Module 1
Give the definition of the concept:
1) controlled rectifiers;
2) the voltage converters.
What is:
1) inverter;
2) Inverter with DC link.
Draw:
1) diode (ASB, connection), thyristor;
2) thyristor (ASB, connection), the triac.
1) Purpose and scope of direct frequency converters.
2) The purpose and scope of the AC voltage switches.
Module 2
Give the definition of the concept:
1) single- phase thyristor rectifier;
2) fully managed thyristor rectifier.
Describe:
1) ways to enhance the reliability of the semiconductor converters;
2) protection circuits in the power thyristor converters.
Describe the technique:
1) choice of parameters RC - circuit
2) select the active elements of the thyristor converter.
Describe:
1) The functionality of the structural elements of the scheme;
2) phase control system.
7.3 Examination tickets (tests) tests
1. Contact resistance is called:
A) the resistance in the transition contacts made of different materials;
B) additional resistance that occurs in the area of the current transition from one to the other live parts;
C) resistance that occurs at the moment of contact closure;
D) resistance that occurs at the time of opening of the contacts.
E) the resistance resulting from heating contact surfaces.
2. Contact resistance is due to:
A) uneven surfaces wetted parts;
B) the contact details of heterogeneous materials;
C) the presence on the contact surfaces of the various films of high resistivity;
D) points A) and B);
E) points A) and C).
3.
In the formula, the transition of the contact resistance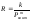 ,
the degree is determined by:
,
the degree is determined by:
A) force contact force;
B) contact material;
G) processing method, the contact surface;
D) contact surface cleanliness;
E) the number of contact points of contact surfaces.
4. In the remote arc quenching chambers arc is:
A) moving under the influence of a magnetic field;
B) via interrupter grid;
C) a high pressure;
D) in transformer oil;
E) in a vacuum environment.
5. In the fuse arc quenching is carried out:
A) moving under the influence of a magnetic field;
B) via interrupter grid;
C) a high pressure;
D) in transformer oil;
E) in a vacuum environment.
6. The following materials are electrical contacts are arranged in order of increasing melting points:
A) silver, aluminum, tungsten, copper, steel;
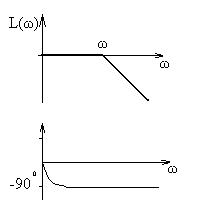
B) aluminum, silver, copper, stainless steel, tungsten;
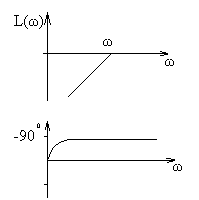
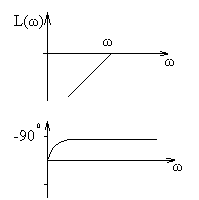
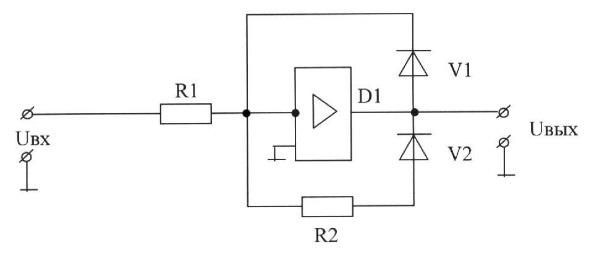
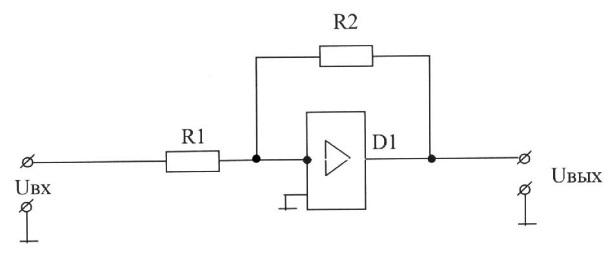
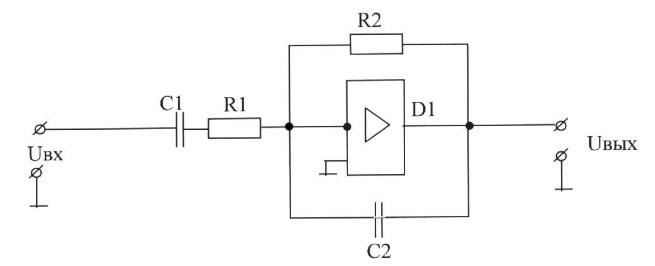
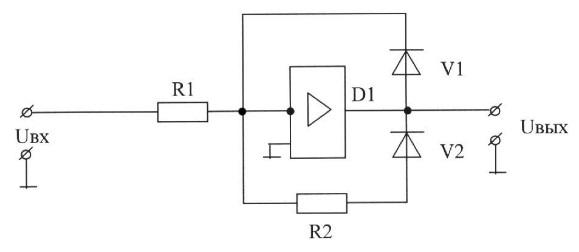
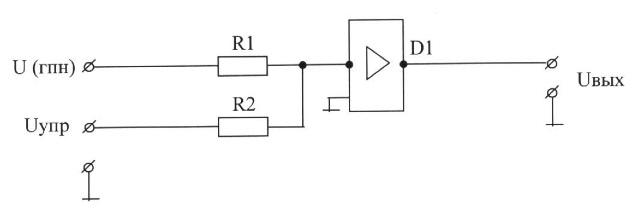
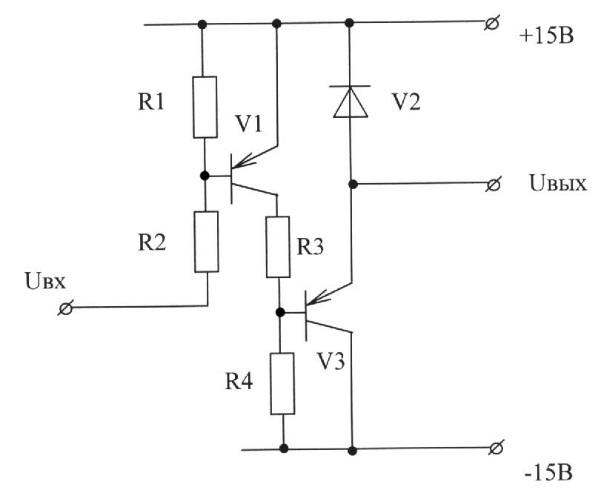
C), tungsten, silver, copper, steel, aluminum;
D) copper, tungsten, steel, aluminum, silver;
E) steel, aluminum, copper, silver, tungsten.
7. If Bounce is:
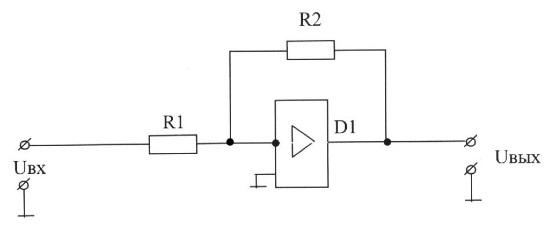
A) wear of the contact springs;
B) wear spring electromagnet;
C) the occurrence of sound effect;
D) repeated arcing and melting and fusing the contact material;
E) reducing the contact resistance of the transition.
8. The decrease results in the failure of contacts:
A) to increase the current through the contact;
B) a decrease in contact pressure and an increase in contact resistance;
C) to reduce the current through the solenoid coil;
D) to the spring tension of the electromagnet;
E) to increase the loss in the coil of the electromagnet.
• 9. The picture shows the contact
• A)
instantaneous;
• B) with a slowdown when triggered;
• C) with a slowdown in the return;
• D) with a slowdown in the set and reset;
• E) break.
10. What form does the static current-voltage characteristic of the arc:

11. The picture shows contact:
A)
Instantaneous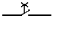
B) with a slowdown when triggered;
C) with a slowdown in the return;
D) with a slowdown in the set and reset;
E) break.
12. The picture shows contact:
A)
instantaneous;
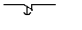
B) with a slowdown when triggered;
C) with a slowdown in the return;
D) with a slowdown in the set and reset;
E) NO.
13. The picture shows contact:
A)
instantaneous;
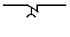
B) with a slowdown when triggered;
C) with a slowdown in the return;
D) with a slowdown in the set and reset;
E) NO.
14. The picture shows contact:
A)
instantaneous;
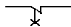
B) with a slowdown when triggered;
C) with a slowdown in the return;
D) with a slowdown in the set and reset;
E) NO.
15. The picture shows contact:
A)
instantaneous;

E) with a slowdown when triggered;
C) with a slowdown in the return;
D) with a slowdown in the set and reset;
A) break.
16.
The picture shows contact: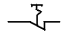
A) with a slowdown when triggered;
B) with a slowdown in the return;
C) with the return of the hand;
D) closed;
E) with a slowdown in the closing and opening.
17. On what is the way Dolivа-Dobrovolskа used in quenching the arc:
A) on the reduction of the contact opening time;
B) to increase the contact opening time;
C) the use of an electrode around the voltage drop;
D) on the use of a magnetic field;
E) on the forced cooling of the arc.
18. Contact is connected in series with the load impedance 200 ohms to a DC voltage of 220 V. What is the voltage across the junction, if it is open?
A) 220 V;
B) 110 V;
C) 200 V;
D) 0 V;
E) 218 V.
19. How does the strength of contact force on the contact resistance with its increasing?
A) resistance increases;
B) resistance is not changed;
C) the resistance increases slightly;
D) resistance decreases hyperbolically;
E) the resistance increases linearly.
20. The principle of operation managed converter, performed by the system GD (choose the correct answer):
A) principle of the GD-converter is based on a two-stage electro-mechanical energy converter and the property of the DC machine with separate excitation in generator mode is proportional to the rotational speed of the rotor of the generator;
B) the principle of G-D-converter is based on a two-stage electro-mechanical energy converter and the property of the DC machine with separate excitation in generator mode by changing the coil current excitation;
C) the principle of D-D converter is based on a two-stage electro-mechanical energy converter and the property of the DC machine with separate excitation in generator mode at a constant rotational speed of the rotor to change the voltage at the terminals of the armature is almost proportional to the current field winding;
D) principle of the D-D converter is based on a two-stage electro-mechanical energy converter and the property of the DC machine with separate excitation in generator mode by switching the pairs of poles;
E) the principle of D-D converter is based on a two-stage electro-mechanical energy converter and the property of the DC machine with separate excitation in generator mode by reversing the drive motor.
21.Ukazat basic properties of the transducer system GD (choose the most complete version of the answer):
A) the absence of pulsations in the power transmitter terminals, ease of circuit solutions; circuit can operate in four quadrants, low reliability, low gain on the control channel, high dimensions and weight per unit of power inverter;
B) the absence of pulsations in the power transmitter terminals, ease of circuit solutions; circuit can operate in four quadrants;
C) the absence of fluctuations in the power transmitter terminals, ease of circuit solutions; circuit can operate in four quadrants, the low gain channel control, low reliability, small dimensions and weight per unit of power inverter;
D) ease of circuit solutions; circuit can operate in four quadrants, low reliability, absence of pulsations in the power transmitter terminals, low gain on the control channel;
E) the simplicity of circuit solutions; circuit can operate in four quadrants, low reliability, low gain on the control channel.
22. The principle of operation of the magnetic amplifier (choose the correct answer):
A) The principle of operation of the magnetic amplifier is based on the change in the transformation ratio of saturation inductors;
B) Schematic saturation inductors included so that when the control signal changes the frequency and amplitude of the voltage source;
C) the principle of magnetic amplifier is based on the saturation effect of the magnetic saturation of the choke wire. In this connection, the saturation throttle inductive component connected in series with the load and reduces energy redistribution occurs between the active component and the saturation throttle resistance of the load;
D) the change of the control signal causes the asymmetry characteristics drasselya saturation;
E) the principle of saturation inductors, which are the basis of the magnetic amplifier, based on the change in the ratio of transformation.
23. Comparative characteristics of the magnetic amplifier with respect to F-D-converter (choose the correct answer):
A) high reliability GD converter due to the lack of rotating parts, magnetic amplifier allows you to develop a small gain stages that can be used in automatic control systems, magnetic amplifiers require high capital costs, magnetic amplifiers do not require frequent maintenance work;
B) high reliability magnetic amplifier lack of rotating parts, A-D converter can develop small amplifier stages, which can be used in automatic control systems, magnetic amplifiers do not require high capital expenditures, magnetic amplifiers do not require frequent maintenance works;
C) high reliability G-D-converter due to the lack of rotating parts, A-D converter can develop small amplifier stages, which can be used in automatic control systems, F-D-converters do not require high capital expenditures, D-D- transducers do not require frequent maintenance work;
D) high reliability magnetic amplifier lack of rotating parts, magnetic amplifier can develop small amplifier stages, which can be used in automatic control systems, F-D-converters do not require high capital expenditures, D-D converters require frequent maintenance works ;
E) high reliability magnetic amplifier due to the lack of rotating parts, magnetic amplifier allows you to develop a small gain stages that can be used in automatic control systems, magnetic amplifiers do not require high capital costs, magnetic amplifiers do not require frequent maintenance.
24. A promising direction of development of controlled (choose the correct answer):
A) lowering the switching frequency of the power components, reducing the weight and size per unit of power, the transition to digital control systems, use as power converters rotating converters are not compatible with digital control computer;
B) decrease in the frequency switching power components, reducing the weight and size per unit of power, the transition to digital control systems, use as power converters rotating converters;
C) increase in the frequency switching power components, reducing the weight and size per unit of power, the transition to digital control systems, compatibility with digital control computer, use as power converters magnetic amplifiers;
D) increase in the frequency switching power components, reducing the weight and size per unit of power, the transition to digital control systems, compatibility with digital control computer, use as power converters rotating converters;
E) increase the frequency switching power components, reducing the weight and size per unit of power, the transition to digital control systems, compatibility with digital control computer.
25. Classification of mass-produced in the CIS controlled (choose the correct answer):
A) power diodes, power thyristors, triacs;
B) controlled rectifiers, pulse transformers, switches AC voltage cyclo-converter, inverter with DC link, inverter with DC link voltage;
C) power diodes, power thyristors, triacs, inverters with DC link, inverter with DC link voltage;
D) switches; cyclo-converter, inverter with DC link, inverter with DC link voltage controlled rectifiers, pulse converters.
E) controlled rectifiers, pulse transformers, switches, cyclo-converter, inverter with DC link, inverter with DC link voltage controlled rectifiers, pulse converters.
26. Applications controlled rectifier (choose the most complete version of the answer):
A) control modes of the electric arc welding;
B) DC motor transformer facilities;
C) food chain anchors and OS of the DC motor, the power circuits of the rotor synchronous motor / generator power circuit induction motor stator in the dynamic braking mode control battery charging, management modes arc welding;
D) control the starting and reversing induction motor high power management modes in the heating elements;
E) is used as an addition to the system GD.
27. In DC contactors are used for permanent magnets:
A) increase the traction of the electromagnet;
B) create a magnetic flux arc rotation;
C) create the initial traction;
D) reduce the power consumed by the solenoid coil;
E) protection of the contactor from external magnetic fields.
28. Classification of power valves (choose the correct answer):
A) power diodes, power thyristors, triacs;
B) controlled rectifiers, pulse converters;
C) switches, the cyclo-converter, inverter with DC link / voltage;
D) switches; cyclo-converter, inverter with DC link / voltage controlled rectifiers, pulse converters;
E) controlled rectifiers, pulse transformers, switches, cyclo-converter, inverter with DC link / voltage controlled rectifiers, pulse converters.
29.Osnovnye performance of power valves (choose the correct answer):
1. CVC diode.
2. CVC thyristor.
3. CVC triac.
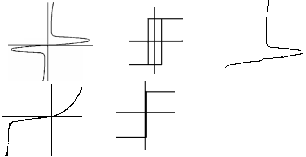
А) 1-в, B) 1-в, C) 1-д, D) 1-в, E) 1-д
2-г, 2- б, 2-б, 2-г, 2-г,
3-а; 3-г; 3-а; 3-д; 3-а;
30. Classification of commercially available valves controlled by constructed (choose the most complete version of the answer):
A) open frame, male, pill, male pigtail, male pigtail, modular, hybrid;
B) male, tablet;
C) pin, tablet, male pigtail, male pigtail, modular, hybrid;
D) open frame, male, pill, male pigtail, male pigtail, modular design;
E) pin, tablet, male pigtail, modular design.
31. In which case, a parallel connection of valves (choose the correct answer):
A) when the load current is more than the open state of the valve current (excluding the power circuitry of the transmitter);
B) in the case when the load current is more than the current valve open state (including the circuitry of the power converter);
C) in the case where the amplitude of the voltage of the power supply converter is more than the maximum allowable class valve;
D) in the case when the load current is more than the current valve open state (power channel) with the characteristics of the power section of circuit solutions, as well as the cooling of the valve;
E) in the case when a voltage more than the voltage load valve closed state.
32. Features thyristor control channel with galvanic coupling with the power channel (choose the correct answer):
А) B) С)
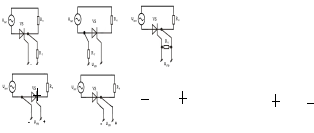
D) Е)
Where
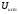 - voltage power supply;
- voltage power supply;
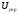 - voltage control.
- voltage control.
33. In which case, a series connection of valves (choose the correct answer):
A) when the load current is more than the open state of the valve current (excluding the power circuitry of the transmitter);
B) in the case when the load current is more than the current valve open state (including the circuitry of the power converter);
C) in the case where the amplitude of the voltage of the power supply converter is more than the maximum voltage valve closed state (power channel) with the characteristics of the power section of circuit solutions;
D) in the case when the load current is more than the current valve open state (power channel) with the characteristics of the power section of circuit solutions, as well as the cooling of the valve;
E) in the case when a voltage more than the voltage load valve closed state.
34. Marking controlled rectifiers (choose the correct answer):
 35.
The curve of the electric heating unit
35.
The curve of the electric heating unit
 matches:
matches:
A) Intermittent duty work;
B) temporary service;
C) continuous operation at constant load;
D) Continuous operation with intermittent load;
E) of the short-circuit.
 36.
The curve of the electric heating unit
36.
The curve of the electric heating unit
matches:
A) Intermittent duty work;
B) temporary service;
C) continuous operation at constant load;
D) Continuous operation with intermittent load;
E) of the short-circuit.
 37.
The curve of the electric heating unit is identical:
37.
The curve of the electric heating unit is identical:
A) Intermittent duty work;
B) temporary service;
C) continuous operation at constant load;
D) Continuous operation with intermittent load;
E) of the short-circuit.
 38.
The curve of the electric heating unit is identical:
38.
The curve of the electric heating unit is identical:
A) Intermittent duty work;
B) temporary service;
C) continuous operation at constant load;
D) Continuous operation with intermittent load;
E) of the short-circuit.
39. Steady state electric heating devices are:
A)
mode, the temperature within 2 hours of heating does not increase by
more than
 C;
C;
B)
mode, when the temperature in 1 hour of heating does not increase by
more than
 C;
C;
C)
mode, when the temperature in 1 hour of heating does not increase by
more than
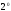 C;
C;
D)
mode, when the temperature in 1 hour of heating does not increase by
more than
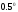 C;
C;
E)
when the color temperature in 8 hours of heating does not increase by
more than
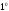 C;
C;
40. In continuous operation the contactor more than 8 hours, the temperature of contacts:
A) remains the same;
B) is increased;
C) decreases;
D) becomes independent of the load current;
E) is no longer dependent on the ambient temperature.
41. The functional purpose of static balancing valves in series (choose the correct answer):
A) is intended to align the voltage drop between the series-connected thyristors in the closed state;
B) is designed to align the time of opening and closing the channel power thyristor;
C) to align the channel control;
D) to align the dynamic characteristics of the valve;
E) to align the current valve open state.
42. The functional purpose of the dynamic balance (choose the correct answer):
A) is intended to align the closed-state voltage drop across the thyristor;
B) is designed to align the time of opening and closing of series-connected power thyristors;
C) to align the channel control;
D) to align the dynamic characteristics of the valve;
E) to align the current valve open state.
43. Magnetic switch protects the motor from:
A) short-circuits;
B) overloads;
C) short-circuits and overloads;
D) the disappearance of the supply voltage;
E) short-circuits and mains power failure.
44. Features of the parallel connection of valves using resistive balancing (choose the correct answer):
A) is used in the case of parallel-connected thyristors in the voltage drop across the cathode electrode more than 15%;
B) is used in case if you want to work thyristors strictly regimented time;
C) used in the event that requires high heat;
D) is used in the case of parallel-connected thyristors in the spread open condition of the voltage drop of the power valve channel does not exceed 15%;
E) is used in the case of series-connected thyristors in the voltage drop across an open circuit condition of the channel does not exceed 5%.
45. Transformer balancing valves in parallel operation (choose the correct answer):
A) should be used when time is unlimited;
B) feature is the fact that the group SCR operates strictly regimented time;
C) used in the event that requires high heat;
D) is used in the case of parallel-connected thyristors in the voltage drop across an open circuit condition of the channel does not exceed 15%;
E) if a reverse voltage variation exceeds 15%.
46. The main modes of a single-phase half-wave and full-wave rectifier (choose the most complete version of the answer):
A) reversible, regenerative, dynamic braking;
B) reversible, regenerative, motor, dynamic braking;
C) reversible, regenerative, a motor;
D) heat recovery, a motor;
E) heat recovery, motor, dynamic braking.
47. Main technical characteristics of a single-phase full-wave rectifier (choose the correct answer):
A) recommended power ≥ 500 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 100 Hz, the angle of control: 0 ≤ α ≤ 180;
B) recommended power 1000 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental harmonic voltage at the load of 300 Hz, the angle of control: 0 ≤ α ≤ 180;
C) the recommended power of 2000 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 300 Hz, steering angle: 180 ≤ α;
D) recommended power ≤ 50 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 100 Hz, the angle of control: 0 ≤ α ≤ 180;
E) the recommended power of 500 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental harmonic voltage at the load of 100 Hz, a steering angle: α ≤ 180.
48. The main technical characteristics of the three-phase half-wave rectifier (choose the correct answer):
A) recommended power ≥ 500 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 100 Hz, the angle of control: 0 ≤ α ≤ 180;
B) recommended power ≤ 75 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 150 Hz, the angle of control: 0 ≤ α ≤ 150;
C) the recommended power of 2000 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 300 Hz, steering angle: 180 ≤ α;
D) recommended power ≤ 50 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 100 Hz, the angle of control: 0 ≤ α ≤ 180;
E) the recommended power of 500 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental harmonic voltage at the load of 100 Hz, a steering angle: α ≤ 180.
49. The main technical characteristics of the three-phase full-wave rectifier (choose the correct answer):
A) recommended power ≤ 2000 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 300 Hz, the angle of control: 0 ≤ α ≤ 120;
B) the recommended power of 75 kW, the pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 150 Hz, the angle of control: 0 ≤ α ≤ 150;
C) the recommended power of 2000 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 300 Hz, steering angle: 180 ≤ α;
D) recommended power ≤ 50 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental voltage at the load of 100 Hz, the angle of control: 0 ≤ α ≤ 180;
E) the recommended power of 500 kW, pulse frequency of the fundamental harmonic voltage at the load of 100 Hz, a steering angle: α ≤ 180.
50. Functionality of the motor operating mode controlled rectifiers (choose the correct answer):
A) provides a controlled transfer of energy from the EMF of the electrical energy source to a load;
B) provides a controlled transfer of energy from the load to the EMF source of electrical energy;
C) allows to speed up the bi-directional mode for the armature circuit;
D) can speed bi-directional mode for the chain winding;
E) is used for energy recovery in the network
51. Inverter mode rectifiers (choose the correct answer):
A) provides a controlled transfer of energy from the EMF of the electrical energy source to a load;
B) provides a controlled transfer of energy from the load to the EMF source of electrical energy;
C) allows to speed up the bi-directional mode for the armature circuit;
D) can speed bi-directional mode for the chain winding;
E) is intended for forming characteristics in electric motor mode.
52. The concept of the angle control thyristor rectifier (choose the correct answer):
A) the angle of the control depends on the peak value of the supply voltage;
B) angle is determined by the load current control;
C) is determined by the angle of the control of the active component of the load;
D) steering angle corresponds to the time of opening the thyristor by supplying the control pulse in relation to the time closing thyristor;
E) a steering angle meets A) and B).
53. Classification of controlled rectifiers (choose the most complete version of the answer):
A) untethered, fully managed, half-controlled, three-phase power, single-phase, half-wave, full-wave;
B) a fully managed, half-controlled, three-phase power, single-phase, half-wave, full-wave;
C) completely manageable, half-controlled, controlled by a PWM three-phase power, single-phase, half-wave, full-wave;
D) a fully managed, half-controlled, managed by PFM, with three phase, single-phase, half-wave, full-wave;
E) untethered, fully managed, half-controlled, controlled by PWM or PFM, with three phase, single-phase, half-wave, full-wave.
54. To determine the current in the coils, unless they are connected in parallel and connected to a voltage source 100B. The resistance of each coil 200Om.
A) 1A;
B) 0,5 A;
C) 2A;
D) 0,25 A;
E) 1,5 A.
55. Main technical characteristics of controlled rectifiers (select the most comprehensive answer);
A) the frequency of the pulsations of the fundamental harmonic of the load, the recommended power to the load, steering angle, load voltage, load current, number of phases AC power supply voltage;
B) the fundamental frequency of the pulsations of the load, the time constant of the smoothing filter in the load, the recommended power to the load, steering angle, the load voltage, load current;
C) the pulsation frequency of the fundamental harmonic of the load, the recommended power to the load, steering angle, the load current;
D) the pulsation frequency of the fundamental harmonic of the load, the recommended power to the load, steering angle, the range of duty cycle switching power thyristors converter load voltage, load current;
E) the fundamental frequency ripple across the load range of the switching frequency thyristors, the recommended power to the load, the load voltage, load current.
56. Compliance unit name IFSB and its functionality (choose the correct answer):
a) selective filter;
b) zero-body;
c) the sawtooth generator;
d) comparing the logic element;
e) The device differentiation;
e) pulse amplifier;
g) galvanic cell isolation;
1) forms on your site linearly falling unipolar signal, normalized by the duration and amplitude;
2) is intended to highlight the first harmonic sinusoidal synchronization signal, and performs enhancement function IFSB immunity;
3) generates short control pulse synchronized with a working front output logical reference element;
4) performs the function of converting the output signal to selectively filter a rectangular shape, and its output is its state at the time the zero crossing input sinusoidal signal;
5) is designed to match the output of the pulse amplifier with the technical characteristics of the control circuit power thyristor rectifier;
6) forms the front desktop at a time point when the control voltage is compared with the instantaneous value of the output signal of the sawtooth generator in the working area;
7) operates in the switching mode and is designed for amplifying the voltage and current signal output unit differentiation.
|
А) а)-1 |
B)а)-2 |
C) а)-2 |
D) а)-2 |
E) а)-1 |
|
б)-3 |
б)-1 |
б)-4 |
б)-4 |
б)-3 |
|
в)-2 |
в)-4 |
в)-1 |
в)-6 |
в)-5 |
|
г)-6 |
г)-6 |
г)-6 |
г)-7 |
г)-7 |
|
д)-5 |
д)-7 |
д)-3 |
д)-3 |
д)-2 |
|
е)-7 |
е)-3 |
е)-7 |
е)-1 |
е)-4 |
|
ж)-4 |
ж)-5 |
ж)-5 |
ж)-5 |
ж)-6 |
57. Determine the power consumption of the coil control if Rc = 1 k, Uc = 110 V
A) 121 W;
B) 12,1 W;
C) 1, .12 W;
D) 11 W;
E) 2,4 watts.
58. Functionality of the IFSB (choose the correct answer):
A) is designed to generate an analog control voltage power thyristors;
B) is designed for generating a PWM signal;
C) is designed to generate a pulse sequence through which the control of the power rectifier or thyristor AC switch. This sequence of pulses synchronized with the voltage converter, and the phase delay of the pulse train is proportional to the control signal;
D) is designed to generate a signal from the PFM;
E) intended to form a pulse signal for closing thyristor.
59. Features noise immunity IFSB (choose the correct answer):
A) installed at the entrance IFSB differentiator;
B) installed at the entrance IFSB proportional differentiator;
C) to set the input pulse amplifier;
D) to set the input phase shifter link;
E) a synchronization channel at the inlet installed selective filters to isolate the first harmonic of the clock signal, wherein the filter is configured so that the phase delay of the output signal relative to the input does not exceed 5.
60. Determine the inductance coil control if Z = 10 ohms; R = 6 ohms.
A) 4 ohms;
B) 8 Ohm
C) 0,4 Ohm;
D) 0,8 Ohm;
E) 2 ohms;
61. Functionality of the gate comparisons used in the pulse-phase control (choose the correct answer):
A) are designed to improve noise immunity;
B) are designed to isolate the first harmonic clock signal;
C) intended to form a sawtooth voltage;
D) are designed to highlight the work of the front;
E) are intended to generate a pulse signal at the time of transition voltage switching AC sinusoidal voltage by 0.
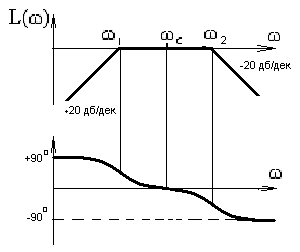
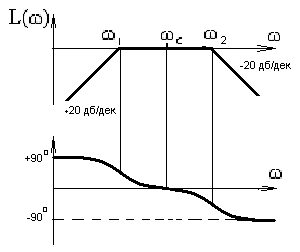
62. Requirements for selective filter system of pulse-phase control (choose the correct answer):
|
+20
дб/дек
The roots of the characteristic equation of the transfer function must be imaginary; |
+20
дб/дек
The roots of the characteristic equation of the transfer function can be arbitrary; |
|
C)
LACHH and phase must be of the form The roots of the characteristic equation of the transfer function must be valid; |
D)
LACHH and phase must be of the form The roots of the characteristic equation of the transfer function must be comprehensive; |
|
E) LACHH and phase must be of the form
The roots of the characteristic equation of the transfer function to be valid. | |
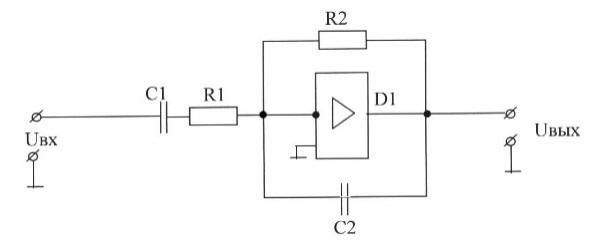
63. Selective filter circuit solution (choose the correct answer):
|
А) |
В) |
|
C) |
D) |
|
E) | |
64. Inverting circuit solution of zero - the body (choose the correct answer):
|
А) |
В) |
|
C) |
D) |
|
E) | |
65. Circuit solution of the sawtooth generator (choose the correct answer):
|
А) |
В) |
|
C) |
D) |
|
E) | |
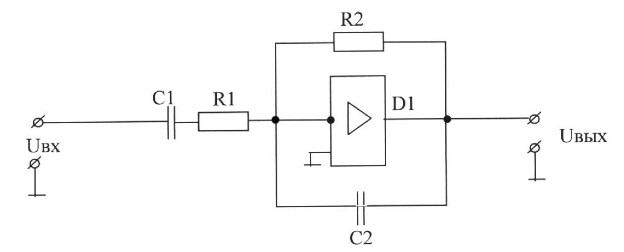
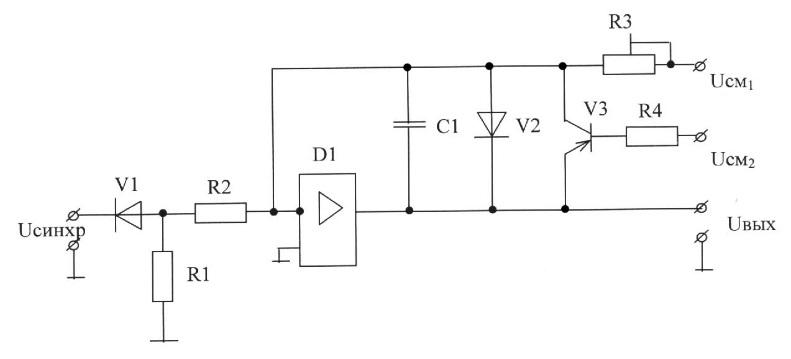
66. The functional purpose of correcting circuit elements and signals the sawtooth generator (choose the correct answer):
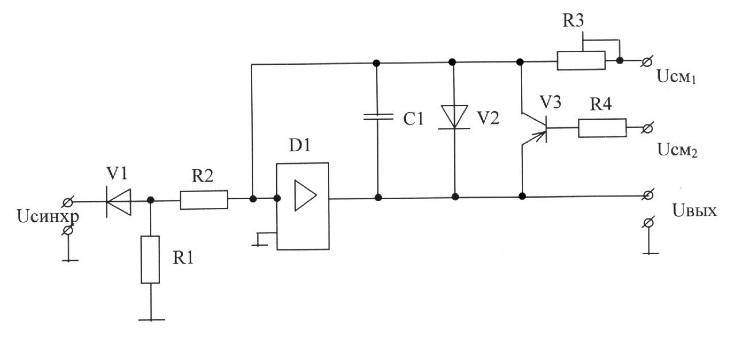
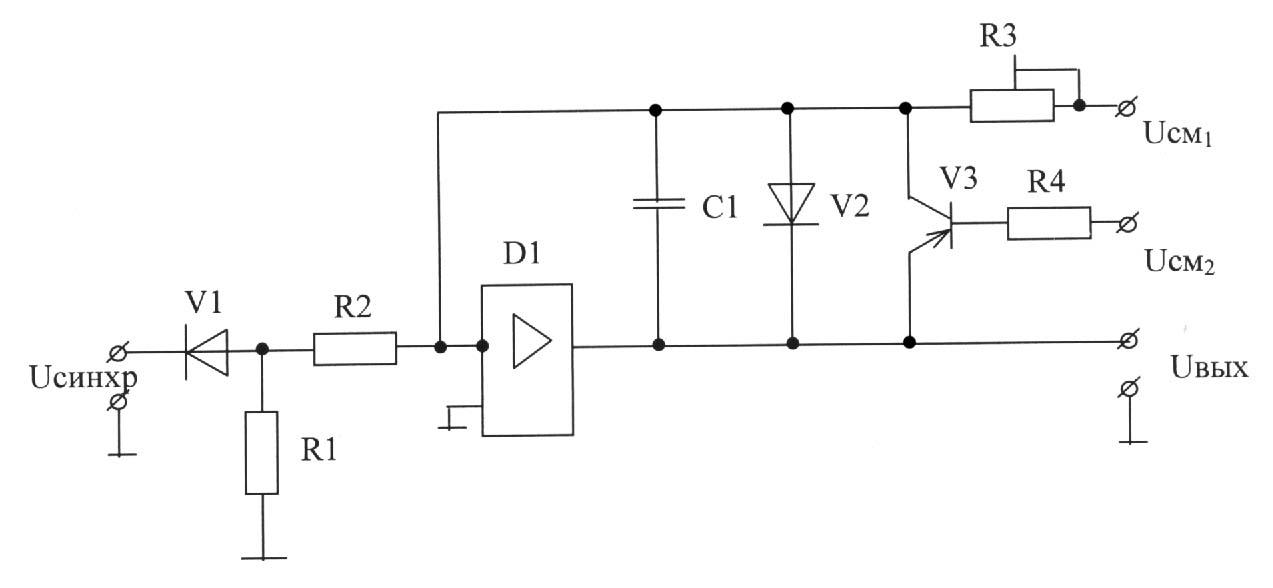
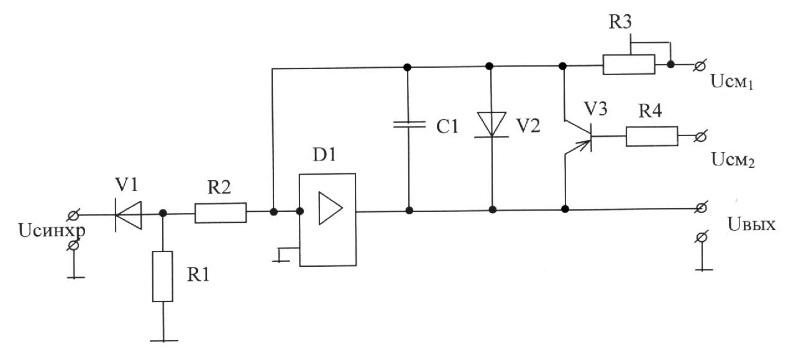
A) R2, D1-load current limit preceding stage;
Usm1, R3, C1-elements that determine the slope of the working portion of the sawtooth generator;
V3-limit the maximum value of the output signal;
V2-generates an output signal strongly positive polarity;
B) R2-load current limits preceding stage;
R3, C1 V3, R3, V2-elements that form a negative feedback;
C) R2-load current limits preceding stage;
Usm1, R3, C1-elements that determine the slope of the working portion of the sawtooth generator;
V3, R3-limit the maximum value of the output signal;
V2-generates an output signal strongly positive polarity;
D) R2-load current limits preceding stage;
Usm1, R3, C1-elements that determine the slope of the working portion of the sawtooth generator;
V3, R3, V2-limit the maximum value of the output signal;
E) Usm1, R2, R3, C1-elements that determine the slope of the working portion of the sawtooth generator;
V2, V3, R3-generates an output signal strongly positive polarity.
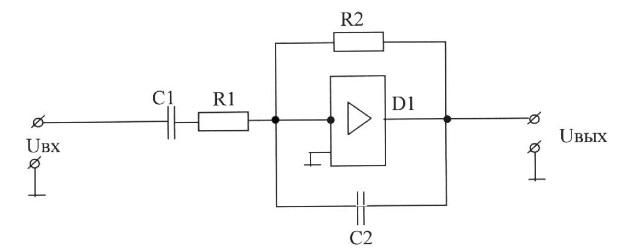
67. The functional purpose of correcting circuit elements selectively filter (choose the correct answer):
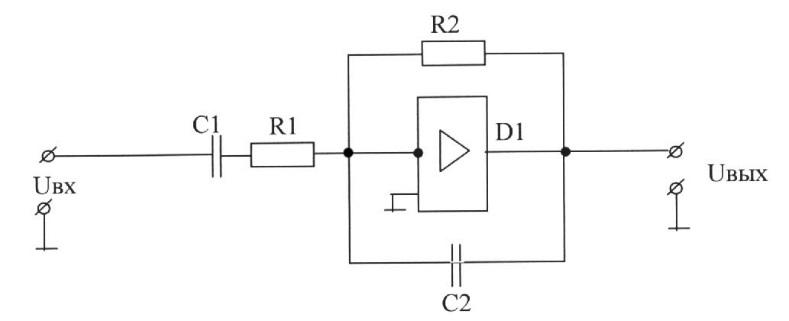
A) R1, C1-correcting elements of the negative feedback loop; R2, C2-correcting elements of the input circuit;
B) R1, C1-correcting elements of the input circuit; R2, C2-correcting elements of the negative feedback loop;
C) R1, C1-correcting elements of the input circuit; R2, C2, D1-correcting elements of the negative feedback loop;
D) R1, C1-correcting elements of the input circuit; R2, C2, D1-correcting elements of the output circuit;
E) R1, C1-correcting elements of the input circuit; R2, C2 - adjusting elements of the output circuit.
68. The value of the time interval of the working area the output of the sawtooth generator for single-phase full-wave rectifier (choose the correct answer):
A)
2 ms;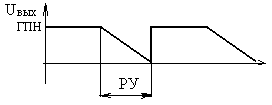
B) 3,2 ms;
C) 8,3 ms;
D) 6,7 msec;
E) 10 ms.
69. The value of the time interval of the working area the output of the sawtooth generator for three-phase half-wave rectifier (choose the correct answer):
A)
2 ms;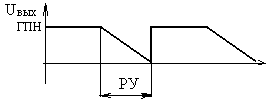
B) 3,2 ms;
C) 8,3 ms;
D) 6,7 msec;
E) of 10 ms.
70. The value of the time interval of the working area the output of the sawtooth generator for a three-phase full-wave rectifier (choose the correct answer):
A) 2 ms;
B)
3,2 ms;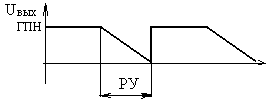
C) 8,3 ms;
D) 6,7 msec;
E) of 10 ms.
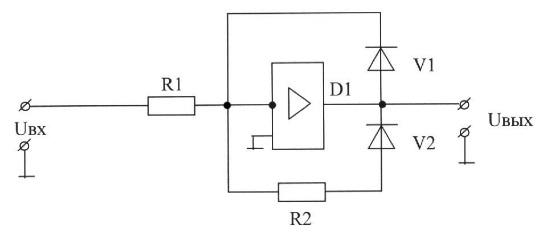
71. Circuit solution gate comparison (choose the correct answer):
|
А)
|
В) |
|
C)
|
D) |
|
E) | |
72. The functional purpose of correcting circuit elements gate comparison (choose the correct answer):
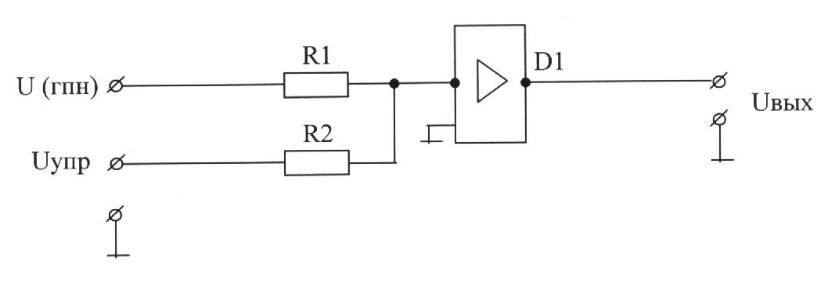
A) R1, R2-correcting elements of the input circuit;
B) R1 - Adjustment element of the input circuit; R2-correction in the output circuit;
C) R1, R2-correcting elements of the output circuit;
D) R1, R2-correcting elements of the negative feedback loop;
E) R1 - Adjustment element of the input circuit; R2, D1-correcting element negative feedback.
73. Circuit solution device differentiation (choose the correct answer):
|
А) |
B) |
|
C)
|
D) |
|
E) | |
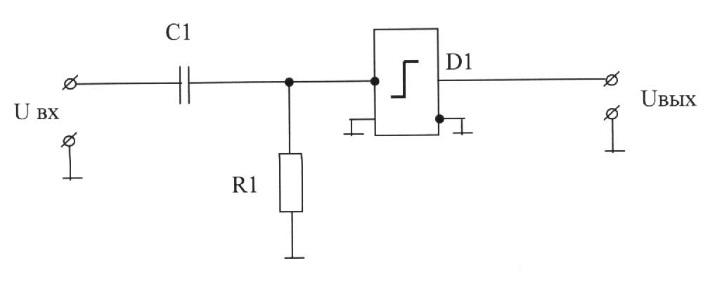
74. The functional purpose of correcting circuit elements differentiating device (select the correct answer):
A) R1, C1 form a passive differentiating circuit and the function of the differentiation signal output from the logical reference element;
D1-operational amplifier operates in a discrete mode and generates a square wave;
B) R1 - the adjustment element of the input circuit; C1-adjustment member negative feedback circuit;
D1-operational amplifier operates in a discrete mode and generates a square wave;
C) R1, C1 to form a differentiating circuit and function differentiation signal output from the logical reference element;
D1-integrated circuit-running in discrete mode;
D) R1, C1, D1-form the differentiating circuit and the function of differentiating the signal output from the logical reference element;
E) R1-forms a differentiating circuit and serves as a differentiation signal output from the logical reference element, C1, D1-correcting elements of the negative feedback.
75. For what purpose are made fuses with variable cross-section:
A) In order to save metal
B) In order to increase the elasticity
C) In order to increase performance when short-circuit
D) In order to reduce the speed at sc and to prevent rupture of the body guard
E) In order to simplify mounting
76. Edge current fuse - it is current:
D) At which time cross-current characteristics of the fuse and protected object;
E) for which the fuse burns when reaching its steady temperature;
F) In which fuse does not burn at a significant excess of the rated current;
G) In which the fuse is heated to 300C;
H) at which the fuse is heated to 500C.
77. Specify the full plot of the germanium diode current on the applied voltage:
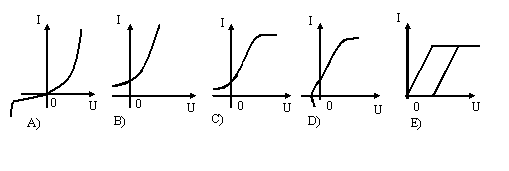
78. Whether the presence of p-n junction in a semiconductor diode required?
A) diode may have p-n junction;
B) the presence of a p-n junction required;
C) must be at least two p-n junctions;
D) diode may or may not have a p-n junction;
E) The availability of the three p-n junctions.
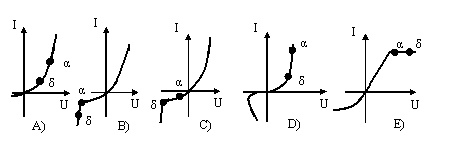
79. Specify the characteristics of the zener diode, and its workspace.
80. Why use a serial connection diodes?
A) to improve the shape of the output voltage of the rectifier;
B) for reducing the amount of drift current;
C) to reduce the effect of temperature on diode current;
D) to increase the permissible reverse voltage;
E) to increase the load current.
# # # 81
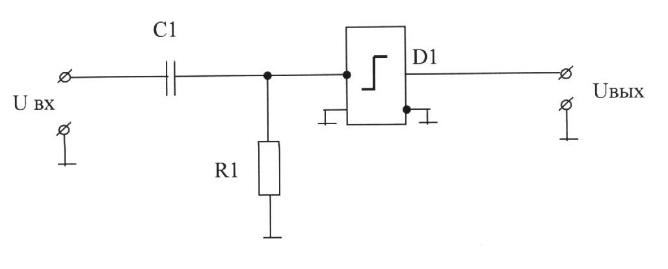
What element is taken into account in the presented converter block diagram?
A) vibrational levels;
B) aperiodic link;
C) The differentiator;
A) proportional to the link;
B) integrating link.
82. Enter the formula for determining the coefficient of zero for single-phase pulse rectifier circuit:
А)
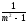 ;В)
;В)
 ;С)
;С)
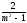 ;
;
D)
 ;
E)
;
E)
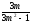 .
.
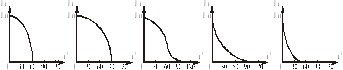
83. Specify the type of the control characteristic for 3-phase bridge rectifier with resistive load:
A) B) C) D) E)
84. What is the main disadvantage of converters with a joint management?
A) of the complicated structure of the power transformer;
B) the need for special measures for reliable switching thyristors;
C) the need to take measures to reduce the circulating current;
D) the need for a higher class of thyristors;
E) the need for more power thyristors.
85. In which case, use the asynchronous IFSB?
A) if no synchronizing circuit power transformer.
B) with significant distortions of the supply voltage.
C) in the case of joint administration.
A) only in cases of separate management.
E) only in bridge circuits.
86. Enter element drive time constant which does not depend on the element parameters (power, etc.)
A) generator;
B) thyristor;
C) a DC motor;
D) tacho;
E) magnetic amplifier.
87. Why is applied parallel diodes?
A) to reduce the internal resistance of the circuit;
B) to enhance rectification coefficient circuit;
C) to reduce the voltage drop across the diode open;
D) to increase the total direct current;
E) to increase the permissible reverse voltage.
88. Specify the correct wiring of the zener diode as voltage reference:
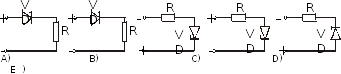
89. Enter the current-voltage characteristic of the thyristor at the maximum control current:
 I
I I I
I
I
I I I
I
90. Specify the type of the control characteristic for single-phase rectifier with resistive load:
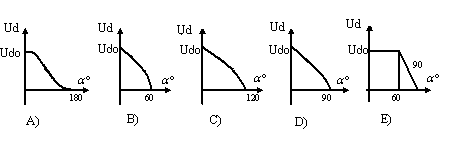
91. For whatever reason, have to increase the cross section of the magnetic transformer zero-phase rectifier circuit?
A) because the pulse frequency is 150 Hz;
B) because the conduction interval of each valve is 120;
C) to provide a full load current of the valves;
D) in order to avoid saturation of the magnetic transformer DC component;
E) to enhance the power transformer.
92. What phenomenon is called rollover Inverter?
A) phenomenon associated with the breakdown of one of the thyristor inverter;
B) a phenomenon associated with the disappearance of gating;
C) the phenomenon of short circuit in the circuit associated with the violation of switching thyristors;
D) a phenomenon associated with the excess of the permissible current through the thyristors;
E) is a phenomenon associated with the disappearance of the supply voltage.
Модуль 1
Дайте определение понятию:
1) управляемых выпрямителей;
2) преобразователей напряжения.
Что такое:
1) инвертор;
2) инвертор со звеном постоянного тока.
Нарисуйте:
1) диод (УГО, схема подключения), тиристор;
2) тиристор (УГО, схема подключения), симистор.
1) Назначение и область применения непосредственных преобразователей частоты.
2) Назначение и область применения коммутаторов переменного напряжения.
Модуль 2
Дайте определение понятию:
1) однофазных тиристорных выпрямителей;
2) полностью управляемого тиристорного выпрямителя.
Опишите:
1) способы повышения надежности работы полупроводниковых преобразователей;
2) средства защиты в силовых цепях тиристорных преобразователей.
Опишите методику:
1) выбора параметров RC - цепи
2) выбора активных элементов тиристорного преобразователя.
Опишите:
1) функциональное назначение элементов структурной схемы;
2) систему фазового управления.