
Chapter09
.pdf
Chapter 9, Problem 69.
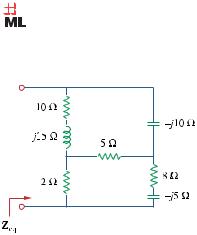
Find the equivalent admittance Y eq of the circuit in Fig. 9.76.
Figure 9.76
For Prob. 9.69.
Chapter 9, Solution 69.
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
= |
|
|
(1+ j2) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Y |
|
|
4 |
- j2 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
o |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y = |
|
4 |
|
|
= |
|
(4)(1− j2) |
= 0.8 − j1.6 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
1+ j2 |
5 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
o |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Yo + j = 0.8 − j0.6 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
= |
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
= (1) +( j0.333) +(0.8 + j0.6) |
||||||||||||
Yo′ |
1 |
- j3 |
|
0.8 − j0.6 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
1 |
|
|
=1.8 + j0.933 = 2.028 27.41° |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Y ′ |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
o |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y ′ |
|
= 0.4932 - 27.41°= 0.4378 − j0.2271 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
o |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y ′ |
|
+ j5 = 0.4378 + j4.773 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
o |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
= |
1 |
+ |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
= 0.5 + |
0.4378 − j4.773 |
||||||||||||
Y |
|
|
|
2 |
|
0.4378 + j4.773 |
|
22.97 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
eq |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
= 0.5191− j0.2078 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
eq |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y |
|
= |
0.5191− j0.2078 |
= 1.661 + j0.6647 S |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
eq |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.3126 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
Chapter 9, Problem 70.
Find the equivalent impedance of the circuit in Fig. 9.77.
Figure 9.77
For Prob. 9.70.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
Chapter 9, Solution 70.
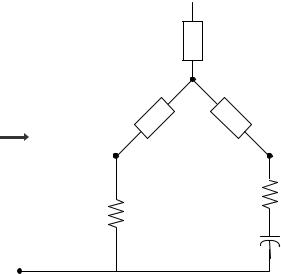
Make a delta-to-wye transformation as shown in the figure below.  a
a
Zan
Zbn
Zeq
n Zcn
b |
c |
8 Ω
2 Ω
 -j5 Ω
-j5 Ω
Zan = |
(-j10)(10 + j15) |
= |
(10)(15 − j10) |
= 7 − j9 |
|||||||
|
5 − j10 +10 + j15 |
15 + j5 |
|
||||||||
Zbn = |
(5)(10 + j15) |
= 4.5 + j3.5 |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
15 + j5 |
|
|
|
||||||
Zcn = |
(5)(-j10) |
= -1− j3 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
15 + j5 |
|
|
|
|||||||
Zeq = Zan +(Zbn + 2) || (Zcn |
+8 − j5) |
|
|||||||||
Zeq = 7 |
− j9 |
+(6.5 + j3.5) || (7 − j8) |
|
||||||||
Zeq = 7 |
− j9 |
+ |
(6.5 + j3.5)(7 − j8) |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
13.5 − j4.5 |
|
|||||
Zeq = 7 |
− j9 |
+5.511− j0.2 |
|
|
|
||||||
Zeq =12.51− j9.2 = 15.53 -36.33° Ω
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
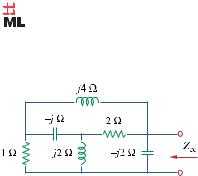
Chapter 9, Problem 71.
Obtain the equivalent impedance of the circuit in Fig. 9.78.
Figure 9.78
For Prob. 9.71.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Solution 71.
We apply a wye-to-delta transformation. j4 Ω
Zab
a 

 b
b
Zac Zbc |
Zeq |
1 Ω |
-j2 Ω |
c |
Zab = |
2 − j2 + j4 |
= |
2 + j2 |
=1− j |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
j2 |
|
|
|
j2 |
|
|||||||
Zac = |
|
2 + j2 |
=1+ j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Zbc = |
2 + j2 |
|
= -2 + j2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
- j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
j4 || Zab = j4 || (1− j) = |
|
|
( j4)(1− j) |
=1.6 − j0.8 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
1+ j3 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1|| Zac |
|
=1|| (1+ j) = |
(1)(1+ j) |
= 0.6 + j0.2 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 + j |
|
|||||
|
j4 || Zab +1|| Zac = 2.2 − j0.6 |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
1 |
= |
|
|
1 |
+ |
|
1 |
|
+ |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
- 2 + j2 |
|
2.2 − j0.6 |
|
|||||||||||
|
Zeq |
|
- j2 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
=j0.5 −0.25 − j0.25 +0.4231+ j0.1154
=0.173 + j0.3654 = 0.4043 64.66°
Zeq = 2.473 -64.66° Ω = 1.058 – j2.235 Ω
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
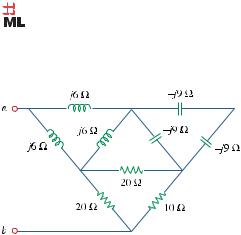
Chapter 9, Problem 72.
Calculate the value of Z ab in the network of Fig. 9.79.
Figure 9.79
For Prob. 9.72.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
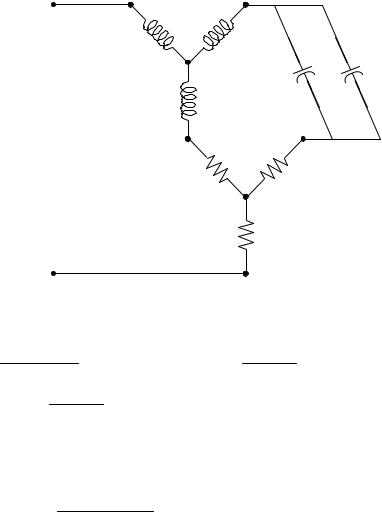
Chapter 9, Solution 72.
Transform the delta connections to wye connections as shown below.
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
j2 Ω |
j2 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-j9 Ω |
-j18 Ω |
|
|
|
|
j2 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R1 |
|
R2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
R3 |
|
|
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
- j9 || -j18 = -j6 , |
|
|
|
|
|
||
R1 |
= |
(20)(20) |
|
= 8 Ω, |
R 2 = |
(20)(10) |
= 4 Ω, |
|
|
20 + 20 +10 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
R 3 = (20)(10) = 4 Ω |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
Zab |
= j2 +( j2 +8) || (j2 − j6 + 4) + 4 |
|
|
|
|||
Zab |
= 4 + j2 +(8 + j2) || (4 − j4) |
|
|
|
|||
Zab |
= 4 + j2 + (8 + j2)(4 − j4) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
12 - j2 |
|
|
|
Zab |
= 4 + j2 +3.567 − j1.4054 |
|
|
|
|||
Zab |
= 7.567 + j0.5946 Ω |
|
|
|
|||
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 73.
Determine the equivalent impedance of the circuit in Fig. 9.80.
Figure 9.80
For Prob. 9.73.
Chapter 9, Solution 73.
Transform the delta connection to a wye connection as in Fig. (a) and then transform the wye connection to a delta connection as in Fig. (b).
a
j2 Ω |
j2 Ω |
|
|
-j9 Ω |
-j18 Ω |
j2 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
R1 |
|
R2 |
|
R3 |
|
b
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
Z1 = |
|
|
( j8)(-j6) |
= |
48 |
= -j4.8 |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
j8 + j8 − j6 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
j10 |
|
|||||||||||
Z2 = Z1 = -j4.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Z3 |
= |
|
|
( j8)( j8) |
= |
- 64 |
= j6.4 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
j10 |
j10 |
|
|||||||||||
(2 + Z1 )(4 + Z2 ) +(4 + Z2 )(Z3 ) +(2 + Z1 )(Z3 ) = |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2 − j4.8)(4 − j4.8) +(4 − j4.8)( j6.4) +(2 − j4.8)( j6.4) = 46.4 + j9.6 |
|||||||||
Za |
= |
|
|
46.4 + j9.6 |
|
=1.5 − j7.25 |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
j6.4 |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Zb |
= |
|
|
46.4 + j9.6 |
|
= 3.574 + j6.688 |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
4 − j4.8 |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Zc |
= |
|
|
46.4 + j9.6 |
|
=1.727 + j8.945 |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
2 − j4.8 |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
j6 || Zb = |
(6 90°)(7.583 61.88°) |
|
= 07407 + j3.3716 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.574 + j12.688 |
|
||||||||
- j4 || |
Za |
= |
|
(-j4)(1.5 − j7.25) |
= 0.186 − j2.602 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 − j11.25 |
|
||||||||
j12 || |
Zc |
= |
(12 90°)(9.11 79.07°) |
= 0.5634 + j5.1693 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
1.727 + j20.945 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Zeq |
= ( j6 || Zb ) || (-j4 || Za + j12 || Zc ) |
|||||||||||||||||
Zeq |
= (0.7407 + j3.3716) || (0.7494 + j2.5673) |
|||||||||||||||||
Zeq = 1.508 75.42° Ω = 0.3796 + j1.46 Ω
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
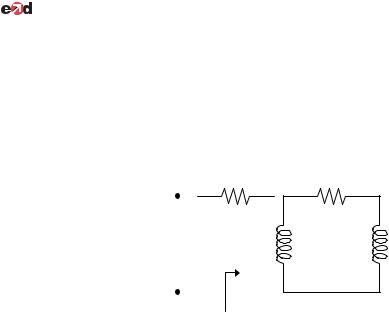
Chapter 9, Problem 74.
Design an RL circuit to provide a 90 o leading phase shift.
Chapter 9, Solution 74.
One such RL circuit is shown below.
|
20 Ω V |
20 Ω |
+ |
|
+ |
Vi = 1 0° |
j20 Ω |
j20 Ω Vo |
|
|
− |
Z
We now want to show that this circuit will produce a 90° phase shift.
Z = j20 || (20 + j20) = |
|
( j20)(20 + j20) |
= |
- 20 + j20 |
= 4(1 |
+ j3) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
20 + j40 |
|
|
|
1+ j2 |
||||||||||||||||
V = |
|
Z |
|
V = |
4 + j12 |
(1 0°) = |
1+ j3 |
= |
1 |
(1+ j) |
|
||||||||||||
Z + 20 |
|
|
|
6 + j3 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
i |
|
24 + j12 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
j20 |
|
|
|
j 1 |
|
|
|
j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
V = |
|
|
|
V |
= |
|
|
|
|
|
(1+ j) |
= |
|
|
= 0.3333 90° |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
o |
|
20 + j20 |
|
1+ j 3 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
This shows that the output leads the input by 90°.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
