
New_Method
.pdfA call to the Bar
In English-speaking countries, the Bar is a term for the legal profession itself; while a bar association is the association which regulates the profession. A person who qualifies to practise law is admitted to the Bar; on the other hand, to disbar a lawyer is to make him or her unable to practise law.
The following text is an excerpt from a guide written for school leavers about courses of study in English-speaking countries. This section of the guide deals with the study of law and the requirements for entering the legal profession in the UK and the USA.
11. Read the text and say whether legal education in your country is more similar to the UK or the US model.
Studying law in the UK
In the UK, a legal education usually begins with the completion of a bachelor degree in law, known as an LLB, which usually takes three years. In the subsequent vocational stage, a person who wishes to become a : barrister joins one of the Inns of Court before beginning the Bar Vocational Course. The completion of this stage is marked by a ceremony referred to as the call to the Bar. A third stage, known as pupillage, is a year-long apprenticeship, usually at a set of barristers' chambers, which customarily consists of groups of 20— 60 barristers. Similarly, a person wishing to become a solicitor must also complete three stages: the first stage involves gaining a law degree; the second stage requires passing a one-year Legal Practice Course (LPC); and the final stage entails working for two years as a trainee solicitor with a firm of solicitors or in the legal department of a local authority or large company.
Studying law in the USA
In the USA, a legal education comprises four years of undergraduate study followed by three years of law school. A law-school graduate receives the degree of juris doctor (J.D.). In order to qualify as a lawyer, a law-school graduate must pass the bar examination.
10
Vocabulary 3
barrister - адвокат, выступающий в высших судах attorney – юрист, адвокат, поверенный (в суде)
in-house counsel – консультант, поверенный в делах корпорации solicitor – солиситор, стряпчий
the Bar – адвокатура, коллегия адвокатов
to disbar – лишить права адвокатской практики LLB – звание солиситора
Inns of Court – один из четырех адвокатских объединений, к которому необходимо принадлежать каждому адвокату
Bar Vocational Course – курс обучения (по окончании юридического факультета) на получение квалификации адвоката
call to the Bar – принять в коллегию адвокатов
pupilage – один год адвокатской практики по окончании курса Bar Vocational Course
barristers’ chambers – группа адвокатов, офисы адвокатов a trainee - стажер
juris doctor (J.D.) – юридическое звание
bar examination – письменный экзамен на присвоение квалификации, дающей право вести юридическую практику
Using exercises 9-11 write down the English for the following phrases
1.В американских фильмах часто бывает показана карьера успешного юриста, легко выигрывающего дела в суде против крупных корпораций.
2.Быть поверенным в делах корпорации непростая работа для юриста.
3.Я решил стать стряпчим, так как для меня представляет интерес проводить исследования и давать юридические советы и справки.
4.В Великобритании юридическое образование начинается с прохождения 3-х летнего курса обучения и получения степени бакалавра.
5.Человек, желающий стать адвокатом, выступающим в высших судах, должен вступить в один из 4-х адвокатских объединений до получения квалификации адвоката.
6.Третья ступень включает в себя один год адвокатской практики в одной из адвокатских контор, в которой обычно работают от 20 до 60 адвокатов.
11
What is important when choosing a legal profession? Ground your opinion.
-studying at a prestigious University
-aspirations
-salary
-premises
-abilities
-age
-demand
-talent
-?
A lawyer’s curriculum vitae
12. Read the following CV (curriculum vitae) of a young British lawyer and answer these questions.
1 Where did he work in summer 2002?
2 What languages does he speak?
3 Where did he complete his first degree?
4 What was his main duty at the European Commission? 5 What is he doing now?
12

Linus Walker
Address: |
Frejg 17, SE-118 25, Stockholm, Sweden |
Nationality: British |
Email address |
linuswalker@eli.se |
Date of birth: 12 May 1982 |
EDUCATION |
|
|
|
|
|
2005 - present |
University of Stockholm, Sweden |
|
|
Master's Programme in Law and Information Technology |
|
|
Course covers the legal aspects of Information Technology and the legal |
|
2000-2004 |
implications of the use of the Internet |
|
University of Essex, Colchester, United Kingdom |
||
|
LLB (English &French law degree) |
|
|
Course included all the core legal subjects, with a focus on contract law, |
|
2002-2003 |
company law, common law, property law and European law |
|
Universite Paris X, Paris, France |
|
|
|
DEUG (French law degree), Nanterre |
|
|
Part of the degree programme at University of Essex included an intensive |
|
course in French. Among subjects studied: European Community Law, Information Law, Civil Law and Penal Law
LEGAL WORK EXPERIENCE
June 2004- European Commission, Brussels, Belgium
February 2005 Legal Assistant within the Legal Department of the Service Commune Relex (SCR). Drafting opinions in English and French dealing with contracts awarded for projects
Summers G. R. Foster & Co. Solicitors, Cambridge, UK Liaison with clients; 2001-2004 conducting research into multiple legal areas, including family law, tort
law and contracts; assisting with trial preparation
Summer 2000 Westlake Chambers, Bath, UK Mini-pupillage, involving shadowing a number of counsel; assisted in daily activities
SKILLS AND QUALIFICATIONS
Languages: |
Native English speaker; fluent in French (written and spoken); upper- |
|
intermediate Swedish |
Computing: |
Proficient in Word, Windows, email |
Membership: |
The Law Society Strong researching and writing skills |
INTERESTS
Skiing, French history, chess
References available upon request
13
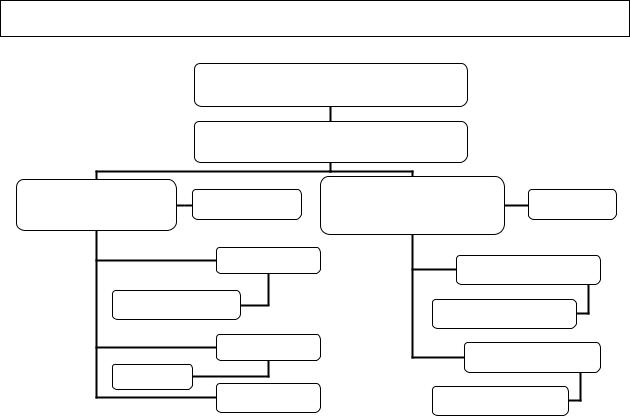
Law firm structure
13.Linus Walker has applied for a position at a law firm. Listen to his job interview and answer these questions.
1.What does Mr Nichols say about the atmosphere of the firm?
2.What does Linus say about the size of the firm?
14.Listen again and complete this organigram of the firm using the words in
the box.
Associate |
Full Partners Mr Robertson |
Paralegal Real Property |
Salaried Partner |
||
|
|
1)……….,Mr Michaels |
|
||
|
|
Senior Partners |
|
||
|
|
Ms Graham, Mr Nichols |
|
||
|
|
2)............................ |
, |
|
|
3).............. |
Department |
Secretary |
Debtor-Creditor Department |
Secretary |
|
Salaried Partner |
4) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
Associate |
5)……………. |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
6)………….. |
|
Paralegal |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Associate |
|
Associate |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Paralegal |
Associate |
|
|
|
|
|
Paralegal |
|||
Speaking. Describing a law firm
15.Look at the following phrases used by Mr Nichols to describe the firm. Which can be used to speak of a department or company, and
which of a person? Which can be used for both?
…is/are headed by …
…is/are assisted by …
…is/are managed by …
…is/are responsible for …
…is/are in charge of … …report to …
16.Describe the structure of a law firm with which you are familiar or the one just described . Refer to the positions and duties of the personnel.
14
Practice Areas
17.Listen to five lawyers talking about their firms, practice areas and clients. Tick the information you hear about each speaker.
Speaker 1 ...
1.has a few years' working experience.
2.works as a clerk at a mid-size commercial law firm.
3.will get to know other departments of the firm.
4.meets with clients regularly.
5.plans to specialise in commercial litigation.
Speaker 2 ...
1.is a sole practitioner.
2.works in the area of employment law.
3.deals with wage disputes.
4.represents clients in mediation.
5.has many clients who are small businesses.
Speaker 3 ...
1.works in the area of secured transactions.
2.carries out trade-mark registrations.
3.assists clients who are in artistic professions.
4.serves as an expert witness in court.
5.is a partner in a large IP firm.
Speaker 4 ...
1.is a senior partner in a mid-size law firm.
2.specialises in competition law.
3.represents clients before the employment tribunal.
4.deals with infringements of the Competition Act.
5.has clients in the telecommunications sector.
Speaker 5 ...
1. owns shares in his firm.
2.argues cases in court.
3.works in the area of real property law.
4.represents landlords but not tenants.
5.teaches courses on litigation at the law university.
18. Discuss these questions.
1.Which kind of firm do you work in or would you like to work in?
2.Which areas of the law have you specialised in or would like to specialise in?
15
Vocabulary 4
associate – помощник, младший юрист
full partners – полноправные члены товарищества paralegal - непрофессионал
real property - недвижимость salaried partner – штатный сотрудник litigation - судебный процесс, спор mediation - посредничество
tenant – арендатор
Using exercises 15, 17 write the following phrases in English
1.Программа «Магистр Права и Информационных Технологий» рассматривает юридические аспекты информационных технологий и возможности применения Интернета в юридических целях.
2.Другой курс включает в себя все базовые юридические дисциплины со специализацией в сфере контрактного права.
3.Он работал в качестве ассистента по правовым вопросам в отделе Права, составляя юридические заключения на английском и французском языках, имеющие отношение к контрактам по различным проектам.
4.Он возглавлял эту юридическую фирму в течение пяти лет, затем он был поставлен во главе другой, более крупной компании.
5.Она имеет дело со спорами по заработной плате.
6.Он ведет дела о недвижимости, представляя интересы владельцев, но не арендаторов.
7.Он читает курс лекций по судебному процессу в Юридическом университете.
What is important when choosing a firm to work for? Why?
-atmosphere
-size
-salary
-the Head
-position
-duties to fulfill
-location
-perks and benefits
16
Law Firm Culture
19. Read this excerpt from an article in a law-school newspaper about law firm culture. Which type of firm would you prefer to work for? Why?
One factor which |
sole practitioner) to |
lawyers, is |
lawyers, while a |
plays an important |
global firms |
sometimes known as |
large law firm is |
role in the culture of |
employing hundreds |
a boutique firm, as it |
considered to be one |
a law firm is its size. |
of attorneys all over |
often specialises in a |
employing 50 or |
Law firms can range |
the world. A small |
specific area of the |
more attorneys. |
from a one-person |
law firm, which |
law. A mid-size law |
|
solo practice |
typically engages |
firm generally has |
|
(conducted by a |
from two to ten |
ten to 50 |
|
|
|
|
|
20. Listen to Richard, a law student, talking to a group of first-year law
students at an orientation event at law school. He tells them about his experience as a clerk in different law firms. Answer these questions.
1. Why do the professors encourage students to do work experience? 2. How long have Richard's clerkships generally lasted?
3. What is Richard's final piece of advice?
21. Listen again and tick the advantages of small and large law firms Richard mentions. In some cases, he says both types of firm have the same advantages
Advantages |
Small firms |
Large firms |
more autonomy and responsibility |
|
|
opportunity to work on prestigious cases |
|
|
chance to rotate through different practice areas |
|
|
asked to write briefs and letters |
|
|
allowed to conduct research and manage court books |
|
|
opportunity to make many contacts |
|
|
more training offered |
|
|
made to feel part of a team |
|
|
invited to participate in social events |
|
|
family-like atmosphere |
|
|
made good use of time |
|
|
22. Discuss these questions.
1. Do you have any experience working as a clerk in a law firm? In what ways was it similar or different from Richard's experience?
2. What kinds of tasks and responsibilities do clerks in your firm have?
3. Do you agree with the way Richard characterises small and large law firms?
17

II. Company Law. Company formation
Lawyers play important roles in the formation of a company, advising clients which entities are most suited to their needs and ensuring that the proper documents are duly filed.
You are going to hear a conversation between an American lawyer, Ms Norris, and her client, Mr O'Hara. The lawyer describes how a specific type of corporation is formed in the state of Delaware.
23.Listen to the conversation and tick the documents required for formation that the lawyer mentions.
1.DBA filing
2.articles of incorporation
3.stock ledger
4.general partnership agreement
5.stock certificates
6.IRS & State S Corporation election
7.bylaws
8.organisational board resolutions
24.Company types (USA) Look at the following table, which provides information on the documents required to form and operate the different company types in the United States. Based on what you heard in Exercise 4, which type of business association was the lawyer discussing with her client?
US entities |
Documents required for formation and operation |
sole proprietorship |
DBA filing |
|
|
general partnership |
General Partnership Agreement, local filings if partnership holds real estate |
limited partnership |
Limited Partnership Certificate, Limited Partnership Agreement |
C corporation |
Articles of Incorporation, Bylaws, Organisational Board Resolutions, Stock |
|
Certificates,! Stock Ledger |
S corporation |
Articles of Incorporation, Bylaws, Organisational Board Resolutions, Stock |
|
Certificates, Stock Ledger, IRS & State S corporation election |
Forming a business in the UK
You will hear a dialogue in which a lawyer, Mr Larsen, discusses some of the characteristics of two business entities with Mr Wiseberg, a client who is interested in forming a company in the UK.
18
25.Listen to the phone conversation and tick the two company types the men are discussing.
1.sole proprietor
2.UK limited partnership
3.UK private company limited by shares
4.UK private company limited by guarantee
5.UK public limited company
6.US C corporation
7.US S corporation
26.Listen again and decide whether these statements are true or false.
1. The client has not yet decided what type of company he wants to form. 2. The client has never founded a company before.
3. The lawyer points out that the two types of company differ with regard to the matter of personal liability.
4. The shares of a US C corporation can be freely traded on a stock exchange. 5. Both company types mentioned by the lawyer can be formed by a person who is a citizen of another country.
6.The UK company type discussed places a restriction on the number of people permitted to buy shares in the company.
7.The fastest way to form a company is to submit the documents directly to Companies House.
27. Complete the sentences below using the phrases a - f.
a are like each other |
b are similar to |
c differs |
d in both |
|
e |
that’s not the case with |
f there is one big difference between |
|
|
1) |
C corporations ................................................... |
|
private limited companies in the |
|
|
UK in many ways, particularly in respect of liability. |
|
||
2) |
Shareholders are not personally liable for the debts of the corporation |
|||
|
................................................... |
a C corporation and a private limited company. |
||
3) |
In this respect, a private limited company ................................................... |
|
. Its |
|
|
shares are not available to the general public. |
|
|
|
4) |
The two types of company ................................................... |
|
in that both can be |
|
|
founded |
|
|
|
|
by persons of any nationality, who need not be a resident of the country. |
|||
5) |
And ................................................... |
a C corporation in the US and our private |
||
|
limited company: that's the limit on the number of shares. |
|
||
6) |
But............................................. |
a private limited company. The Companies Act |
||
|
stipulates that not more than 50 members can hold shares within the company. |
|||
19
