
Lecture
1. STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION OF CIRCULATING ASSETS
The elements of the structure of circulating assets are as follows (fig. 1):
- Industrial stocks (inventory) (raw materials and basic materials, purchased semi-processed materials, auxiliary materials, fuel, spare parts, etc.);
- Work-in-process;
- Deferrals;
- Finished commodity in warehouses;
- Factory shipments;
- Accounts receivable;
- Cash assets (resources) in the enterprise cash department and on bank accounts.
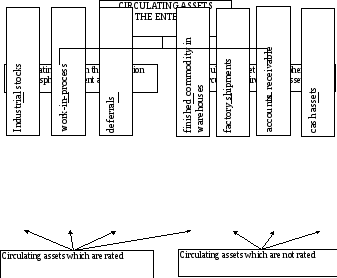
Figure 1. The structure of circulating assets of the enterprise
Raw materials represent the production of extraction industry branches.
Materials represent the production which has already had certain processing.
Materials are subdivided into basic ones and auxiliary ones.
Basic materials are materials which are a direct part of a product that is being manufactured (metal, fabrics).
Auxiliary materials are materials which are necessary for providing the normal production process. They do not belong to the composition of a finished product (greasing, lubrication, reagents). Semifinished goods are products finished by processing at one repartition (redivision) and transmitted for processing to the other repartition. Semifinished goods can be owned ones and purchased ones. If semifinished goods are not made at the owner's enterprise, and are bought from the other enterprise, they belong to purchased objects and are part of industrial stocks.
Work-in-process is production (work) which did not undergo all stages (phases, repartitions), stipulated by the technological process, and also products which are short of components, incomplete, which did not undergo tests and technical acceptance.
Deferrals are expenses (charges) of the given period subject to repayment due to the prime cost of the subsequent periods.
Finished commodity in warehouses represents completely perfected finished goods or the semifinished goods which were received at the enterprise warehouse.
Accounts receivable represent money, which physical or legal persons owe for delivery of goods, services or raw materials.
Cash assets (cash means) are money resources which are in the enterprise cash department, in settlement of accounts of banks and in calculations.
On the basis of element structure of circulating assets it is possible to calculate their structure which represents specific weight of cost of separate elements of circulating assets in their general cost.
According to sources of formation circulating assets are divided into owned ones and borrowed ones. Owned circulating assets are formed at the expense of the enterprise company's equity (authorized capital stock (chartered capital), capital reserves, profit accumulation, etc.). The structure of borrowed circulating assets includes bank credits, and also bills payable. They are given to the enterprise for temporary usage. One part is paid (credits and loans), the other part is free of charge (bills payable).
According to the degree of controllability circulating assets are divided into rated and non rated ones. Rated circulating assets are those, which provide manufacturing continuity and promote effective usage of resources. These are industrial stocks, deferrals, work-in-process, finished goods in warehouses. Money means, factory shipments, accounts receivable belong to non-rated circulating assets. The absence of norms does not mean that volumes of these assets can change at random. The operating procedure of payments between enterprises stipulates the system of sanctions against the growth of defaults in payment.
Rated circulating assets are planned by the enterprise whereas non-rated circulating assets are not the object of planning.
