- •1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1.
- •2. Прочтите текст и скажите, как вы понимаете термины «информационное общество» и «компьютерная грамотность».
- •3. Просмотрите текст 1 еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
- •4. Прочтите, переведите и запомните следующие выраже ния:
- •5. Вспомните образование и случаи употребления The Past Simple Tense.
- •6. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2
- •7. Прочтите текст 2 и скажите, что такое компьютер и каковы его основные функции.
- •9. Найдите в тексте 2 английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
- •11. Выполните письменный перевод текста 3 по вариантам.
- •1. Выберите вариант, который лучше всего выражает глав ную идею текста 2.
- •2. Вставьте необходимые слова вместо пропусков.
- •3. Подберите к терминам, данным в левой колонке, определения, представленные справа.
- •1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1.
- •1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1
- •2. Прочтите текст и скажите, о каких первых вычислительных приборах рассказывается в нем.
- •3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
- •5. Вспомните значение следующих глаголов и подберите к ним производные. Например: to calculate — calculating, calculator, calculation.
- •2. Прочтите текст и скажите, как вы понимаете термины «обработка информации» и «иерархия запоминания информации».
- •5. Переведите следующие цепочки существительных:
- •6. Подберите к терминам, данным в левой колонке, опре деления, представленные справа.
- •10. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
- •11. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
- •12. Вспомните значение новых слов и догадайтесь о зна чении их производных.
- •2. Прочтите текст и скажите, о каких типах компьютеров и сферах их применения вы узнали.
- •3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, ис пользуя информацию текста.
- •4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
- •5. Образуйте (и переведите) имена существительные от приведенных ниже глаголов с помощью суффиксов:
- •6. Переведите предложения, содержащие Participle I и Participle II, в функции обстоятельства.
- •9. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
- •10. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
- •11. Вспомните значение новых слов и попытайтесь пере вести словосочетания, употребляемые с этими словами.
- •12. Озаглавьте каждый компонент текста и составьте небольшой реферат к нему (по вариантам).
- •2. Согласуйте слова в левой колонке с их интерпретацией, предложенной справа.
- •3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Дайте ответы на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
- •6. Вспомните значение новых слов и попытайтесь переве сти словосочетания, употребляемые с этими словами.
- •7. Вспомните значение следующих прилагательных и пре образуйте их в сравнительную и превосходную степени.
- •8. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2.
- •9. Прочтите текст 2 и скажите, какую дополнительную информацию вы узнали о действии основных устройств компьютера.
- •3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
- •4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
- •5. Вспомните значение новых слов и попытайтесь переве сти словосочетания, употребляемые с этими словами.
- •6. Найдите в тексте слова, близкие по значению следующим:
- •7. Переведите предложения, содержащие Perfect Participle Active и Perfect Participle Passive.
- •8. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2.
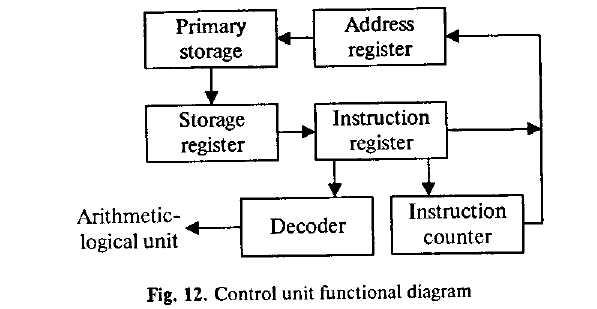
- •12. Опишите схему.
- •14. Выполните письменный перевод текста по вариантам.
- •4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
- •5. Вспомните значение новых слов и попытайтесь перевести словосочетания, употребляемые с этими словами.
- •6. Переведите предложения, содержащие независимый причастный оборот.
- •8. Прочтите текст и скажите, о каких компонентах центрального процессора и их назначении вы узнали. Переведите текст.
- •14. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 3.
- •3. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
- •4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
- •12. Расшифруйте следующие аббревиатуры и переведите их.
- •13. Переведите безличные предложения. Обратите внима ние на их специфику.
- •14. Вспомните формы причастий, проанализируйте и пе реведите следующие предложения:
- •16. Прочтите текст и составьте письменно реферат на английском языке.
- •1. Вставьте необходимые слова вместо пропусков.
- •2. Прочтите текст и объясните, как вы понимаете термин «компьютерное программирование».
- •3. Просмотрите текст еще раз и ответьте на вопросы, ис пользуя информацию текста.
- •4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
- •6. Переведите предложения, содержащие сослагательное наклонение.
- •8. Прочтите текст и объясните, что представляют собой языки программирования.
- •12. Переведите условные сложноподчиненные предложе ния. Обратите внимание на форму выражения разных типов условия.
- •13. Выполните перевод следующих текстов письменно по вариантам.
- •14. Прочтите тексты (по вариантам) и составьте рефераты на английском языке.
- •3. Определите неличные формы глагола, содержащиеся в следующих предложениях. Переведите их.
- •4. Выполните перевод грамматикализованных предложе ний.
- •197 Англо-русский словарь
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 100
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, ис пользуя информацию текста.
1. What words in computer science are used interchangeably and why? 2. What components make up the heart of the computer system. 3. What is the function of the CPU? 4. In what way does the CPU control the operation of the whole system? 5. Name the sequence of operations the CPU performs (use five verbs). 6. What are the CPU functional units made of? 7. What is the function of the CU? 8. What operations are performed in the ALU? 9. Where are data processed? 10. Where are data to be processed loaded into?
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
Хорошо известно; к компьютеру относятся; внутренняя память; составлять суть; выполнять; координировать деятельность; определяя в каком порядке; управлять работой всей системы; при необходимости; в соответствии с командами; уровни памяти; порт ввода-вывода; переключатели; режим включения или выключения; передавать сигналы; указывать последовательность пошаговых операций; основная память; управлять ходом выполнения програм-
101 Unit 8. Central Processing Unit
мы; с другой стороны; выполнять вычитание, сложение, возведение в степень, деление, умножение; для того чтобы.

5. Вспомните значение новых слов и попытайтесь перевести словосочетания, употребляемые с этими словами.
Direction: backward direction; clockwise direction; counterclockwise direction; data direction; forward direction; inverse / reverse direction; negative direction; positive direction; printing direction; transmission direction.
Level: access level; application level; data level; device level; difficulty level; error level; function level; hardware level; high level; input level; output level; performance level; presentation level; program level; protection level; resource level; security level; software level; structural level; system level; transmisson level.
Processor: arithmetic processor; central processor; command processor; control processor; data processor; error processor; general-purpose processor; special-purpose processor; image processor; language processor; mail processor; message processor; numeric processor; parallel processor; peripheral processor; text processor.
Switch: to switch between programs; to switch between windows; to switch disks; to switch on; to switch off; to switch over; binary switch; command switch.
Step: conversion step; final step; procedure step; program step; programming step; step by step; one step at a time; to step down; to step out; to step up; to take steps.
6. Переведите предложения, содержащие независимый причастный оборот.
1. Data being accessed randomly, semiconductor memories are called random access memory (RAM). 2. The information capacity of a single bit being limited to two alternatives, codes are based on combination of bits. 3. Primary storage having similarity to a function of the human brain, the storage is also called memory. 4. An electron leaving the surface, the metal becomes positively charged. 5. Computer system architecture being organized around the primary storage unit, all instructions must pass through it. 6. Computer system architecture is organized around the primary storage unit, all instructions passing through it.
7. Electromechanical memories depend upon moving mechan-