
- •Lesson 1
- •Preparation for Printing
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Lesson 2
- •Letterpress.
- •Vocabulary notes.
- •Lesson 3
- •Intaglio.
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Lesson 4
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Lesson 5
- •History
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Lesson 6
- •Industry organization
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Part II
- •Industry organization
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Lesson 7
- •Recent developments
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Lesson 8
- •Occupations in the industry
- •Vocabulary notes:
Exercise
1.
Read
and translate the text.
Before any material can be
printed, the text must be set in type and checked for accuracy, and
illustrations must be prepared for reproduction. When a manuscript
is delivered to a printer, the first step is to choose a type for
the text and typeset the material. Until recently hot-metal
typesetting was used, so called because the type was cast from a
molten lead alloy. Today most typesetting is done by a procedure
called photocomposition, also known as cold-type composition.
In the early days of
photocomposition, an operator typed the text into the composing
machine, following instructions on type size and style, the length
of each text line, and the space between lines. With the advent of
computers, the process has become more automated. In many systems,
operators can typeset text directly from an author's floppy disk or
through telecommunication lines that transmit the text from the
author's computer to the composing machine.
When typesetting is complete,
a preliminary copy of the text, in the form of galley proofs or page
proofs, is sent to a proof-reader. The proof-reader checks these
proofs against the original material and marks misspelled words,
typographical mistakes, lines dropped or repeated, and other errors.
The corrected proofs are returned to the typesetter, who makes the
necessary changes.
Because typesetting can
produce only letters, numbers and symbols, and punctuation marks,
illustrations are prepared separately from the text. A simple line
drawing, without grey tones, can be printed as a line reproduction
without any special handling. More complicated black-and-white
illustrations, particularly photographs, must undergo a halftone
process. Each illustration is photographed through a screen that
breaks down the tones and shading into tiny dots of varying sizes.
Larger and more closely packed dots create the impression of darker
shades, while smaller, more widely spaced dots convey lighter
shading. By a special process, colour illustrations and photographs
are analysed into four basic colours--red, blue, yellow, and black.
Each colour is then applied separately in the printing process to
re-create the four-colour image.
The text, line drawings, and
other illustrations are arranged as they will appear on the final
printed pages. All but the halftones are pasted down on a board or
stiff paper; space is left where the halftones will be placed later.
The completed page is called a mechanical, or camera-ready copy. In
the 1980s computerized, or electronic, publishing (also known in
some instances as desktop publishing) had begun to replace these
methods.
The mechanicals are
photographed, and the negatives are processed. Halftones are
prepared on separate negatives and then stripped in, or aligned, in
the blank spaces left for them during paste-up. The resulting
composite negative is then used to make what is known as a printing
plate. Usually this is a metal plate that has been coated with a
photosensitive material and subsequently exposed to the composite
negative. The texts and illustrations are finally burned, or
chemically etched, into the plate, which is then ready for printing.
to
typeset – набирати
cold-type
composition – «холодний
набір»
advent
– поява
floppy
disk
– гнучкий диск, дискета
galley
proof
– відбиток
гранки, коректура в гранках
proof
reader – коректор
a
mechanical
– монтаж
(полос) оригінал – макет
a
camera-ready copy – оригінал-макет
shade
– відтінок, тон
to
strip
in
– вклеювати (ілюстрації, текст) при
монтажі
to
align
– лінірувати
рядок (линировать строку – выравнивать)
paste up
– фотомонтаж
combined
(composite) negative – комбінований
негатив
to
etch
– протравляти,
гравірувати
Exercise
2. Answer
the questions:
What must be done before
any material can be printed?
Why was the typesetting
called hot-metal typesetting?
When did the process of
typesetting become more automated?
Can operators typeset text
directly from an author’s floppy disk?
Where is a preliminary copy
of the text sent to?
What is the function of a
proof-reader?
Are the corrected proofs
returned to the proof-reader?
Who makes the necessary
changes?
Why are illustrations
prepared separately from the text?
What
kind of dots create the impression of darker shades?
What is called a
mechanical, or camera-ready copy?
What has a metal plate been
coated with?
Exercise
3.
Find
in the text the English for:
фотонабір; рукопис;
шрифт; набирати матеріал; набірна
машина; поява комп’ютерів; коректор;
ряди, що пропущені; помилка; окремо;
оригінал-макет; полутонові зображення;
обробляти негативи; бути покритим
будь-чим.
Exercise
4.
Translate
into Ukrainian.
accuracy;
to be delivered to; the space between lines; floppy disk; to
transmit the text; a preliminary copy; galley proof; misspelled
words; to undergo; a printing plate; the composite negative; to be
burned.
Exercise
5.
Give
the four forms of the verbs:
to choose to check
to do to apply
to call to leave
to become to to use
to make to to know
Exercise
6.
Write
T (True) or F (False) next to each sentence.
Today most typesetting is
done by a procedure called photocomposition.
The corrected proofs are
returned to the proof-reader.
A preliminary copy of the
text is sent to an editor.
Smaller, more widely spaced
dots convey lighter shading.
The typesetter makes the
necessary changes.
A printing plate is a metal
plate that has been coated with photochromic material.
Colour illustrations and
photographs are analysed into five basic colours – red, blue,
green, yellow and black.
Exercise
7.
Join
the broken sentences. 1.
Hot-metal typesetting was so called
because 2.
Illustrations are prepared 3.
With the advent of computers
4.
The proof-reader marks 5.
The completed page is called 6.
Space is left where a.
misspelled words, typographical mistakes and other errors. b.
the halftones will be placed later. c.
the type was cast from a molten lead alloy. d.
a mechanical, or camera-ready copy. e.
separately from the text. f.
the process has become more automated.
Exercise
8.
Put
the sentences in the right order.
Larger and more closely
packed dots create the impression of darker shades.
An operator typed the text
into the composing machine.
The first step is to choose
a type for the text and typeset the material.
Before any material can be
printed, the text must be checked for accuracy.
The composite negative is
used to make what is known as a printing plate.
More complicated
black-and-white illustrations must undergo a halftone process.
The mechanicals are
photographed, and the negatives are processed.
Each colour is then applied
separately in the printing process to re-create the four-colour
image.
Exercise
9.
Find
pairs of words.
1.
black-and-white a. composition
2.
four-colour b. material
3.
floppy c. words
4.
cold-type d. machine
5.
photosensitive e. illustrations
6.
misspelled f. image
7.
composing g. disk
Exercise
10.
Fit
the meaning and the words.
a
type; a computer; a mark; a manuscript; a shade; illustration
something that illustrates;
a picture or drawing;
an electronic device
designed for performing operations on data at high speed:
a written or typed piece of
writing before set in type;
a symbol used in writing or
printing;
a block with a raised
surface used in printing a letter or a character on paper;
the degree of darkness of a
colour.
Exercise
1. Read
and translate the text.
Letterpress, or relief,
printing is one of the oldest processes. The type is raised from the
background plate so that when the type is inked and pressed against
paper, only the raised portions transmit the image to the paper's
surface. Originally type was cast piece by piece in small, hand-held
casters. By the 19th century, type could be cast and set into text
in a single operation, either by Monotype machines, which set single
characters, or Linotype machines, which set entire lines in a single
slug. The soft metal casts tended to wear down quickly in the
printing process, however, and had to be replaced with fresh type.
To solve this problem, a
means of making more durable plates was invented. Two of the most
common methods are electrotyping and stereotyping. Electrotyping
uses an electroplating process to create printing plates. Type is
set and a cast made, usually out of wax, which is then coated in
graphite and placed in an electroplating bath. A copper shell, or
casting, is built up in the shape of the original type. When backed
with metal, it makes a durable letterpress plate for high-volume
printing. Stereotyping begins by making a mould of set type using a
heat-resistant papier-mâché. Molten metal is then poured into the
mould to create the cast plate. In more recent years, lighter and
less expensive plates of rubber and plastic have been developed.
Letterpress printing uses
three designs of printing press: sheet fed platen, sheet fed
flatbed, and rotary presses, which can be sheet fed or web fed. In
sheet fed presses, individual sheets of paper are fed into the
press. In web fed presses, a continuous roll of paper is fed through
the press.
Platen presses are the oldest
type and are used for small printing jobs. They consist of a flat
bed on which the images (type or plates) are laid and another flat
surface, the platen, which is connected to a screw or lever. Paper
is laid on the bed and pressed by the platen to transfer the image
to the surface. Printing on early presses was a slow process, since
the paper had to be fed one sheet at a time into the press.
Improvements made in the 1830s and 1840s featured automatic inking
and mechanical power, which increased printing speed from a few
dozen sheets an hour to more than a thousand.
Sheet fed flatbed presses
feature a cylinder, on which the paper is attached, that rolls over
the bed of inked type. This design overcame the problem of uneven
impression on the paper surface that often occurred in platen
presses.
In rotary web fed presses a
continuous roll of paper is fed between two cylinders, the plate
cylinder and the impression cylinder. The plate cylinder, either
electrotype or stereotype, is automatically inked and pressed
against the paper as it unrolls. After the paper is printed, it can
be cut into individual sheets and folded. Flatbed and rotary presses
can be designed to print on both sides of the paper simultaneously
and to reproduce colour illustrations. These machines were
responsible for the enormous growth of newspapers during the 19th
century.
letterpress
– високий
друк
to
cast
–
виливати, лити
a
slug
– рядок,
відлитий на лінотипі
caster
–
ливарна машина
electroplating
bath–
ванна
для нанесення гальванічного покриття
a
mould
– форма, шаблон, матриця
to
ink
– вкривати фарбою друкарську форму
platen
press
– прес валіком
web
fed
printing
press
–
рулонна друкарська машина
sheet
fed printing press –
листова друкарська машина
flat
– плаский
impression
– тиснення, відбиток
plate
cylinder
– формний циліндр
impression
cylinder – друкарський
циліндр
Exercise
2.
Answer
the questions:
What
is “letterpress” or “relief printing”?
Why
did casts wear down so quickly?
What
two methods are used to make more durable plates?
What
kind of plates have been developed in more recent years?
Does
letterpress printing use two designs of printing press?
What
are platen presses used for?
What
do they consist of ?
Was
the printing on early presses a slow process? Why?
When
were the improvements made to increase printing speed?
What
helped to overcome the problem of uneven impression on the paper
surface?
What
happens after the paper is printed?
What
presses were responsible for the growth of newspapers in the 19th
century?
Exercise
3.
Find in the text the English for:
відливок;
винаходити; вкривати фарбою друкарську
форму; гумові та
пластикові
печатні форми; прес валіком; ванна для
нанесення гальванічного покриття;
довговічний; рулонна подача паперу;
величезний; поверхня; листова друкарська
машина; зображення.
Exercise
4.
Translate
into Ukrainian.
To wear
down; a mould; to coat; automatic inking; to transfer the image
a
screw; improvements; to overcome the problem; platen press; uneven
impression; simultaneously; to be responsible for; a continuous roll
of paper.
Exercise
5. Write
T(True) or F(False) next to each sentence.
Monotype
machines set entire lines in a single slug.
Electrotyping
uses an electrotyping process to create printing plates.
Copper
is poured into the mould to create the cast plate.
In
web fed presses, individual sheets of paper are fed into the press.
Paper
is laid on the bed and pressed by the platen to transfer the image
to the surface.
Platen
presses are used for small printing jobs.
Printing
on rotary presses is a slow process.
Exercise
6. Complete
the sentences with suitable preposition. For,
of (2), upon, by(3), on, over, up, through
A
copper shell, or casting, is built _____ in the shape of the
original type.
Rotary
drum printing was invented_____ Richard March Hoe, and then
improved _____William Bullock.
Paper
is laid _____ the bed and pressed _____the platen to transfer the
image to the surface.
When
a final text is agreed _____, the next phase is design.
Currently,
most books and newspapers are printed using the technique ____
offset lithography.
Across
the world, _____ 45 trillion pages are printed annually.
Flexible
rubber instead _____ glass or metal plates is used on web presses
_____ relief printing.
In
web fed presses, a continuous roll of paper is fed_____ the press.
Exercise
7. Find
pairs of opposites.
expensive
a. late
slow
b. to destroy
light
c. detailed
minority
d. uneven
to
create e. majority
early
f. heavy
even
g. quickly
general
h. cheap
Exercise
8. Complete
the sentences:
The
soft metal casts tended … .
A
means of making more durable plates… .
Molten
metal is then poured into … .
In
web fed presses, a continuous roll of paper … .
Paper
is laid on the bed and … .
Lighter
and less expensive plates of rubber … .
Exercise
9. Join
the broken sentences.
Platen
presses
electrotyping
and stereotyping. In
sheet fed presses individual sheets of paper to
print on both sides of the paper simultaneously. A
copper shell is built up
are
used for small printing job. Two
of the most common methods are are
fed into the press. Flatbed
and rotary presses can be designed in
the shape of the original type.
Exercise
10. Fit
the meaning and the word.
To
cast, job, fresh, newspaper, mould, illustration, to improve,
sheet
a
piece of paper on which to write;
a
daily or weekly publication of news on large sheets of paper folded
but not fixed together;
to
make something better;
to
form by pouring metal into a mould and letting it harden;
newly
made;
a
hollow form for giving a particular shape to a liquid;
work
which a person does regularly to earn his living;
something
that illustrates; a picture or drawing.
Exercise
1.
Read
and translate the text.
In intaglio printing, the
text or image to be reproduced is not raised above the plate's
surface, as in the letterpress method, but is engraved or etched
into the plate. Ink applied to the surface fills these depressions,
then plate and paper are pressed together. The paper is actually
forced into the ink-filled depressions to transfer an image to the
paper.
Intaglio printing often uses
highly polished copper plates on which a design has been engraved
with sharp steel or diamond-tipped tools. These methods date back to
about 1440 in Germany and Italy and were used by Albrecht Durer and
other artists of the 1500s. In some instances, the copper plates can
be coated with an acid-resistant substance and a design traced on
the surface with a fine-pointed tool that exposes the copper. The
plate is then placed in an acid bath so that the lines of exposed
copper are chemically etched by the acid into the plate's surface.
When the acid-resistant substance is cleaned off, the plate can be
used to print etchings. Since copper wears quickly when subjected to
great pressure, in some cases steel plates are used to make a large
number of prints.
Traditional intaglio plate
making had to be done by a skilled artist or draftsman and was a
slow process. In the early 1880s, a photographic process was
invented that came to be known as photogravure. The image to be
printed is photographed through a screen, breaking the image into a
series of small dots. The screened image is transferred to a special
carbon-coated tissue that is mounted on a coated plate. When the
paper is peeled off, the carbon dots remain on the plate, allowing
the image to be burned into the plate in an acid bath. The deeper
the dots are etched, the more ink they hold, and the darker the
image.
Photogravure
can be used on platen, flatbed, or rotary presses. When rotary web
fed presses are used, the process is called rotogravure. The
advantage of this process is that it allows a greater density of
pigment per unit area than any other method of printing. Multiunit
rotogravure presses can produce one- to four-colour images at high
speed and today are used mainly for high-volume magazine production
and by the packaging industry.
Intaglio
– глибокий друк
tool
–
різець
a print
–
відтиск
to
engrave
–
гравіювати
depression
–
заглибина
to force
into
–
удавлювати, утискувати
to polish
–
полірувати, шліфувати
diamond-tipped
tool
– різець з алмазним наконечником
to
trace
on
–
копіювати, намічати, простежувати,
креслити
acid-resistant
–
кислостійкий
etching
–
протравлення
a
draftsman
–
кресляр
photogravure
– глибокий друк, геліогравюра
carbon
tissue
– пігментний папір, копіювальний папір
to
peel
–
відшаровувати, обдирати, сходити,
очищати
rotogravure
–
ротаційний глибокий друк
to
expose
–
піддавати дії, показувати, викривати,
копіювати.
design
–
проект, малюнок, візерунок, креслення,
ескіз, розробка
Exercise
2.
Answer
the questions.
What is the difference
between intaglio printing and letterpress printing?
What is
the paper forced into to transfer an image to the paper?
What can the copper plates
be coated with?
What tools are used to
engrave a design?
When can the plate be used
to print etchings?
Why are steel plates used to
make a large number of prints?
Who did traditional intaglio
plates?
When was a photographic
process invented?
Where is a special
carbon-coated tissue mounted on?
What is the advantage of
rotogravure?
What presses are used mainly
for high-volume magazine production?
Exercise
3.
Find
in the text the English for:
Підніматися над;
шліфувати; відтиск; великомасштабне
виробництво; зазнавати великого тиску;
покриватись чимось; кислостійка
речовина; досвідчений художник; в деяких
випадках; протравлення; пакувальне
виробництво; заглибина; утримувати;
щільність; ротаційний глибокий друк.
Exercise
4.
Translate
into Ukrainian.
Ink-filled
depression; highly polished copper plate; an acid bath; to clean
off; to be mounted on; to invent; great pressure; to break the
image; advantage; a design; density of pigment; four-colour image; a
flatbed press; a multiunit rotogravure press; a sharp steel tool.
Exercise
5.
Give
four forms of the verbs:
to burn
to allow
to fill
to hold
to coat
to break
to mount
to know
to do
to force
to raise
to etch
Exercise
6.
Complete
the following sentences:
The paper is actually forced
into the ink-filled depression … .
Sharp steel or
diamond-tipped tools are used to … on polished copper plates.
Albrecht Durer and other
artisti of the 1500s used … .
The image is photographed
through a screen, breaking the image into … .
The carbon dots remain on
the plate when … .
… the more ink they hold,
the darker is the image.
In the process of
rotogravure … are used.
Exercise
7. Join
the broken sentences:
When rotary web fed
presses are used,
Printing on early presses
was a slow process,
In intaglio printing, the
text or image
The plate can be used to
print etchings
Illustrations can be read
by an optical scanner and
Rotogravure allows a
greater density of pigment per unit area than
The name offset refers to
the fact that
any
other method of printing.
when
the acid-resistant substance is cleaned off. since
the paper had to be fed one sheet at a time into the press. the
process is called rotogravure.
the
printing plates do not come into direct contact with the paper. is
engraved or etched into the plate.
entered
into the computer in the form of electronic signals.
Exercise
8.
Write
T (True) or F (False) next to each sentence.
In the letterpress method
the text or image is not raised above the plate’s surface.
Steel plates are used to
make a large number of prints because copper wears quickly when
subjected to great pressure.
When the acid-resistant
substance is cleaned off, the plate can be used to print etchings.
The deeper the dots are
etched, the less ink they hold, and the darker is the image.
The image to be printed is
photographed through a screen, breaking the image into a series of
small dots.
The advantage of
photogravure is that it allows a greater density of pigment per
unit area than any other method of printing.
Multiunit rotogravure
presses are used mainly for high-volume magazine production.
Exercise
9.
Fit
the meaning and the word.
Substance,
advantage, to date, tissue, to engrave, pigment, acid.
a dry substance that when
mixed in liquid becomes a paint or dye;
a circumstance favorable to
success;
the physical matter that
makes up some thing, object, etc.;
a chemical substance that
when strong enough can burn holes in what it touches;
to cut (letters, designs,
etc.) into a hard surface, as of metal or wood;
to belong to a particular
period;
soft paper used for various
purposes.
Exercise
10.
Find
pairs of words.
unpublished optical fine-pointed rubber carbon-coated technological oil-based letterpress
tissue innovations scanner ink works tool printing blanket
Exercise
11.
Complete
the sentences with suitable preposition.
On,
with, of (2), into, off, above, through, down.
A continuous roll of paper
is fed ____ the press.
In intaglio printing, the
text or image to be reproduced is not raised ____ the plate’s
surface.
The soft metal casts tended
to wear ____ quickly in the printing process and had to be replaced
____ fresh type.
Photogravure allows a
greater density ____ pigment per unit area than any other method
____ printing.
A design traced ____ the
surface with a fine-pointed tool that exposes the copper.
Molten metal is then poured
____ the mould to create the cast plate.
One need
only brush ____ surrounding powder after the printing process.
Exercise
1.
Read
and
translate
the
text.
OFFSET
In the past few decades,
offset printing (also called offset lithography) has replaced
letterpress and intaglio methods almost entirely for commercial
work. The name offset refers to the fact that the printing plates do
not come into direct contact with the paper. Instead, the inked
printing plates (which are attached to a cylinder) transfer, or
offset, the image to a rubber blanket covering another cylinder. As
the inked blanket cylinder rotates, it deposits the image onto the
paper, which is fed from another set of rollers.
The offset technique was made
possible at the beginning of the 20th century after the development
of certain photographic processes and the rotary web fed press.
Offset printing plates are usually made of steel, aluminium, or a
chrome-copper alloy.
Unlike letterpress or
intaglio printing, offset does not depend on raised or etched
surfaces to transfer images. Instead it relies on the fact that
grease and water do not mix. As the plate cylinder rotates, the
plate passes first under water-soaked damping rollers and then under
inking rollers that carry a grease-based ink. The offset plate is
chemically treated so that the area to which the ink is transferred
retains the greasy ink and repels water. The rest of the plate
retains water and repels ink. As the cylinder continues to rotate,
the plate presses against the rubber blanket, which accepts ink from
the plate and transfers it to the paper. Since there is no type to
wear out, an offset plate can make a large number of impressions.
Offset presses can be
designed to print both sides of the paper at once and to reproduce
images with one or more colours. Because web fed presses are usually
used for this method, material can be printed at high speed. Offset
plate making and storage costs are much lower than the costs of
letterpress methods.
1. offset
– плаский офсетний друк
2. rubber
blanket
– офсетне (гумове) полотно, офсетна
гумовотканинна пластина
3. instead
–замість того, натомість
4. etched
surface
– протравлена поверхня
5. grease
– пластичний мастильний матеріал,
мастило
6. to
grease
– зажирювати (друкарську форму)
7. roller
– валик, матричний каландр
8. inking
roller
– фарбовий валик
9. damping
roller
– зволожуючий валик
10. ink
– друкарська фарба
11.
grease-based
ink
– чорнило, яке містить в собі мастило
12. to
treat
- обробляти
13. to
repel
- відштовхувати
14. to
retain
– утримувати, удержувати
15.
storage
– зберігання
Exercise
2.
Answer
the
questions:
Why
has offset printing replaced letterpress and intaglio methods?
Do the
printing plates come into direct contact with the paper?
When was
the offset technique made possible?
What
metals are offset printing plates usually made of?
Does
intaglio printing depend on raised or etched surfaces to transfer
images?
What fact
does offset printing rely on?
How is
the offset plate treated?
Why can
an offset plate make a large number of impressions?
What kind
of presses are usually used for offset printing?
What are
the advantages of offset printing?
Exercise
3.
Find
in
the text the English for:
Заміняти,
удержувати, фарбовий валик, відтворювати
зображення, певний, сплав, гумове
полотно, офсетний циліндр (барабан),
фотографічні процеси, змішувати,
фарбовий валик, зволожуючий валик, на
відміну від…,покладатися на….
Exercise
4.
Translate
into Ukrainian:
Intaglio
method, inked blanket cylinder, offset plate, raised surfaces,
greasy ink, rotary web fed press, chrome-copper alloy, to transfer,
to be designed, at once, storage, to cost, to carry, to wear out,
grease-based ink.
Exercise
5.
Give
the four forms of the verbs: to
begin to have to
use to retain to
make to come to
rely to rotate to
set to feed
Exercise
6.
Write
T (True) or F(False) next to each sentence.
The inked blanket cylinder
deposits the image onto the paper.
Offset depends on raised or
etched surfaces to transfer images.
Letterpress and intaglio
printing has replaced offset printing in the past few decades.
Offset presses can be
designed to print only one side of the paper.
An offset plate can make a
large number of impressions because there is no type to wear out.
Offset
plate making and storage costs are much lower than the costs of
letterpress methods.
Because web fed presses are
used, material can be printed at high speed.
Exercise
7.
Join
the broken sentences:
Grease and water
Letterpress printing depends
on
The rest of the plate
Chrome-copper alloy
The four-colour press has
Offset presses can be
designed
Material can be printed at
high speed because
retains water and repels
ink.
to reproduce images with one
or more colours.
web fed presses are usually
used.
raised and etched surfaces
to transfer images.
do not mix.
is used to make offset
printing plates.
a colour
plate cylinder for each negative.
Exercise
8.
Put
the sentences in the right order.
The
offset plate is chemically treated so that the area to which the
ink is transferred retains the greasy ink and repels water.
After the rotary web fed
press was developed the offset technique was made possible.
Offset presses can be
designed to print both sides of the paper at once.
The rest of the plate
retains water and repels ink.
Offset
lithography has replaced letterpress and intaglio methods almost
entirely for commercial work.
Offset printing relies on
the fact that grease and water do not mix.
The inked printing plates
are attached to a cylinder.
The rubber blanket accepts
ink from the plate and transfers it to the paper.
Exercise
9.
Complete
the following sentences:
The name offset refers to
the fact that the printing plates…
After certain photographic
processes were developed…
…deposits the image onto
the paper.
The inked printing plates
transfer the image to…
Letterpress and intaglio
printing depends on…
As the plate cylinder
rotates, the plate passes under inking rollers that…
The rubber blanket accepts
ink from the plate and…
…to reproduce images with
one or more colours.
Exercise
10.
Find
pairs of synonyms. make vacant begin work nearly at
once transfer decade image speed immediately picture do move ten
years job empty velocity almost start
Exercise
11.
Fit
the meaning and the word.
Photography,
a decade, to develop, ink,
a
press, to attach, an alloy
any of
various devices or machines for squeezing,
stamping
or crushing;
to fasten
or affix;
to
join,
to connect;
the process of producing
images of object on special
paper by
the chemical action of light;
a period
of ten years;
a
substance made up of two or more metals;
a
coloured liquid used for writing or drawing;
to come or to bring to a
more advanced state.
Exercise
1.
Read
and
translate
the
text.
Although printing has been
used in Western countries for more than 500 years, the creation of
reproductions by mechanical means has a much longer history. Relief
printing using stamps to impress designs into soft clay or wax has
been known for thousands of years in the Middle East and in other
parts of Asia. Designs or inscriptions were also carved into stone
or cast into metal to make seals.
China was
the fist country to print with paper, ink, and carved wooden blocks,
a process called xylography. The invention of paper in China in the
8th
century AD provided a smooth, flexible surface on which to reproduce
an image. In this process, a single carved wooden block of text was
used to print impressions on whole pages. By the 11th
century, the Chinese had cut the blocks into individual characters,
creating the word’s first movable type.
Xylography
was also the fist printing method used in Europe in the early 1400s.
By 1450, Gutenberg’s combination of movable metal type and the
printing press had produced Europe’s first typeset book – the
Gutenberg Bible. Gutenberg’s process spread quickly to other
European nations. Over time, the literacy rate gradually rose among
the population of Europe. Literature and scientific and religious
texts, once read only by scholars, nobility, and the educated
priesthood, were now available to an ever-widening audience.
As the demand for printed
books steadily increased, printers had to improve their methods and
equipment. They developed sturdy metal presses to replace the common
wooden press, created stereotype and electrotype plates to make
greater numbers of copies, and designed mechanically driven and
automatically inked presses to increase printing speed and quality.
Not all advances in printing
technology came from printers or designers and manufacturers. In
1796 German author Aloysius Senefelder, in his search for an
inexpensive means of publishing his own plays, developed the
techniques of lithography. Joseph-Nicephore Niepce, a French
landowner and inventor, discovered in the 1820s that certain
chemical compounds were sensitive to light. His work marked the
origins of photogravure and eventually led to the invention of
photography and the use of photographic processes to reproduce
images.
Beginning with the invention
of the offset technique in the United States, a series of
20th-century innovations made mass production, high speed, and
economy in printing possible. Automated composition, first developed
after the 1920s, gave way to programmed composition in the 1950s.
Many of today's computerized typesetting machines can set 1,000
characters (individual letters or symbols) per second.
Phototypesetting equipment of the future could conceivably reach
speeds of nearly 3,000 characters per second, or about 10,000,000
characters per hour.
Inventors
also created pressureless printing, which eliminated the need for a
printing press. In 1948, two Americans conceived of a type of
electrostatic printing in which the colouring agent is not ink but a
powder that is sensitive to the pull of an electric charge induced
on a plate. This technique gave birth to xerography and the
now-familiar copying machines. The various processes developed to
duplicate and reproduce documents have been grouped under the name
reprography.
relief
printing –
високий друк
to carve
–
вирізати
xylography
–
ксилографія
priesthood
–
духовенство
photogravure
–фотогравюра
offset –
офсетний
typesetting
equipment –
набірне обладнання
movable
type –розбірний
шрифт
pressureless
printing –
безконтактний друк
to
conceive –
зачинати, задумувати
composition
–набір
reprography
–репрографія
Exercise
2. Answer
the questions:
Where and
when was relief printing created?
What process of printing was
developed in China?
When was paper invented?
How was
the first process of printing developing in the 8th
century?
What
changes had taken place in printing by the 11th
century in China?
What method of printing was
used in Europe in 1400s?
What book
was the first typeset book in Europe?
What was
the result of production Europe’s first typist book – the
Gutenberg Bible? How did printers improve their methods and
equipment?
What advances in printing
technology were made in 1796 by Aloysius Seinfelder?
What discovery was made by
Joseph – Nicephore Niepce in 1820s?
What innovations were made
in 1950s with the invention of the offset technique?
What technique gave birth to
xerography?
Exercise
3.
Find
in the text the English for:
Відтискати;
дерев’яна друкувальна форма
друку;
створювати; розбірний шрифт; швидко
розповсюджуватись; перша набірна книга;
бути доступним; швидкість друкування;
замінювати; недорогі засоби друку;
підвищити швидкість та якість друку;
фотонабірне обладнання; безконтактний
друк.
Exercise
4.
Translate
into Ukrainian.
Printed
books; to print with paper; single carved wooden blocks; literary
rate; invention of paper; available to; printing speed; to reproduce
images; offset technique; mass production; inventor; reproduce
documents.
Exercise
5.
Give
the four forms of the verbs: to
print to reproduce to
read to reach to
lead to rise to
give to drive to
develop to cut
Exercise
6.
Write
T (True) or F (False) next to each sentence.
Relief printing was used in
Asia.
In the
8th
century paper was invented.
By 1450 the literacy rate
was pour in Europe.
Xylography
was the only printing method in 1400s.
Gutenberg developed the
technique of lithography.
The offset technique was
invented in France.
Electrostatic printing was
invented in America.
Exercise
7.
Join
the broken sentences.
Designs or inscriptions
were carved
Relief printing has been
known
China was the first
country
Printers invented sturdy
metal presses
Many of today’s
computerized typesetting machines can set The
various processes which duplicate documents
in the Middle East.
to replace the common
wooden press.
1000 individual letters
or symbols.
to
print with paper, ink and carved wooden blocks.
into stone or cast into
metal.
are
called reprography.
Exercise
8.
Put
the sentences in the right order.
Inventors
also created pressureless printing.
Relief printing has been
known for thousand years in the Middle East.
Automated composition gave
way to programmed composition in 1950s.
Xylography
was the first printing method used in Europe in 1400s.
Not all advances in printing
technology came from printers or designers and manufacturers.
Phototypesetting equipment
of the future could conceivably reach speed of nearly 3000
characters per second.
As the demand for printed
books steadily increased, prints had to improve their methods and
equipment.
Gutenberg’s process spread
quickly to other European nations.
Exercise
9.
Find
pairs of words.
relief
mechanical
individual
smooth, flexible
phototypesetting
pressureless wooden
means
characters
printing
blocks
equipment
printing surface
Exercise
10.
Fit
the meaning and the words.
Stamp;
inscription; invent; movable; spread; advance
words cut on a stone;
create or design something
not existing before;
that can be taken from place
to place;
become more widely extended
or distributed;
piece of printed paper stuck
on envelopes;
forward movement; progress.
Exercise
11. Find
pairs of synonyms.
reproduce
soft
image
demand
carve constant
cut
requirement
multiply
character
steady mild
Exercise
12. Find
pairs of opposites.
rise
type
sensitive
beginning
reduce create
rough
end
face
raise
destroy write
Exercise
13. Complete
the sentences with suitable prepositions.
China was
the first country … print … paper and ink.
Paper was
invented … China … the 8th
century AD.
In xylography a single
carved wooden block … text was used … print impressions …
whole pages.
Gutenberg’s
process spread quickly … other European nations.
Not all advances …
printing technology came … printers or designers and
manufacturers.
Pressureless printing
eliminated the need … a printing press.
Phototypesetting equipment …
the future could reach speeds … nearly 3000 character … second.
Electrostatic printing gave
birth … xerography and copying machines.
Exercise
14. Complete
the following sentences:
Designs or inscriptions were
carved into stone or …
The
innovation of paper in China in the 8th
century AD…
Xylography was the first …
Gutenberg’s process spread
quickly …
The literacy rate gradually
rose …
Sturdy metal presses
replaced …
A French inventor discovered
that certain chemical compounds were …
Pressureless
printing eliminated
Exercise
1.
Read
and
translate
the
text.
PART I
The printing industry
includes establishments primarily engaged in printing text and
images on to paper, metal, glass, and some apparel and other
materials. Printing can be divided into three distinct stages:
prepress, the preparation of materials for printing; press or
output, the actual printing process; and postpress or finishing, the
folding, binding, and trimming of printed sheets into their final
form. Companies that provide all three services first prepare the
material for printing in the prepress department, then produce the
pages on the pressroom floor, and finally trim, bind, or otherwise
ready the material for distribution in the postpress department.
The printing industry is
broken into 12 segments that generally reflect the major type of
printing method that is used at the establishment or product that is
produced. Establishments that use printing plates, or some other
form of image carrier, to distribute ink to paper, are broken into
five industry segments: lithography, flexography, gravure, screen
printing and letterpress. Lithography, which uses the basic
principle that water repels oil, is the most widely used printing
process in the industry. Lithography lends itself to computer
composition and the economical use of color, which accounts for its
dominance. Commercial lithographic printing establishments make up
the largest segment of the industry, accounting for about 39 percent
of employment and about 30 percent of total establishments. Although
most newspapers use the lithographic process, their printing
activities are not included in this industry, but rather in the
publishing industry. Flexography uses printing plates made of rubber
or plastic. It is a high-speed process that uses fast-drying inks
and can be used on a variety of materials, qualities valued for
labels, shopping bags, milk cartons, and corrugated boxes. Gravure's
high-quality reproduction, flexible pagination and formats, and
consistent print quality have won it a significant share of
packaging and product printing and a growing share of periodical
printing. Screen printing prints designs on clothes and other fabric
items, such as hats and napkins. Where letterpress is still used, it
prints images from the raised surfaces on which ink sits. The raised
surfaces are generated by means of casting, acid etching, or
photoemulsion.
prepress
–
приготування до друку
postpress
–
оздоблювальні роботи
folding –
переплетіння
trimming
–
обрізування
printing
plate –форма
для друку
repel
–відштовхувати
account
for –
пояснювати, свідчити
pagination
–
нумерація сторінок
screen
printing –
трафаретний друк
letter
press –
високий друк
Exercise
2. Answer
the questions:
What does the printing
industry include?
What stages is printing
divided into?
How many
segments is the printing industry
broken
into?
What segments are
establishments broken into?
What is
the most widely used process in the industry?
What makes up the largest
segment of the printing industry?
What industry is printing of
newspapers included into?
What printing plates does
flexography use?
What process is flexography?
Where does screen printing
print designs on?
What are the raised surfaces
generated by?
Exercise
3.
Find
in the text the English for:
Підготовка
матеріалів до друку; процес друку;
оздоблювальні роботи; фальцовка;
переплетіння; обрізування; підготувати
матеріал до друку; поліграфічна
промисловість; друкарська форма; гнучка
нумерація сторінок; екранований друку;
високоякісне відтворення гравюри.
Exercise
4.
Translate
into Ukrainian.
To print
images; to prepare the material for printing; prepress department;
material ready for distribution; postpress; printing plates;
computer composition; economical use of colour; to account for; to
print designs on colours; raised surfaces; printing activities.
Exercise
5.
Give
the four forms of the verbs:
to include to grow
to produce to generate
to design to sell
to spend to serve
to learn to make
Exercise
6.
Write
T (True) or F (False) next to each sentence.
Companies that provide
printing first produce the pages on the pressroom floor.
Screen printing prints
designs on clothes and other fabric items.
Flexography uses printing
plates made of iron.
Lithography is the most
widely used printing process in the industry.
Printing activities of the
newspapers are included in lithographic industry.
Printing can be divided into
three stages.
Exercise
7. Complete
the following sentences:
Lithography is the most
widely used …
Printing can be divided into
…
The printing industry is
broken into …
Printed companies first
prepare the material …
Lithography lends itself to
…
Commercial lithographic
printing establishments make up …
Exercise
8.
Join
the broken sentences.
Printing can be devided
Although newspapers use
the lithographic process
The raised surfaces are
generated
Screen printing
Flexography uses
Establishments
that use printing plates are broken
by
means of casting, acid etching or photoemulsion.
printing
plates made of rubber or plastic.
into
five industry segments.
into
three distinct stages.
prints
designs on clothes and other fabric items. their
printing activities are not included in lithographic industry.
Exercise
9.
Put
the sentences in the right order.
The raised surfaces are
generated by means of casting, acid etching, or photoemulsion.
Flexography used printing
plates made of rubber or plastic.
Screen printing prints
designs on clothes and other fabric items.
It is a high-speed process
that use fast-drying inks.
Where
letterpress is still used, it printings images from the raised
surfaces on which ink sits.
The printing industry
includes establishments primarily engaged in printing text and
images on to paper, metal, glass and other materials.
Printing can be devided into
three distinct stages: prepress, press and postpress.
The printing industry is
broken into 12 segments.
Exercise
10. Complete
the sentences with suitable prepositions.
Printing can be divided …
three distinct stages.
Companies first prepare the
materials … printing … the prepress department.
Lithography lends itself …
computer composition.
Screen
printing prints designs … clothes and other fabric items.
Flexography uses printing
plates made … rubber or plastic.
Commercial lithographic
printing establishments make … the largest segment of the
industry.
The raised surfaces are
generated … means … casting, acid etching or photoemultion.
Lithography is the most
widely used printing process … the industry.
Exercise
11. Find
pairs of words.
printing
produced
basic
printed
widely
lithographic screen
sheet
principle
used
process
printing
industry product
Exercise
12. Find
pairs of synonyms.
include
primarily
distinct
total
company basic
firm
separate
originally
consist of
whole main
Exercise
13. Find
pairs of opposites.
plateless
advanced
shot
quick
low volume wide
old
high volume
slow
long
plate narrow
Exercise
14.
Fit
the meaning and the words.
Engage;
pressure; reflect; provide; dominant; flexible
throw back (light, heat,
sound)
give, supply (what is needed
or useful)
easily bent without breaking
take part in
having control or authority
force on or against
something
Exercise
15. Complete
the following sentences:
printing can be devided into
…
Lithography is … .It lends
itself to …
Commercial lithographic
printing establishments make up …
Flexography uses …
Screen printing prints on
clothes and …
The raised surfaces are
generated by means …
Exercise
1.
Read
and
translate
the
text.
Plateless
or nonimpact processes, which are the most technologically advanced
methods of printing, are included in the digital printing segment of
the industry. These include electronic. electrostatic, or inkjet
printing, and are used mainly for copying, duplicating, and
speciality printing. Although currently much of the work done using
digital printing is low volume and often done by small shops,
plateless printing is being used more and more throughout the
industry. Digital printing, also known as "variable data
printing", offers quick turnaround capabilities and the ability
to personalize printed materials. Establishments offering primarily
digital printing services constitute one of the smallest segments of
the industry — 3
percent
of total employment.
Quick
printing is the industry’s third largest segment in terms of the
number of jobs and is the industry's second largest segment in terms
of number of establishments. Used mostly by small businesses and
households, quick printing establishments use a variety of printing
and copying methods for projects that have short runs and require
quick turnaround. Many of these establishments have expanded into
other office-related services, such as shipping and selling office
supplies to satisfy the small business user. Other segments of the
printing industry include establishments that provide specialty
services to the printing industry, such as prepress services and
trade binding and related work.
plateless
or
nonimpact
process
– процес,
у якому
не використовуються
форми,
безконтактний процес
digital
printing –
цифровий друк
inkjet
printing –
струйний друк
capabitily
–
можливість
constitute
–
складати, засновувати
turnaround
capabilities –різноманітні
можливості
binding –
переплетіння
Exercise
2. Answer
the questions:
What processes are the most
technologically advanced methods of printing?
What printing do plateless
processes consist of?
What are
plateless processes used for?
What are
the capabilities of plateless process?
What capabilities does
digital printing offer?
Whom is quick printing used
by?
Why do many of quick
printing establishments use a variety of printing and copying
methods?
What have
small printing establishments expended into and why?
What
establishments do other segments of the printing industry include?
What industry is printing?
Exercise
3.
Find
in the text the English for:
Безконтактний
процес; технологічно-прогресивні
методи; цифровий друк; дублювання;
матеріал для друку; швидкий друк;
різноманітні методи друку та копіювання;
розростись до інших офісно-споріднених
служб; забезпечувати спеціальними
послугами поліграфічну промисловість;
підготовка до друку.
Exercise
4.
Translate
into Ukrainian.
Quick
printing; digital printing; primarily digital printing services; to
personalize printed materials; technologically advanced methods;
inkjet printing; to provide special services to the printing
industry; trade binding; to have short runs and require quick
turnaround.
Exercise
5.
Give
the four forms of the verbs:
to print to copy
to use to understand
to see to provide
to sleep to bind
to offer to be
Exercise
6.
Write
T (True) or F (False) next to each sentence.
Establishments offering
primarily digital printing services constitute one of the biggest
segments of the industry.
Plateless processes are the
most technologically advanced methods of printing.
Quick printing is mostly
used by large businesses and households.
Many of quick printing
establishments have expended into other related services.
Digital printing does not
offer quick turnaround capabilities.
Quick printing
establishments have expended into other-related services to satisfy
the small business user.
Exercise
7. Complete
the following sentences:
Digital printing is also
known as …
Digital printing offers …
Plateless
processes are the most technologically advanced …
Plateless or nonimpact
processes include …
Quick printing is mostly
used by …
Other segments of the
printing industry include …
Exercise
8.
Put
the sentences in the right order.
Other segments of the
printing industry include establishments that provide speciality
services to the printing industry.
Plateless or nonimpact
process are the most technologically advanced methods of printing.
Quick
printing is the industry’s third largest segment in terms of the
number of jobs and is the industry’s second largest
segment in terms of number of establishments.
Plateless printing incudes
electronic, electrostatic or inkjet printing.
Many of quick printing
establishments have expended into other office-related services.
Plateless printing is used
for copying, duplicating and speciality printing.
Exercise
9. Complete
the sentences with suitable prepositions.
by,
to, of, into, throughout, for
Nonimpact
processes are the most advanced methods … printing.
Quick printing is used
mostly … small businesses and households.
Digital printing offers the
ability … personalise printed material.
Quick printing is the
industry’s third largest segment … terms … the number …
jobs.
Most …
printing establishments have expended … other related services.
Plateless printing is being
used more and more … the industry.
Plateless processes are used
mainly … copying, duplication and speciality printing.
Exercise
10.
Join
the broken sentences.
Digital printing is known
Plateless processes are
Use a
mostly by small businesses quick printing establishments
Many of printing
establishments have expended Printing
is a large industry composed
Use a variety of printing
and copying methods for projects that have shot runs.
The most technologically
advanced methods of printing.
Into other office-related
services.
Of many shops that vary
in size.
As
variable data printing.
Exercise
11. Find
pairs of synonyms.
new methods
plateless processes
include
variable
mainly
offer grow
consist of
different
generally
technologically advanced
nonimpact
propose rise
Exercise
12.
Fit
the meaning and the words.
Advantage,
ability, segment, employment, throughout, service
part cut off by a line
one’s regular work or
occupation
something usefull, helpful
department or branch of
public work
in every part; in all ways
or respects
to do something physical or
mental
Exercise
13. Find
pairs of opposites.
primary
straight
meter
increase
segment
slowly external
sentimeter
internal
quickly
secondary
entire
decrease curve
Exercise
14. Find
pairs of words.
advanced
work
printing
plateless or nonimpact
digital office-related
done
processes
printing
method
services services
Exercise
1.
Read
and
translate
the
text.
The
printing industry, like many other industries, continues to undergo
technological changes, as computers and technology alter the manner
in which work is
performed.
Many of the processes that were once done by hand are becoming more
automated, and technology's influence can be seen in all three
stages of printing. The most notable changes have occurred in the
prepress
stage.
Instead of cutting and pasting articles by hand, workers now produce
entire publications on a computer, complete with artwork and
graphics. Columns can be displayed and arranged on the computer
screen exactly as they will appear in print, and then be printed.
Nearly all prepress work is becoming computerized, and prepress
workers need
considerable
training in computer software and graphic communications. Technology
has also affected the printing process itself. Press operators
increasingly use computers to make adjustments to printing presses
in order to complete a job. The same is also true of bindery and
other finishing workers.
Although
digital printing is currently a small portion of the industry, it is
the fastest growing industry segment as printers embrace this
technology. Most commercial printers now do some form of digital
printing. Printing processes today use scanners and digital cameras
to input images and computers to manipulate and format the graphic
images prior to printing. Digital
printing
is transforming prepress operations as well as the printing process.
It eliminates much of the lengthy process in manually transferring
materials to the printing press by directly transferring digital
files to an electronically driven output device.
The printing industry is also
taking on new responsibilities that provide further value for
clients. This means customers can now have their finished products
labeled, packaged, and shipped directly by printing companies. Other
ancillary services that printers are adding include database
management, warehousing, and prefabricated design work for clients
who want to fill out design templates on the Internet rather than
creating original design work. Printers feel that these services are
increasingly important to their current and potential customers.
alter –
змінювати
pasting –
склеювати
prepress
worker –
спеціалісти, які виконують підготовчі
операції
affect –
впливати
embrace –
охоплювати
eliminate
–
усувати, виключати, ліквідувати
libeled
products –
товари з ярликом, етикеткою
ancillary
services –
підлеглі служби
warehousing
–
утримання на складі
prefabricated
– виготовлений
заводським способом
arwork –
ілюстрація
Exercise
2. Answer
the questions:
Why does the printing
industry undergo technological changes?
Where
have the most notable changes occured?
What are
these changes?
How can
columns be displayed on the computer screen?
How has technology affected
the printing process itself?
What is the role of digital
printing in printing industry?
What device do printing
processes use today and for what aims?
What responsibilities is the
printing industry taking to provide further value for clients?
What do other ancillary
services that printers are adding include?
Why do printers add these
ancillary services for clients?
Exercise
3.
Find
in the text the English for:
Змінювати;
стадії друку; стадія підготовки до
друку; вплив технології; склеювання
вручну; повне публікування; ілюстрації;
впливати на процес друку; переплетіння;
цифровий друк; швидко зростаючий сегмент
економіки; ліквідувати більшість
довготривалих процесів; запакований
товар.
Exercise
4.
Translate
into Ukrainian.
To undergo
technological changes; to alter; done by hand; prepress stage;
pasting; by hand; technology’s influence; notable changes;
considerable training in computer software; prepress workers; to
eliminate much of the lengthy process; transferring digital files;
electronically driven output device.
Exercise
5.
Give
the four forms of the verbs:
to continue
to undergo
to perform
to occur
to make to
translate
to grow
to eliminate
to mean
to pack
to add to
design
Exercise
6.
Write
T (True) or F (False) next to each sentence.
The printing industry is not
taking on new responsibilities to provide further value for
clients.
Printers consider that new
services are important to their customers.
Printing processes today use
scanners and digital cameras.
The printing industry
continues to undergo technological changes.
The printing industry has
not been computerized yet.
Press operators increasingly
use computers.
Digital printing is the
fastest growing industry segment.
Exercise
7. Complete
the following sentences:
Technology has also affected
…
Press operators increasingly
use computers to make …
Printing processes today use
…
Digital printing is
transforming …
The printing industry is
also taking on …
Printers use other services
which include …
Exercise
8.
Put
the sentences in the right order
Printers feel that these
services are increasingly important to their current and potential
customers.
The printing industry
continues to undergo technological changes.
The printing industry is
also taking on new responsibilities that provide further value for
clients.
Many of the processes that
were once done by hand are becoming more automated.
The most notable changes
have occurred in the prepress stage.
Printing processes today use
scanners and digital cameras to input images and computers to
manipulate and format the graphic images prio to printing.
Other ancillary services
that printers are adding include database management, warehousing
and prefabricated design work for clients.
Digital printing is
transforming prepress operations as well as the printing process.
Exercise
9. Complete
the sentences with suitable prepositions.
Computers and technology
alter the manner … which work is done.
Press operators increasingly
use computers … make adjustments … printing presses.
Printers are adding other
ancillary services … clients who want … fill out desigh
templates … the internet.
Most commercial printers now
do some form … digital printing.
Printing processes today use
scanners and digital cameras … input images and computers …
manipulate and format the graphic images prior … printing.
The printing industry is
also taking … new responsibilities that provide further value …
clients.
Instead … cutting and
pasting articles … hand, workers now produce entire publications
… a computer.
The most notable change have
occurred … the prepress stage.
Exercise
10.
Join
the broken sentences.
Printers feel that these
services are important
Press operators use
computers
Although digital printing
is a small portion of industry
Many of the processes
that were once done by hand Technology
has also affected
to make adjustment to
printing presses in order to complete a job.
are becoming more
automated.
the printing process
itself.
it is the fastest growing
industry segment. to
their current and potential customers.
Exercise
11. Find
pairs of synonyms.
try
connect
occur
considerable
act
portion
manner exchange
appear
important
affect
mode
test
join
interchange part
Exercise
12.
Find
pairs of opposites.
continue
often
strong
long
begin
close
top recent
short
distant
stop
weak
bottom
seldom
old finish
Exercise
13.
Fit
the meaning and the words.
continue
ancillary
original
transferring
complete
eliminate
something having all its
parts
something having a
service to those carrying on the main business
something changing
position, moving
first or earliest
to go farther, to go on remove;
to take or put away
Exercise
14. Find
pairs of words.
printing
technological
digital
prepress
computer
labled
ancillary automated
printing
services
processes
screen
products
industry
operations changes
Exercise
1.
Read
and
translate
the
text.
Printing
occupations range in skill from those found in quick printing to
specialized
production occupations rarely found in other industries. Production
occupations make up 53 percent of industry employment with printing
machine operators accounting for the most employment of any single
occupation in the industry at 16 percent.
Production
occupations. Prepress
technicians prepare print jobs for the presses. They take text or
images from clients and ensure that coloring and other issues are
resolved before the job goes to press. For those processes that
require it, technicians then create the printing plate.
Increasingly, prepress technicians receive the material for the
pages as electronic computer files, which they upload to their
computers, and use digital imaging software to lay out the pages. In
very small shops or shops with small format digital equipment,
prepress technicians may also design materials for those clients who
need it. "Preflight" technicians, a type of prepress
worker, examine and edit the pages to ensure that the design,
format, settings, quality, and all other aspects of the finished
product will be completed according to the client's specifications.
Larger printers may add customer service duties to the traditional
list of prepress duties in order to streamline business workflow.
When material is ready,
printing machine operators review the material with the prepress
technician, and then install and adjust the printing plate on the
press. They must also meter the flow of fountain solution, adjust
pressure, ink the printing presses, load paper, and adjust the press
to paper size. Operators must correct any problems that might occur
during a press run, which means they must monitor the process
throughout the run and make minor repairs when necessary. Job
printers, who usually work in small print shops, perform the
prepress work as well as operate the press.
During
the binding or finishing stage, the printed sheets are transformed
into products such as books, catalogs, magazines, or directories.
Bindery workers fold and fasten groups of sheets together, often
using a machine stapler, to make "signatures". They then
feed the signatures into various machines for stitching or gluing—a
process that now relies mainly on computers. Bookbinders assemble
books from large, flat, printed sheets of paper. They cut, saw, and
glue parts to bind new books. They also perform other finishing
operations, such as decorating and lettering, often using hand
tools. A small number of bookbinders work in hand binderies. These
highly skilled workers design original or special bindings for
publications with limited editions, or restore and rebind rare
books.
range
–
коливатися (в певних межах), простиратися
prepress
technician
–
фахівець, який виконує підготовчі
роботи
resolve –
вирішувати, узгоджувати
printing
plate –
друкувальна форма
to lay
out the pages –
зробити макет сторінок
edit –
готувати до друку, редагувати
fountain
solution –
зволожуючий розчин
printing
press –
друкувальна машина, верстат
binding –
оправа, обкладинка
bindery
worker, bookbinder –
палітурник
fold –
фальцювати
signature
–
зфальцьований аркуш, зошит
stritching
–
брошуровка
gluing –
склеювання
lettering
–
напис, тиснення
glue –
склеювати
bindery –
палітурна майстерня
meter –
вимірювати
Exercise
2. Answer
the questions:
What is
the range of printing occupations?
What is the task of prepress
technicians?
When do technicians create
the printing plate?
How do prepress technicians
receive the material for the pages?
What may
prepress technicians do in very small shops?
What do printing machine
operators do when material is ready?
What is the task of
operators during a press run?
What are printed sheets
transformed into during the binding?
What is the task of bindery
workers?
How do bookbinders assemble
books?
What other finishing
operations do bookbinders perform?
What work do bookbinders
perform in hand binderies?
Exercise
3.
Find
in the text the English for:
Друкарська
професія; підготовка до друку; вирішувати,
дозволяти; друкарська форма; зробити
макет сторінок; спеціалісти, які
виконують підготовчі роботи; редагувати
сторінки; за специфікацією клієнта;
встановити друкарську форму; влити
зволожуючий розчин; пристосувати пресс
за розміром сторінки; складати та
закріпляти аркуші.
Exercise
4.
Translate
into Ukrainian.
Production
occupation; to create the printing plate; to resolve before the job
goes to press; with small format digital equipment; digital imaging
software; customer service duties; to review the material; to adjust
the press to paper size; problems occurred during a press run; to
make minor repairs; binding stage; printed sheets; bindary worker;
to feed the signatures into various machines.
Exercise
5.
Give
the four forms of the verbs:
To range to use
To find to complete
To account to add
To upload to meter
To lay out to run
Exercise
6.
Write
T (True) or F (False) next to each sentence.
Bindary workers prepare
print jobs for the presses.
Operators must correct any
problems that might occur during a press run.
“Preflight” technicians
examine and edit the pages.
Bindery workers feed the
signatures into various machines.
Bindery workers also prepare
print jobs for the presses.
A great number of
bookbinders work in hand binderies.
Bookbinders working in hand
binderies are highly skilled workers.
Exercise
7.
Join
the broken sentences.
Prepress technicians
“Preflight”
technicians
In very small shops
When material is ready
Operators must correct
any problems that Bindery
workers
prepress technicians may
also design materials for clients.
printing machine
operators review the material.
prepare print jobs for
the presses.
examine and edit the
pages.
might occur during a
press run.
fold
and fasten groups of sheets together.
Exercise
8.
Put
the sentences in the right order
When material is ready,
printing machine operators review the material with the press
technician.
During the binding or
finishing stage, the printed sheets are transformed into books,
catalogs, magazines or dictionaries.
Production occupations make
53 percent of industry employment.
Bindery workers fold and
fasten groups of sheets together.
Operators must correct any
problems that might occur during a press run.
A small group of bookbinders
work in hand binderies.
Prepress technicians receive
the material for the pages as electronic computer files.
Bookbinders assemble books
from large, flat, printed sheets of pages.
Exercise
9. Find
pairs of words.
prepress
to prepare print jobs
printing machine
specialized production
binding
(finishing)
hand highly
skilled
occupations
operators
stage
bindery
workers
technician for
the presses
Exercise
10. Find
pairs of synonyms.
occupation
to publish
to edit
finish
quantity to
try
to print
end
amount
profession
to test to
redact
Exercise
11.
Find
pairs of opposites.
to find
load
often
to break
to write
complicated before
rare
to repair
to print
easy
upload
to lose after
Exercise
12. Complete
the following sentences:
Prepress technicians prepare
print jobs …
Larger printers may add …
When material is ready …
Operators must correct any
problem that …
During the finishing stage …
Bindary workers often use …
A small number of
bookbinders work …
Exercise
13. Complete
the sentences with suitable prepositions.
Production occupations make
… 53 percent of industry employment … printing machine
operators.
Prepress technicians ensure
that coloring and other issues are resolved … the job goes …
press.
The printed sheets are
transformed … books, catalogs, magazines or directories.
Operators must correct
problems that occur … a press run.
Bindery workers feed the
signatures … various machines … stretching or gluing.
Bookbinders assemble books …
large, flat, printed sheets … paper.
A small number …
bookbinders work … hand binderies.
Exercise
14.
Fit
the meaning and the words.
occupation
ensure
edit
streamline
complete
assemble
make more efficient
finish, bring to an end
guarantee
gather
together
prepare (another pleson’s
writing) for publication business;
trade
ДЛЯ НОТАТОК
ДЛЯ НОТАТОК
ДЛЯ НОТАТОК
ДЛЯ НОТАТОК
ДЛЯ НОТАТОК
1
76Lesson 1
Preparation for Printing
Vocabulary notes:
Lesson 2
Letterpress.
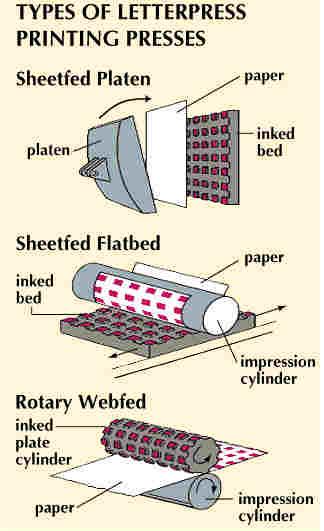
Vocabulary notes.
Lesson 3
Intaglio.
Vocabulary notes:
Lesson 4
Vocabulary notes:
Lesson 5
History
Vocabulary notes:
Lesson 6
Industry organization
Vocabulary notes:
Part II
Industry organization
Vocabulary notes:
Lesson 7
Recent developments
Vocabulary notes:
Lesson 8
Occupations in the industry
Vocabulary notes:
2
75
3
74
4
73
5
72
6
71
7
70
8
69
9
68
10
67
11
66
12
65
13
64
14
63
15
62
16
61
17
60
18
59
19
58
20
57
21
56
22
55
23
54
24
53
25
52
26
51
27
50
28
49
29
48
30
47
31
46
32
45
33
44
34
43
35
42
36
41
37
40
38
39
