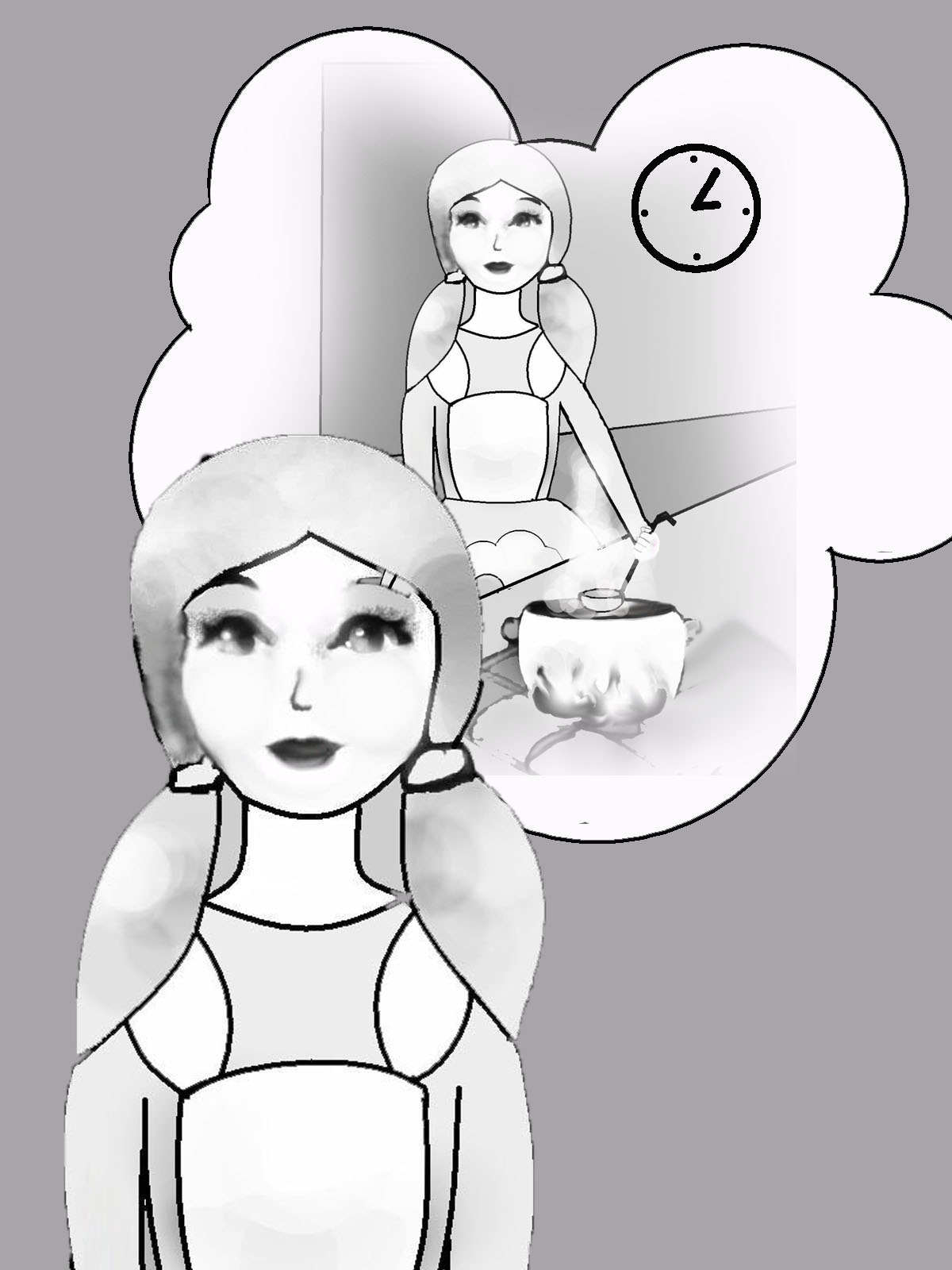
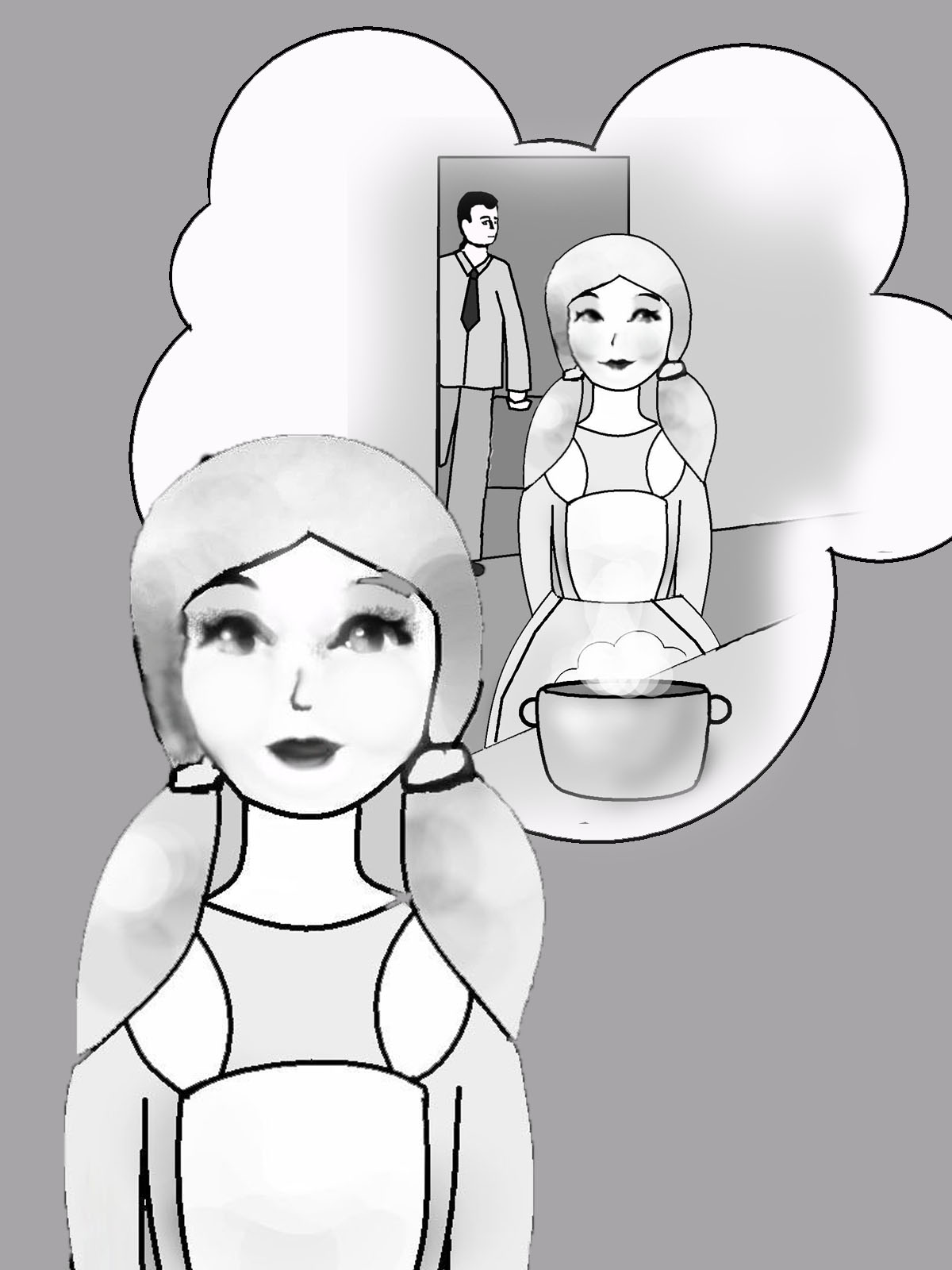
Rebecca will cook porridge.
Rebecca always cooks porridge.
Rebecca had already cooked porridge, when Ed (Edward) came yesterday.
Rebecca is cooking porridge now.
Rebecca will have already cooked porridge, when Ed comes (tomorrow).
Rebecca cooked porridge yesterday.
Rebecca has already cooked porridge today.
Rebecca will be cooking porridge at 3 o’clock tomorrow.
Rebecca was cooking porridge yesterday, when Ed came.
Время действия |
Характер действия |
||
Simple (факт действия) |
Continuous (процесс действия) |
Perfect (результат действия) |
|
Present |
..
1. Ребекка всегда готовит овсянку. |
2. Ребекка готовит овсянку сейчас. |
3. Ребекка уже приго-товила овсянку сегодня. |
Past |
4. Ребекка готовила овсянку вчера. |
5. Ребекка готовила овсянку вчера, когда Эд пришел. |
6.Ребекка вчера уже при-готовила овсянку, когда Эд пришел вчера. |
Future |
7. Ребекка будет готовить овсянку. |
8. Ребекка будет готовить овсянку в 3 часа завтра. |
9.Ребекка уже приготовит овсянку , когда Эд придет (завтра) |
Рис. 14. Видовременные формы глагола