
Методичка №140
.pdf
Vocabulary: |
|
|
arrangement |
|
n. – расположение |
articulate |
|
v. – соединять |
neighbo(u)rhood |
n. – микрорайон |
|
order |
v.– располагать в определенном порядке, упорядочивать |
|
pronounced |
|
a. – резко выраженный, заметный |
service |
|
n. – коммуникации |
weave |
v. – виться |
|
Answer the following questions:
1.What does urban design involve?
2.What parts does urban design blend?
3.What elements does urban design include?
4.What are the most pronounced elements of the urban design?
5.Where do people come together?
6.What function do city streets perform?
7.What are city streets defined by?
8.What are the purposes of the transport system?
9.What does any transport system include?
10.What are the characteristics of the best cities associated with transport systems?
11.What is the landscape?
12.What does the city’s landscape define?
А, РРАН, ДАС, Гр(IVсеместр)
ECO-ARCHITECTURE
Eco-architecture sees buildings as part of the larger ecology of the planetandthebuildingaspartofalivinghabitat.Thehumanhasincreasingly sophisticated technologies to exploit the Earth’s natural resources. But it should be known that buildings are the most damaging polluters on the planet, consuming over half of all the energy used and producing over half of all climate-change gases.
For example, air-conditioning systems represent the greatest source of climate-change gases.
Theshifttowardsgreendesignbeganinthe1970s and was a response to high oil prices. It was then that the first of the oil shocks sent fossil fuel prices sky high and the ‘futurologists’ began to look at the life history of fossil fuels on the planet and make claims about how much oil and gas were left.
The oil crisis of the 1970s resulted in the rise of the solar house movement: homes built to use clean renewable energy from the Sun.
Inthe1980scame thenext bigshockclimatechange.Itwasthenthat the rates of depletion in the ozone layer and the increase in greenhouse gases and global warming became apparent.
Nowadaystheworldneedsanewprofessionofarchitecture-engineers, who can design passive buildings that use minimal energy and the energy they use comes from renewable sources if possible.
The key issues of green buildings are resource conservation, including energy efficiency, renewable energy,andwaterconservationfeatures;usingecological building materials; and waste minimization. The main conceptofeco-architectureisdefinedas“takinglessfrom the Earth and giving more to people.”
Vocabulary:
claim 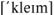
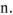 – заявление
– заявление
consume 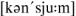 v. – потреблять, тратить, расходовать depletion
v. – потреблять, тратить, расходовать depletion 
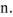 – истончение, уменьшение
– истончение, уменьшение
18 |
19 |

fossil fuel |
|
|
– природное топливо (газ и уголь), полезные |
|
ископаемые |
|
n. – место жительства, среда обитания |
||
habitat |
|
|
||
impact |
|
|
n. – влияние |
|
issue [ |
|
] n. – |
проблема |
|
polluter |
|
|
|
n.– источник загрязнения |
rate |
n.– показатель, величина, скорость |
|||
renewable |
|
|
a. – восстановимый, возобновляемый |
|
result in |
|
|
– приводить к |
|
see [ѕі ] v. – зд. рассматривать |
||||
shift |
n. – изменение, сдвиг |
|||
sophisticated |
|
a. – сложный |
||
waste |
|
n. – отходы |
||
Answer the following questions:
1.How does eco-architecture see buildings?
2.Why are buildings considered to be the most damaging polluters?
3.What represents the greatest source of climate-change gases?
4.When and why did the shift towards green design begin?
5.What did the oil crisis of the 1970s result in?
6.When did the rates of depletion in the ozone layer and the increase in greenhouse gases and global warming become apparent?
7.What new type of buildings do architecture-engineers need to design?
8.What are the key issues of green buildings?
9.How is the main concept of eco-architecture defined?
ПМ,ПМИ (IIсеместр)
COMPUTER SYSTEMS
A mainframe is the most powerful type of computer. It can process and store a large amountofdata.Itsupportsmultipleusersatthe same time and can support more simultaneous processes than a PC. The central system is a largeserverconnectedtohundredsofterminals overanetwork.Mainframesareusedforlargescale computing purposes in banks, big companies, and universities.
A desktop PC has its own processing unit, monitor, and keyboard. It is used as a personal computer in the home and as a workstation for group work.Typical examplesare theIBM PC and theApple Macintosh.
A laptop (also called a notebook PC) is a lightweight computer that can be transported easily.ItcanworkasfastasadesktopPC,with similar processors, memory capacity, and disk drivers, but it is portable and has a smaller screen.Insteadofmouse,theyhaveatouchpad built into a keyboard a sensitive pad that you can touch to move the pointer on the screen. They offer a lot of connectivity options: USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports for connecting peripherals, slots for memorycards, etc.
A tabletPC looks like a book witha screen on which you can write using special digital pen. Itcanbefoldedandrotated180degrees.Auser cantype at the detachedkeyboard oruse voice recognition.
20 |
21 |

Vocabulary: |
|
|
|
access [ |
|
– получать (доступ) |
|
connectivity |
|
–возможность соединения или |
|
подключения |
n. – настольный компьютер |
||
desktop |
|
||
detached |
|
a. – отдельный |
|
disk drive |
|
|
– дисковод |
keyboard |
|
|
– клавиатура |
|
n. |
||
laptop |
|
n – ноутбук |
|
mainframe |
|
n. – сервер, мощный компьютер |
|
memory capacity |
|
– объем памяти |
|
peripheral |
|
|
n.– внешнее устройство |
purpose |
|
n. – цель |
|
simultaneous |
|
a. – одновременный |
|
slot |
n. – слот, разъем на материнской плате |
||
tablet PC |
|
n. – планшетный компьютер |
|
terminal |
|
|
– электронное устройство, ПК (здесь) |
touchpad |
|
n. – сенсорная панель |
|
workstation |
|
n. – рабочая станция |
|
Answer the following questions:
1.What is the purpose of the mainframe?
2.What are the differences between mainframes and PCs?
3.What components does a desktop consist of?
4.What are the differences between desktops and laptops?
5.What unit is used instead of a mouse in laptops?
6.What do tablet PCs look like?
ПМ,ПМИ (III семестр)
THEWIDE WORLD WEB
WWW is a network of documents that works in a hypertext environment, i.e. using text that contains links,
hyperlinks to other documents.
Thefiles,webpages,arestoredincomputers, which actasservers.Aclientcomputerusesaweb browser,aspecialprogramtoaccessanddownload them. The pages are organized in websites, group of pages located on the Web, maintained by a webmaster, the manager of a website.
To find interesting sites a user can apply search engines, where the website information is compiled by spiders, computer-robot programs that collect information from sites by using keywords.
Websites usually have a beginning page or home page. From this startingpointausercannavigatebyclickingamouseonhyperlinksintexts or images.
The Web is an open door to a universe of multimedia resources that people use in many different ways. Here are some of them:
Web design
Web pages are created with a special language HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language), which is interpreted by a web browser to produce a hypertext, a blend of text, graphics and links.
Web pages can also include multimedia files: animation, audio and video files. Sounds are recorded with different audio formats.
To see and hear all these files, a user needs to download the right plug-in, the additional software that enables the web browser to support this new content.
22 |
23 |

Chatting and video conferencing
IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is a system that allows users to meet in channels (or chat rooms) in order to have a live conversation.
To participate you need to install a chat client, a special type of software,onthecomputertoconnecttothechatserver,thecomputerwhere the meeting takes place.
Video conferencing systems allow a live connection between two or more participants to exchange audio and video data. The users need a computer with broadband access, a webcam, a microphone and speakers.
Vocabulary: |
|
access |
v. – получить доступ |
allow |
– позволять, давать возможность (здесь) |
broadband |
– широкополосная сеть |
comply |
v. – подчинять |
content |
n.– информационное наполнение, содержимое |
download |
– загрузить, скачать |
enable |
v. – давать возможность |
environment |
n. – окружение |
hyperlink |
n. – гиперссылка |
hypertext |
n. – гипертекст – многоуровневый способ |
представления информации при помощи связей между документами
interpret |
v. – интерпретировать, переводить |
maintain |
v. – поддерживать |
navigate |
v. – передвигаться |
participant |
n. – участник |
plug-in |
n.– подключаемаяпрограмма,программноерасширение |
search engine |
– поисковая система |
support |
v. – поддерживать, обеспечивать |
universe |
n. – сфера, область, вселенная |
Answer the following questions:
1.What is the Wide World Web?
2.Where are web pages stored?
3.What does a client computer use to access and download web pages?
4.How are web pages organized?
5.What do users need to do to find interesting sites?
6.What is the starting point of a website?
7.What helps to create web pages?
8.What is the purpose of the plug-in?
9.What is IRC used for?
10.What is the purpose of video conferencing system?
24 |
25 |

ПМ,ПМИ (IVсеместр)
COMPUTER SOFTWAREAND HARDWARE
Computersoftwarereferstooneormorecomputerprogramsanddata held in the storage of a computer for some purpose. In computer science and software engineering, computer software is all information, programs and data processed by computer system.
There are three layers of software performing a variety of tasks: platform, application, and user software.
Platform software includes the basic input-output system, device drivers, an operating system, and a graphical user interface which allow a user to interact with the computer and its peripherals.
Typicalexamplesofapplicationsincludeofficesuitesandvideogames. Applicationsoftwareisoftenpurchasedseparatelyfromcomputerhardware. Sometimes applications are bundled with the computer, but applications arealmostalwaystheprogramsindependentoftheoperatingsystem,though they are often tailored for specific platforms.
User software tailors systems to meet the users specific needs. User softwareincludesspreadsheettemplates,wordprocessormacros,scientific simulations,graphicsandanimationscripts.Evenemailfiltersareakindof user software.
Computer software should be “loaded” into the computer’s storage (memory).
Computersoftwareiscalledsoincontrasttocomputerhardware,which includes mechanical, electrical, and electronic components of a computer system which stores and executes the software.
Computersoperatebyexecutingthecomputerprogram.Thisinvolves passing instructions from the application software, through the system software, to the hardware which receives the instruction as machine code.
Each instruction causes the computer to carry out an operation – moving data, carrying out a computation, or altering the flow of instructions.
Vocabulary:
application  n,– приложение bundle
n,– приложение bundle 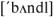
 v.– поставляться в комплекте
v.– поставляться в комплекте
devicedriver – драйвер устройства (программа, которая организует взаимодействие определенного устройства с компьютером)
officesuite |
– офисный пакет |
|
peripherals |
– внешнее устройство |
|
platform |
n.– аппаратная среда |
|
purchase |
v.– покупать |
|
script |
n.– скрипт |
|
spreadsheet |
n.– электроннаятаблица |
|
template |
n. – шаблон |
|
tailor |
v. – приспосабливать |
|
usersoftware |
– программные средства |
|
пользователя |
|
|
wordprocessormarco |
– макроязык |
|
текстового процессора |
|
|
Answer the following questions:
1.What is computer software and where is it held?
2.How many layers does software have?
3.What does platform software include?
4.What are typical examples of applications?
5.What are applications independent of?
6.What does user software include?
7.What are the components of hardware?
8.What does the computer program involve?
26 |
27 |

ТТП ЭТМК, ПМХ (II семестр)
INTERNALCOMBUSTIONENGINE
The principle of the internal combustion engine has not changed in thelast100years.Theenginetakesinfuelandairwhicharecompressedin a combustion chamber. Then, this mixture is ignited by a spark plug to produce an explosion, which moves the piston in the cylinder. The up and downmotionofthepistoninthecylinderisconvertedintorotationalmotion by crankshaft. The rotational force generated by the engine is known as torque. The size of the engine determines the power. The more cylinders thereare,themorepowerfulistheengine.Thispoweristransmittedthrough the clutch, the gearbox, the propeller shaft (in rear-wheel and four-wheel drive),and theaxles to the wheels.The position of theengine canvary,but itisusuallymountedatthefront.Insomesportscars,theengineismounted at the rear, for example Porsche, or in the middle, for example Ferrari or Lamborghini, because of weight distribution.
Enginescanbeclassifiedinmanydifferentways:bytheenginecycle used, the layout of the engine, source of energy, the use of engine, or by cooling system employed.
Commonlayoutsofenginesaretwo-strokeengine,four-strokeengine, six-stroke engine and diesel engine. Cylinder configurations include the straight or inline configuration and the V configuration.
Themostcommonformsofenginecoolingareair-cooledandwater-cooled. Engines are often classified by the fuels they used. They include
petroleum, coal, biofuels and hydrogen.
Vocabulary: |
|
|
combustion chamber |
– камера сгорания |
|
ignite |
v. – зажигать |
|
torque |
n. – крутящий момент |
|
clutch |
n. – сцепление |
|
gearbox |
n. – коробка передач |
|
Answer the following questions:
1.Where are fuel and air compressed?
2.How does the piston move in the cylinder?
3.What does a crankshaft do?
4.How is the power of the engine determined?
5.How is the power transmitted?
6.How can engines be classified?
28 |
29 |

ТТП, ЭТМК, ПМХ (III семестр)
AUTOMOBILESAFETY
Automobilesafetybecameaveryimportantissuefromthebeginning of mechanized road vehicle development. The second steam-powered car created by Nicolas Cugnot in 1771 crashed into a wall during its demonstration run.
Automobile safety is the study and practice of design, construction, equipmentandregulationtominimizethe occurrenceandconsequencesof automobile accidents. Improvements in roadway and automobile designs reduce injury and death rates.
There is active and passive safety. “Active safety” is used to prevent a crash and “passive safety” (airbags, seat belts andthe physical structures of the vehicle) helps to protect occupants during a crash. Crash avoidance systems and devices help the driver to avoid a collision.
Driver assistance systems include Automatic Braking systems to prevent the severity of collision, adaptive headlamps which control the directionandrangeoftheheadlightbeams,backupcamera,anti-lockbraking systems, emergencybrake assist systems, automated parking system.
Therearedifferentsystemsanddeviceswhichpreventtheseverityof injuries when a crash happens.
Seatbelts limit the forward motion of an occupant.Airbags inflate to cushion the impact of a vehicle occupant with various parts of the vehicles interior.Crumplezonesabsorb and dissipate the force of a collision.There are also pedestrian protectionsystems. Cargo barriers are sometimes fitted to provide a physical barrier, between passenger and cargo compartments in vehicles such as station wagons and vans.
Vocabulary: |
|
|
occurrence |
|
n.– происшествие, случай |
consequence |
|
n.– последствие |
injure |
|
– травмировать |
headlamp |
|
n. – фара |
severity |
|
n. – серьезность, опасность (травм) |
airbag |
|
n. – подушка безопасности |
crumple zone [ |
zə ] – зона смятия |
|
barrier[ |
] n. – перегородка |
|
headlight beam[ |
] – луч света фар |
|
Answer the following questions:
1.Whatbecameaveryimportantissuefromthebeginningofmechanized road vehicle development?
2.What does automobile safety mean?
3.What reduces injuries and death rates?
4.What is the difference between active and passive safety?
5.Which systems and devices prevent the severity of injuries?
30 |
31 |

ТТП, ЭТМК, ПМХ (IVсеместр)
HYBRID CARS
Hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine with an electric system. The aim of the electric powertrain is to achieve better fuel economy or better performance. There are many HEV types. Modern HEVs use improved technologywhichconvertsthevehicle’skineticenergyintoelectricenergy. Some HEVsusetheirinternalcombustionenginetogenerateelectricityby spinning an electrical generator.
Many HEVs reduce idle emissions by shutting down the internal combustion engine at idle and restarting it when needed.
Ahybrid-electricvehicleproduceslessemissionthanapure-gasoline burning vehicle. Hybrid electric vehicle can be classified according to the way in which power is supplied to the drivetrain.
Inparallel hybrids,the ICEand the electric motorarebothconnected tothemechanicaltransmissionandcantransmitpowertodrivethewheels.
In series hybrids onlythe electric motor drives the drivetrain, andthe ICE works as a generator to power the electric motor. Power-split hybrids have the benefits of a combination of series and parallel types.
Hybrids can be classified by degree of hybridization. Full hybrid is a vehiclethatrunsonlyonjusttheengine,onlyonthebatteriesorcombination of both. Mild hybrid is a vehicle that cannot be driven solelyon its electric motor,becausetheelectricmotordoesnothaveenoughpowertopropelthe vehicle on its own.
Vocabulary: |
|
|
hybrid electric vehicle |
– гибридный электро- |
|
мобиль |
|
|
powertrain |
– передача, трансмиссия |
|
convert |
v. – превращать |
|
generate |
– производить |
|
emission |
n. – выделение |
|
drivetrain |
n. – привод на ведущие колеса |
|
propel |
v. – двигать вперед |
|
Answer the following questions:
1.What does hybrid electric vehicle combine?
2.What is the aim of the electric vehicle?
3.What does modern HEV use?
4.What is a hybrid-electric vehicle special for?
5.How can HEVs be classified?
32 |
33 |

НТТС (II семестр)
CRANES
Acraneisamachinewhichcanbeusedbothtoliftandlowermaterials and to move them horizontally. It is one of the oldest types of construction equipment and one of the most useful on the building site. The first cranes were invented by ancient Greeks and were powered by men or animals. Modern cranes usually use internal combustion engines or electric motors and hydraulic systems to provide much greater capacity.
The main characteristic of a crane is its lifting capacity which varies with the boom reach and depends on the crane stability. Typical crane mechanismsarethefollowing:hoistingmechanism,travellingmechanism, slewing mechanism and luffing mechanism.
Differenttypesofcranesareavailablenow,forexampletowercranes, gantry cranes, overhead cranes, self-propelled mobile cranes mounted on wheelsorcrawlers.Eachtypeisadaptedtoaspecificuse.Sizesrangefrom thesmallestjibcranesusedinsidetheworkshopstothetallesttowercranes used for constructing high buildings.
Modern cranes are used for many purposes. Most of them are convertible. Versatility is added to the crane by different attachments and devices. They are attached to the end of the hoist line to handle materials. The examples of such devices are buckets for loose bulk material and concrete, hooks and grapples for lumber, pipes and drums.
Using cranes we concentrate building operations on a single site, increase the speed of construction and save building costs.
Vocabulary: |
|
|
|
crane |
|
– кран |
|
machine |
|
– машина |
|
equipment |
– оборудование |
|
|
site |
n. – участок |
|
|
ancient |
|
– древний |
|
power |
|
– приводить в действие |
|
internal combustion engine |
– двигатель |
||
внутреннего сгорания |
|
||
hydraulic |
|
– гидравлический |
|
capacity |
|
n. – мощность, производительность |
|
reach |
|
n.– радиус действия |
hoist |
|
v. – поднимать |
slew |
|
v. – поворачивать |
luff |
v. – перемещать по горизонтали, изменять вылет стрелы |
|
gantry |
|
a. – портальный ,эстакадный, козловой |
overhead |
|
n. – мостовой кран |
crawler |
|
n. – гусеница |
range |
|
v. – колебаться в пределах |
jib |
n. – стрела грузоподъемного крана |
|
purpose |
|
] n. – цель |
convertible |
a. – преобразуемый |
|
versatility |
n. – универсальность |
|
attachment |
n. – приспособление |
|
handle |
|
n. – транспортировать |
bucket |
|
n. – ковш |
hook |
|
n. – крюк |
grapple |
|
n. – захват |
Answer the following questions:
1.What are cranes used for?
2.Where were the first cranes invented?
3.How are modern cranes usually powered?
4.What are the main characteristics of a crane?
5.What crane mechanisms do you know?
6.What types of cranes are there?
7.What are different attachments and devices used for?
8.What attachments are there?
9.Why are cranes one of the most important construction equipment?
34 |
35 |

НТТС (III семестр)
EXCAVATORS
An excavator is an earth-digging machine designed for making trenches and pits, as well as for carrying out other kinds of earthwork involvedinconstruction.Asinglebucketexcavatorisanintermittentaction machine. Its working cycle consists of the following operations: cutting
someamountofearthfromasolidmass,carryingthedugsoiltoadumping place, emptying the bucket and returning to the initial position.
The fundamental mechanism of an excavator consists of the undercarriage which includes the tracks or wheels, the frame and the final drive.The final drive has a hydraulic motor and gears that provide drive to thetracks.Theoperator’scabin,engine,counterweights,hydraulicandfuel tanks are attached to the undercarriage to enable the excavator to swing 360 degrees without hindrance.
The workgroup of an excavator includes the boom, dipper or arm, and attachment (for example, bucket, auger or breaker). Mostly the boom can move only up and down, or in addition also shift towards the left and the right of the machine.An arm is attached to the boom end that imparts the force for digging into the ground. A bucket is fixed at the arm end for carrying the soil. In addition to the buckets, there are numerous other categories of different attachments and devices that are used for boring, crushing,liftingandripping.Thisexpandshydraulicexcavatorcapabilities far beyond excavation tasks with buckets.
Vocabulary: |
|
|
earth-digging |
] a. – землеройный |
|
design |
|
v. – проектировать, конструировать |
intermittent |
a. – периодический |
|
undercarriage |
n. – ходовая часть, шасси |
|
tracks |
|
n. – гусеницы |
frame |
|
n. – рама |
final drive |
|
– главная передача |
gear |
n.– шестерня, зубчатая передача; передаточный механизм, |
|
привод |
|
|
engine |
|
n. – двигатель |
counterweight |
n. – противовес |
|
fuel tank |
|
– топливный бак |
swing |
n. v. – поворот; поворачивать |
|
boom |
n. – стрела |
|
dipper |
|
n. – ковш |
auger |
n. – бур, сверло |
|
breaker |
|
n. – дробилка |
boring |
|
n. – бурение, сверление |
crushing |
|
n. – раздавливание, дробление |
ripping |
|
– рыхление |
Answer the following questions:
1.What are the main functions of an excavator?
2.What does the working cycle of an excavator consist of?
3.What does the undercarriage include?
4.What parts of an excavator do you know?
5.What mechanisms does the working group consist of?
6.How can the boom move?
7.How can an excavator be converted?
8.What expands hydraulic excavator capabilities?
36 |
37 |
