
05.YH_Topic_2
.pdf
Information Page
Walls
The main types of walls used in Australian housing are shown below. Houses may have a combination of these wall types.
Render optional
Brick wall
Cavity
Outside
Plaster or plasterboard
Inside
Brick cavity wall
•Two brick walls with a gap between them called a cavity
•The inside of the wall can be covered with plaster or plasterboard
•The outside of the wall can be rendered which, unlike plaster, is waterproof
•Alternatively, the inside and outside can be left with the bricks exposed. This is called face brickwork.
Render
Brick wall
Cavity
Outside
Insulation
Sarking
Framing
Plasterboard
Inside
Brick veneer wall
•One brick wall and one framed wall with a cavity in between. The frame is usually timber, but can be steel
•The inside can be plasterboard, metal sheeting or timber lining. The outside is the same as for brick cavity
•Insulation is often placed in the frame to reduce changes in the temperature inside the building.
Weatherboards |
Insulation |
|
|
Framing |
Sarking |
|
|
|
Plasterboard |
Outside |
Inside |
Framed wall
•One wall usually with a timber frame but can be steel
•The inside is the same as for brick veneer. The outside can be covered with weatherboards, metal sheeting or fibre cement sheet
•Insulation is often placed in the frame to reduce changes in the temperature inside the building. Sarking helps keep water outside.
Bricks are porous and absorb water if they are wet for long periods of time. The cavity in both the “brick cavity” and “brick veneer” walls stops the water on the outside of the wall soaking through to the inside wall. Framed walls do not need a cavity, because the materials used on the outside are waterproof.
Topic 2 |
Page 11 |
Building Elements and Materials |

Information Page
Roofs
The main types of roof used in Australian housing are shown below. Many houses have a combination of these roof types.
Skillion
A roof which slopes in one direction
Gable
A roof which slopes in two directions
Hip
A roof which slopes in four directions
The slope of the roof is called the pitch. Roofs in areas which have heavy rain or snow are usually steeper than those in dry areas. The steep pitch helps to push the rain or snow off the roof.
Roofs have two main parts – the structure and the roof covering.
Structure
There are two main types of roof structure. Traditionally roofs were built using beams and rafters. More recently trusses have been used to build roofs. Roofs with trusses use smaller pieces of timber than traditional roofs.
Ridge beam |
Collar tie |
|
Tiles |
|
|
|
|
Rafter |
Under purlin |
Steel roof sheeting |
|
|
|
Truss |
|
Prop |
Strut |
Battens |
|
|
|
||
Support |
|
Fascia |
|
|
Support |
|
|
Traditional |
|
|
Truss |
|
|
|
Material
Some of the material that roofs can be built with are steel sheeting or tiles made from clay, concrete or metal can be used.
Corrugated roofing
Flashing
Timber batten or purlin
|
Deck roofing – good |
Battens |
|
for low pitches |
|
Steel sheeting |
|
|
|
Tiles |
Building Elements and Materials |
Page 12 |
Topic 2 |
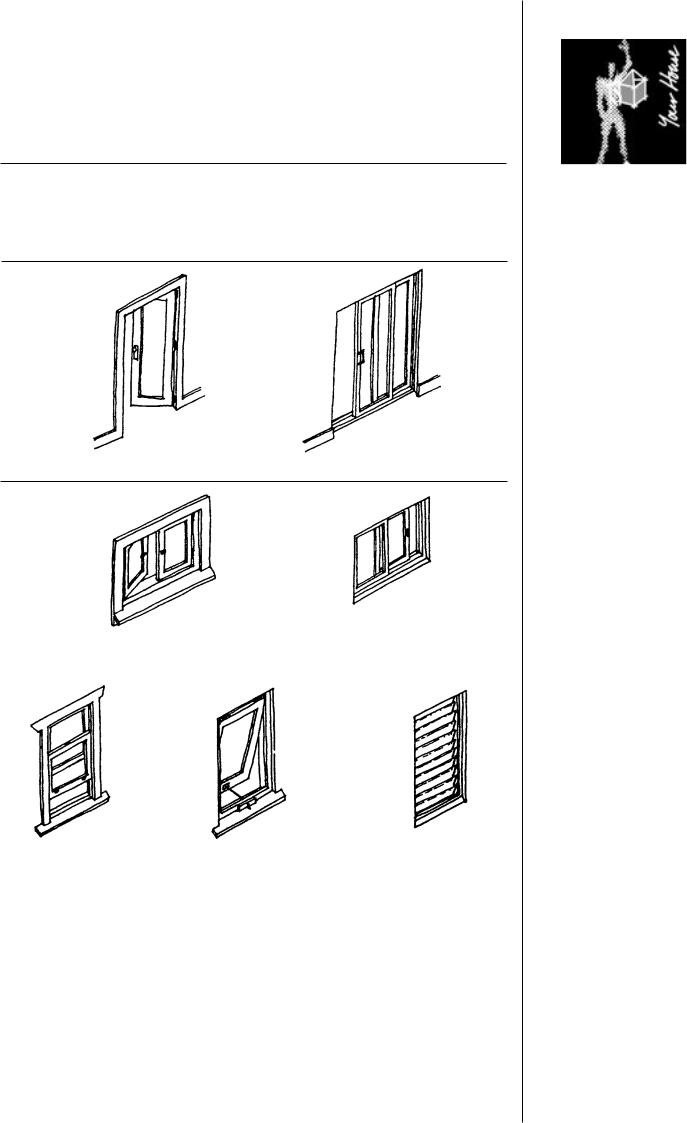
Information Page
Windows and Doors
Walls need holes in them so that people, light and air can pass through. These holes are doors and windows. The main types of windows and doors used in Australian housing are shown below.
Doors
Hinged |
Sliding |
Windows
Casement |
Horizontal Sliding |
Double Hung |
Awning |
Louvre |
|
|
|
Topic 2 |
Page 13 |
Building Elements and Materials |

Information Page
Masonry
Masonry is the word used to describe walls made of brick, concrete block or stone.
Bricks
Mortar
Blocks
Mortar
Stone
Mortar
Raw material – clay
Making – wet clay is pushed into a mould and fired (dried) in an oven
Colour – depends on the colour of the clay and the way it is fired
Other uses – Clay is also used for making roof tiles, walls and floor tiles and pavers.
Raw material – concrete (which is a mixture of cement, sand and gravel) Making – wet concrete is placed in moulds and dried
Colour – depends on the colour of the sand and pigment (colouring agent) Other uses – concrete is also used for making roof tiles, pavers and floor slabs.
Raw material – stone
Making – stone is cut from the ground (quarried). It can used rough shapes or cut into neat blocks
Colour – depends upon the type of stone and where it comes from
Other uses – stone is used for floor and wall tiles, pavers, bench tops.
To make walls out of masonry materials, each piece must be stuck to the others. This is done using a type of cement called mortar. The pattern which bricks or blocks make when they are made into a wall is called the bond. Common bonds are shown below.
Stretcher bond
The most common bond. Strong and cost effective
Flemish bond
An old bond. Strong but expensive as it is two bricks thick
Stack bond
A decorative bond. The continuous vertical joints make it weaker than stretcher bond
English bond
An old bond. Strong but expensive as it is two bricks thick
Building Elements and Materials |
Page 14 |
Topic 2 |
Information Page
Timber
Timber is the word used to describe wood used in buildings.
Timber can be divided into two main groups:
Hardwoods – timber from trees which flower (oak, jarrah, beech)
Softwoods – timber from trees which do not flower (pine, cedar).
Timber comes from trees which grow all over the world. Some trees are grown in specially planted forests and others are cut from naturally growing forests. It is best to use timber from specially planted forests whenever possible as it helps to protect the natural environment.
The main features of timber
Trees have bark which is usually removed before timber can be used in buildings.
Trees have growth rings. When a tree is cut the growth rings can be seen as lines called grain.
A knot is formed when a branch grows out from the main truck of the tree.
Wall framing
Cupboards
Floor boards
Growth rings
Trunk
Knot Grain
Branch
Bark
Roof framing and ceiling framing
Fascia
Weatherboards
Window frames
Door frames
Floor framing
Skirting boards and trims
Topic 2 |
Page 15 |
Building Elements and Materials |

Information Page
Metals
Metals are made of ore, which is rock with metal particles within it. The ore is mined, crushed and heated until the metal melts and can be separated from the rest of the rock.
Metals are generally very strong and can be formed into different shapes by rolling or pouring into moulds. However, they are more expensive than other types of building material. Therefore, they are usually prepared as thin sheets (that is, roofing) or for small objects (that is, door handles, window frames).
The main types of metal used in houses are steel and aluminium.
Pressed metal and corrugated steel can be used for ceilings
Aluminium door and window frames
Steel balustrade
Steel roof sheeting with protective coating
corrugations in the steel give it extra strength
Steel gutters and down pipes
Steel wall sheeting with protective coating steel can also be used to line internal walls
Steel columns and beams
Cast iron or aluminium decorative features
Building Elements and Materials |
Page 16 |
Topic 2 |
