
- •Министерство Финансов Российской Федерации Всероссийская государственная налоговая академия Legal English - 1
- •Unit 2 What Law Is
- •Vocabulary
- •Chapter II sources of law Unit 3 Sources of English Law
- •The Sources of English Law
- •The Principal Sources
- •Legislation
- •Judicial precedent
- •The Subsidiary Sources
- •Customs
- •Books of authority
- •Vocabulary
- •Unit 4 Sources of Modern Law
- •Text a Historical and Political Background
- •Text b Common Law Systems
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary tasks
- •For You to Know
- •Text d Sources of American law
- •Vocabulary
- •Text e Continental Systems
- •For You to Remember
- •Vocabulary
- •Chapter III constitutions Unit 5 The History of Constitution
- •Vocabulary
- •Text b Characteristics of Constitutions
- •Vocabulary
- •Unit 6 British Constitution
- •The Nature of the Constitution
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary tasks
- •Unit 7 us Constitution
- •Founding of the United States
- •Vocabulary
- •13 States convention written constitution
- •Vocabulary tasks
- •Chapter IV the system of government Unit 9 The British Government of Today
- •Text a The Governmental Model
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary tasks
- •Text b The British Parliament
- •Vocabulary
- •The System of Government
- •Stages of a Government Bill
- •The House of Commons
- •The House of Lords
- •Making New Law
- •Text d The Prime Minister and the Cabinet
- •Vocabulary
- •Unit 10 The American Government of Today
- •System of Government in the United States
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary tasks
- •Unit 11 The System of Checks and Balances
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary tasks
- •Checks and Balances
- •Unit 12 Law-making Process in the usa
- •Text a The Concept of Bicameral Legislature
- •How Congress Makes Laws
- •Vocabulary
- •Federalism
- •State and Local Government
- •Three Branches of Government
- •Unit 13 The State System of Russia. The Parliament of the Russian Federation
- •Text a The State System of Russia
- •Vocabulary
- •Text b The Parliament of the Russian Federation
- •Vocabulary
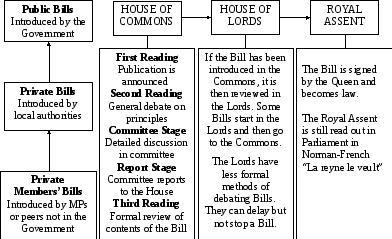
The House of Lords
To spread legislative workload more evenly between the two Houses a sizeable proportion of all Bills begins in the House of Lords. By convention the Lords do not reject legislation on matters which were in the Government's manifesto (election pledge). The Act of 1949 provides that any Public Bill passed by the Commons in two successive parliamentary sessions and rejected both times by the Lords, may be presented for the Royal Assent, even though it has not been passed by the Lords. The Lords, therefore, can only delay the passage of a Public Bill, they cannot reject it.
The Lords cannot make changes to a Money Bill (although it can delay Money Bills for one month). It is the House of Commons which is elected by the public that should make the decisions on the amount of taxes people have to pay and the like.
The stages of a Bill in the House of Lords are pretty much the same as those in the House of Commons.
Any changes made to a Bill in the House of Lords have to be considered in the House of Commons, for which purpose they are taken back to the lower chamber. The Commons normally accept most of the Lords’ amendments which are non-controversial.
The Royal Assent
Once both Houses of Parliament have passed a Bill, it has to go to the Queen for the Royal Assent. No monarchs since the sixteenth century have signed Bills themselves. Queen Ann became the last monarch to reject a Bill in 1707.
Once a Bill has received the Royal Assent it becomes an Act of Parliament.
Bill And Law
In the British Parliament a bill is usually produced by the Government, and discussed in the House of Commons. Then it goes to the House of Lords. Finally, it receives the Royal Assent (it is signed by the Queen) and becomes law.

Analyse the chart.
How Bills Go through Parliament
Vocabulary
Act of Parliament постановление парламента
be in charge (of) стоять во главе, руководить
be short of time испытывать недостаток времени
bill n законопроект; Money Bill финансовый законопроект
chamber n палата (парламента), зал заседаний
clarify v разъяснять, пояснять
Committee of the Whole House комитет всей палаты (заседание палаты общин
и палаты лордов на правах комитета для рассмотрения финансовых
законопроектов)
Committee Stage период/стадия рассмотрения в комитете
comply with v подчиняться, действовать согласно (правилам)
consent (to) v давать согласие, соглашаться
consider v рассматривать, обсуждать
contribute v делать вклад, способствовать
deliberation n совещание, обсуждение
election pledge n предвыборное обязательство
eventually adv в конце концов, в конечном итоге
explanatory note n пояснительная записка
government bill n законопроект, внесенный правительством
Human Rights права человека
in line with в согласии с, в соответствии с
institute v устанавливать, вводить
manifesto n манифест
Member of Parliament (MP) член парламента; член палаты общин
non-controversial adj не спорный, не дискуссионный
obsolete adj устарелый, вышедший из употребления
on behalf of от имени
outdated adj устарелый, устаревший
passage n 1 принятие; 2 прохождение через законодательный орган (о законе)
Public Bill публичный законопроект
reject v отвергать, отклонять
Report Stage 1 стадия доклада; 2 стадия обсуждения законопроекта, второе
чтение
Royal Assent королевская санкция (принятого парламентом закона)
spot v заметить, увидеть
Standing Committee постоянный комитет
Statute Law статутное право, «писаный закон»
to and fro туда и сюда, с одного места на другое
update v 1 модернизировать; 2 приводить в соответствие с требованиями
современности
vote v голосовать
vote n голосование
walk of life 1 общественное положение; 2 занятие, профессия
workload n рабочая нагрузка
Reading tasks
A Answer these questions.
1 How is the UK Constitution being developed through making new laws?
2 What circumstances initiate new legislation?
3 What are the ways of making a new law?
4 What is the essence of law-making in Parliament?
5 What are the reasons for Bills to be sent to committees?
6 Under which circumstances can an amendment be withdrawn?
7 Where is a new legislation initiated?
8 In what way does the Committee stage in the House of Lords differ from that in the House of Commons?
9 Why are Lord’s powers over Money Bills restricted?
10 What is the role of the Royal Assent in making a law?
B Decide which of the statements (a, b or c) corresponds exactly to the meaning of the text and best completes each statement.
1 Parliament sometimes passes a very general law and
a) leaves it as it is
b) leaves the relevant minister to fill in the details
c) leaves it for the House of Lords to fill in the details.
2 No new law can be made by Parliament unless it
a) has been approved by Prime Minister
b) has passed through Parliament and received the Royal Assent
c) is popular with the public.
-
Most stages through which a Government Bill has to pass are known as “readings” because
a) during the discussion of a Bill MPs like to read newspapers
b) only the reading of a Bill but not its discussion is allowed in the Parliament
c) the contents of each bill is read out in each Chamber.
4 If the Bill has been considered by a Committee of the Whole House
a) the Report Stage is not necessary
b) the further consideration is necessary
c) the Report Stage is delayed.
5 During the third reading the House of Commons decides
a) whether the Bill should be changed substantially
b) whether the Bill should be accepted or rejected
c) whether the Bill should go to the Royal Assent.
6 Lords cannot reject a Public Bill because
a) the Act of 1949 provides it
b) the Queen forbids it
c) the Human Rights Act of 1998 provides it.
7 The members of both Houses know that the Royal Assent to a Bill has been given
a) from the Queen herself
b) from a document the Queen sends by mail
c) from certain Lords who inform them.
C Rearrange paragraphs in the text and put them in the correct order.
