
Chapter09
.pdf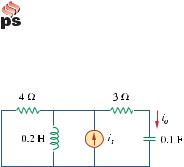
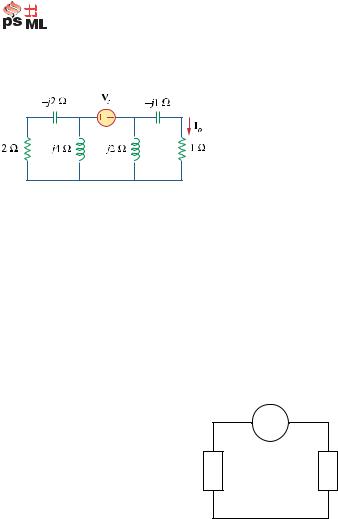
Chapter 9, Problem 46.
If i s = 5 cos(10t + 40 o ) A in the circuit of Fig. 9.53, find i o .
Figure 9.53
For Prob. 9.46.
Chapter 9, Solution 46.
|
is = 5cos(10t + 40°) → |
Is = 5 40° |
|||||||||||||
|
|
0.1 F |
→ |
|
|
1 |
= |
|
1 |
= -j |
|||||
|
|
|
jωC |
j(10)(0.1) |
|||||||||||
|
|
0.2 H |
→ |
jωL = j(10)(0.2) = j2 |
|||||||||||
Let |
Z1 = 4 || j2 = |
|
j8 |
= 0.8 + j1.6 , |
Z2 = 3 − j |
||||||||||
4 |
+ j2 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Io = |
Z1 |
|
Is = |
0.8 + j1.6 |
(5 40°) |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
3.8 + j0.6 |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
Z1 + Z2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Io = |
(1.789 63.43°)(5 40°) |
= 2.325 94.46° |
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
3.847 8.97° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Thus, io (t) = 2.325 cos(10t + 94.46°) A
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
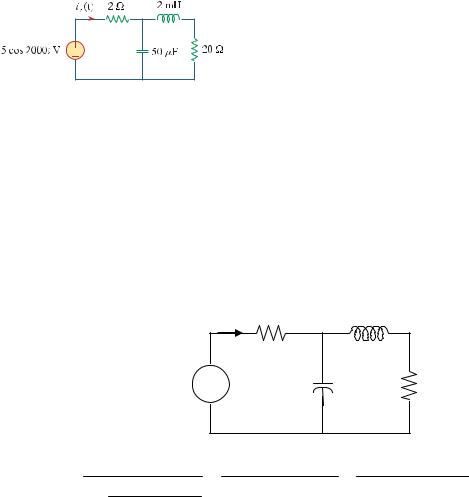
Chapter 9, Problem 47.
In the circuit of Fig. 9.54, determine the value of i s (t).
Figure 9.54
For Prob. 9.47.
Chapter 9, Solution 47.
First, we convert the circuit into the frequency domain.
|
|
|
Ix 2 Ω |
|
|
j4 |
|
|
||
|
5 0˚ |
+ |
|
|
-j10 |
20 Ω |
|
|||
|
− |
|
|
|
||||||
Ix = |
5 |
= |
|
5 |
|
= |
|
5 |
= 0.4607 52.63° |
|
− j10(20 + j4) |
2 |
+ 4.588 |
− j8.626 |
10.854 −52.63° |
||||||
2 + |
|
|
|
|||||||
− j10 + 20 + j4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
is(t) = 460.7cos(2000t +52.63˚) mA
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
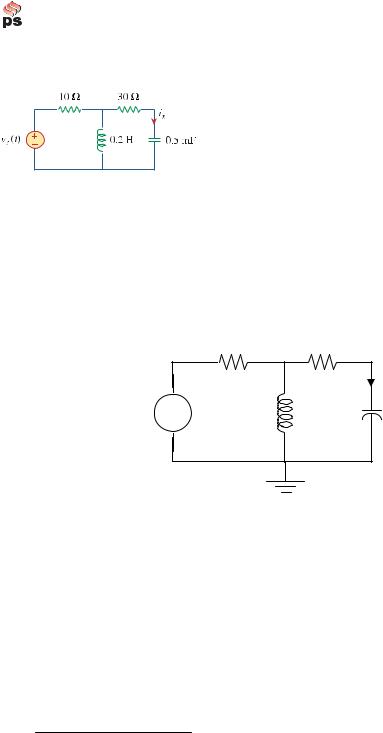
Chapter 9, Problem 48.
Given that v s (t) = 20 sin(100t - 40 o ) in Fig. 9.55, determine i x (t).
Figure 9.55
For Prob. 9.48.
Chapter 9, Solution 48.
Converting the circuit to the frequency domain, we get:
10 Ω V1 30 Ω
|
|
|
Ix |
|
20 -40˚ |
+ |
j20 |
-j20 |
|
− |
||||
|
|
We can solve this using nodal analysis.
V1 −20 −40° |
+ |
V1 −0 |
+ |
V1 −0 |
= 0 |
|
10 |
j20 |
30 − j20 |
||||
|
|
|
V1(0.1− j0.05 +0.02307 + j0.01538) = 2 −40°
V1 = |
2 40° |
|
=15.643 −24.29° |
|
0.12307 − j0.03462 |
||||
|
|
|||
Ix = |
15.643 −24.29° |
= 0.4338 9.4° |
||
30 − j20 |
||||
|
|
|
||
ix = 0.4338sin(100t +9.4°) A
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 49.
Find v s (t) in the circuit of Fig. 9.56 if the current i x through the 1- Ω resistor is 0.5 sin 200t A.
Figure 9.56
For Prob. 9.49.
Chapter 9, Solution 49.
ZT = 2 + j2 || (1− j) = 2 + |
( j2)(1− j) |
= 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
1+ j |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
Ix 1 Ω |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-j Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
j2 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ix |
= |
|
|
|
j2 |
|
|
|
I = |
|
|
|
j2 |
|
I , |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
where |
Ix = 0.5 0°= |
||||||||
|
j2 +1− j |
|
1+ j |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
I = |
|
1+ j |
Ix |
= |
1+ j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
j2 |
|
|
|
|
|
j4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
V = I Z |
|
= |
1+ j |
|
(4) = |
1+ j |
|
=1− j =1.414 - 45° |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
T |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
j4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
vs (t) = 1.414 sin(200t – 45°) V
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 50.
Determine v x in the circuit of Fig. 9.57. Let i s (t) = 5 cos(100t + 40 o )A.
Figure 9.57
For Prob. 9.50.
Chapter 9, Solution 50.
Since ω = 100, the inductor = j100x0.1 = j10 Ω and the capacitor = 1/(j100x10-3) = -j10Ω.
|
|
|
|
j10 |
Ix |
|
|
5 40˚ |
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
-j10 |
20 Ω |
vx |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
− |
Using the current dividing rule: |
|
|
||||
Ix = |
|
− j10 |
|
5 40° = −j2.5 40° = 2.5 −50° |
|
|
− j10 |
+ 20 |
+ j10 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
Vx = 20Ix = 50 −50° vx = 50cos(100t −50°) V
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 51.
If the voltage v o across the 2- Ω resistor in the circuit of Fig. 9.58 is 10 cos2t V, obtain i s .
Figure 9.58
For Prob. 9.51.
Chapter 9, Solution 51.
0.1 F |
→ |
|
1 |
|
|
= |
|
1 |
|
= -j5 |
|
|
|
||||
jωC |
j(2)(0.1) |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
0.5 H |
→ |
|
jωL = j(2)(0.5) = j |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
The current I through the 2-Ω resistor is |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
I = |
|
1 |
|
I |
s |
= |
|
|
Is |
|
, |
|
where I = |
10 |
0° = 5 |
||
1− j5 + j + 2 |
|
3 − j4 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
2 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Is = (5)(3 − j4) = 25 - 53.13°
Therefore,
is (t) = 25 cos(2t – 53.13°) A
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
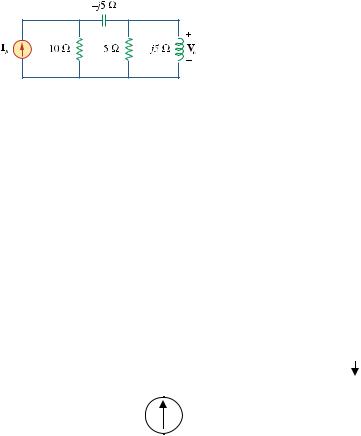
Chapter 9, Problem 52.
If V o = 8 30 o V in the circuit of Fig. 9.59, find I s. .
Figure 9.59
For Prob. 9.52.
Chapter 9, Solution 52.
|
|
|
|
|
j25 |
|
j5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
5 || j5 = |
|
|
|
= |
|
= 2.5 |
+ j2.5 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
5 + j5 |
1+ j |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z1 =10 , |
Z2 |
= -j5 + 2.5 + j2.5 = 2.5 − j2.5 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z1 |
|
|
|
Z2 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Z1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
I2 = |
Is = |
|
10 |
|
Is = |
4 |
Is |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Z1 + Z2 |
|
12.5 − j2.5 |
5 − j |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Vo = I2 (2.5 + j2.5)
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
10(1+ j) |
|
|
||
8 30°= |
|
|
I |
s |
(2.5)(1+ j) = |
|
I |
s |
||
|
|
5 − j |
||||||||
|
5 |
− j |
|
|
|
|||||
Is = |
(8 30°)(5 − j) |
= 2.884 -26.31° A |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||||
|
10(1+ j) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 53.
Find I o in the circuit of Fig. 9.60.
Figure 9.60
For Prob. 9.53.
Chapter 9, Solution 53.
Convert the delta to wye subnetwork as shown below.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z2 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Io |
|
|
|
2 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z3 |
10 Ω |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
60 −30o |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 Ω |
||||||||||
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Z |
= − j2x4 |
= |
|
8 −90° |
= −1− j1, |
Z |
2 |
= |
j6x4 |
= 3 + j3, |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
1 |
|
|
4 |
+ j4 |
|
5.6569 45° |
|
|
|
|
4 + j4 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Z3 |
= |
|
|
12 |
|
=1.5 − j1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
4 |
+ j4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(Z3 +8) //(Z2 +10) = (9.5 − j1.5) //(13 + j3) = 5.691 0.21° = 5.691+ j0.02086 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Z = 2 + Z1 +5.691+ j0.02086 = 6.691− j0.9791 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Io = |
60 −30o |
= |
60 −30o |
= 8.873 −21.67o |
A |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
6.7623 −8.33o |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
Chapter 9, Problem 54.
In the circuit of Fig. 9.61, find V s if I o = 2 0 o A.
Figure 9.61
For Prob. 9.54.
Chapter 9, Solution 54.
Since the left portion of the circuit is twice as large as the right portion, the equivalent circuit is shown below.
+− Vs
+−
2 Z |
V2 |
V1 |
Z |
−+
V1 = Io (1− j) = 2(1− j)
V2 = 2V1 = 4(1− j)
Vs = −V1 −V2 = −6(1− j)
Vs = 8.485 –135° V
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 55.
* Find Z in the network of Fig. 9.62, given that V o = 4 0 o V.
Figure 9.62
For Prob. 9.55.
* An asterisk indicates a challenging problem.
Chapter 9, Solution 55.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 Ω |
|
I |
I1 |
Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I2 |
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
-j20 V |
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
j8 Ω |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-j4 Ω |
Vo |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
I1 |
= |
|
= |
|
4 |
|
|
= -j0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
j8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
j8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
I2 |
= |
|
|
I1 (Z + j8) |
= |
(-j0.5)(Z + j8) |
= |
Z |
+ j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
- j4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- j4 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
I = I1 +I2 |
|
|
= -j0.5 + |
|
Z |
|
+ j = |
Z |
+ j0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
- j20 =12I +I1 (Z + j8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
|
|
|
j |
|
|
- j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Z + j8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
+ 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
- j20 =12 8 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
- 4 - j26 = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Z 2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Z = |
- 4 - j26 |
|
|
|
26.31 261.25° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
=16.64 279.68° |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3 |
− j |
1 |
|
|
1.5811 -18.43° |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Z = 2.798 – j16.403 Ω
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
