
- •II курс, семестр IV, лекция IV
- •Cardiac cycle
- •Phases of ventricular systole
- •Cardiac cycle
- •Ventricular diastole
- •Auscultation of the heart
- •Rules of auscultation
- •Additional maneuvers
- •Points of auscultation
- •Points for auscultation
- •Auscultation of the heart
- •Auscultation of the heart
- •Process of Auscultation
- •Process of Auscultation
- •S1 (systolic )
- •Factors that may influence the intensity of S1
- •S2 (diastolic)
- •Factors that may influence the intensity of S2
- •Differences between S1 and S2
- •Specific features of auscultation
- •I и II тоны
- •Changes of heart sounds
- •Physiological causes of cardiac sounds changes
- •Extracardiac causes of sound changes
- •Intensity of S1
- •Влияние длительности интервала PR на
- •Changes of S2
- •Decreased intensity of both sounds
- •Splitting of S1
- •Physiological split of S2
- •Physiological split of S2
- •Pathological split of S2
- •Paradoxical split of S2
- •Extra sounds
- •Добавочный IV тон
- •Summation gallop (triple rhythm)
- •Opening snap of mitral stenosis
- •Opening snap of mitral stenosis
- •Triple rhythm in mitral stenosis
- •Opening snap of mitral valve
- •Heart murmurs
- •Mechanisms of murmurs
- •Classification of murmurs
- •Description of murmurs
- •Grading the intensity of murmurs
- •Functional (innocent) murmurs
- •Functional murmurs
- •Pathologic murmurs
- •Etiology of systolic murmurs
- •Types of systolic murmurs
- •Mitral valve insufficiency
- •Etiology of diastolic murmurs
- •Types of diastolic murmurs
- •Aortic insufficiency
- •Extracardiac murmurs
- •Pulse and blood pressure
- •Arterial pulse
- •Palpation of the pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Assessment of pulse
- •Assessment of pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Assessment of the pulse on peripheral arteries
- •Assessment of the pulse on peripheral arteries
- •Auscultation of the arteries
- •Blood pressure measurement
- •Methods of BP measurement
- •Н.С.Коротков
- •The auscultatory method is commonly used in medical practice. The method was proposed
- •BP measurement
- •Rules of BP measurement
- •Rules of BP measurement
- •BP measurement
- •Classification of BP levels in adults
- •Arterial hypertension
- •Arterial hypotension
- •Methods of BP measurement
- •Diagnosis of arterial hypertension
- •Applanation tonometry
- •Applanation tonometry is a gold standard of central BP measurement
- •Methods of arterial compliance measurement
- •Спасибо за внимание
- •Выберите положение, верное в отношении I тона:
- •О чем свидетельствует выявляемый во время аускультации «ритм перепела»?
- •Физиологическое ослабление обоих тонов сердца наблюдается при ожирении
- •Для парадоксального расщепления II тона НЕ верно
- •Какие ошибки в измерении клинического АД

Classification of BP levels in adults
Category |
Systolic BP |
Diastolic BP |
|
|
|
|
|
Optimal |
<120 |
и |
<80 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Normal |
120-129 |
и/или |
80-84 |
|
|
|
|
High normal |
130-139 |
и/или |
85-89 |
|
|
|
|
1st degree AH |
140-159 |
и/или |
90-99 |
2nd degree AH |
160-179 |
и/или |
100-109 |
|
|
|
|
3rd degree AH |
≥180 |
и/или |
≥110 |
|
|
|
|
ISH |
≥140 |
и |
<90 |
|
|
|
|
Is assessed only in patients previously not receiving AHT
Arterial hypertension
Stable elevation of
SBP >140 and/or DBP >90 mmHg. In patients not receiving antihypertensive therapy,
At repeated visits to the doctor
Arterial hypotension
Causes:
Acute and chronic vascular insufficiency Acute and chronic adrenal gland insufficiency
Clinical presentation:Severe weaknesssyncopeSweating
Pulsus filiformisLow BP
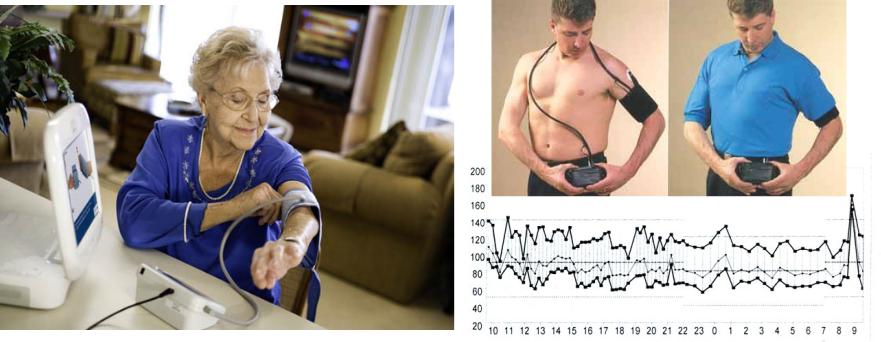
Methods of BP measurement
Office |
|
Ambulatory: |
|
HBPM |
ABPM |
Self-monitoring of BP |
24-h monitoring |

Diagnosis of arterial hypertension
|
Systolic BP, mmHg |
Diastolic BP, |
|
|
mmHg. |
|
|
|
Office |
140 |
90 |
|
|
|
24-hours (ABPM) |
130 |
80 |
|
|
|
daytime |
135 |
85 |
|
|
|
nighttime |
120 |
70 |
|
|
|
HBPM |
135 |
85 |
|
|
|

Applanation tonometry
Pulse wave contour analysis
Indications:
•Non-invasive measurement of central aortic BP
•Assessment of arterial stiffness
Main parameters:
•Central SBP and DBP
•Central pulse pressure
•Augmentation index
•Pulse wave velocity (PWV)
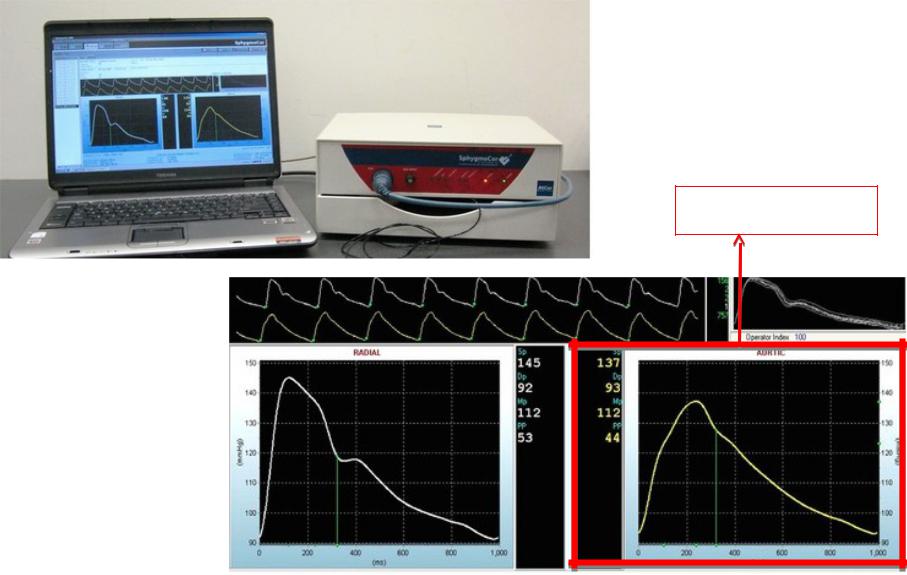
Applanation tonometry is a gold standard of central BP measurement
Aortic BP
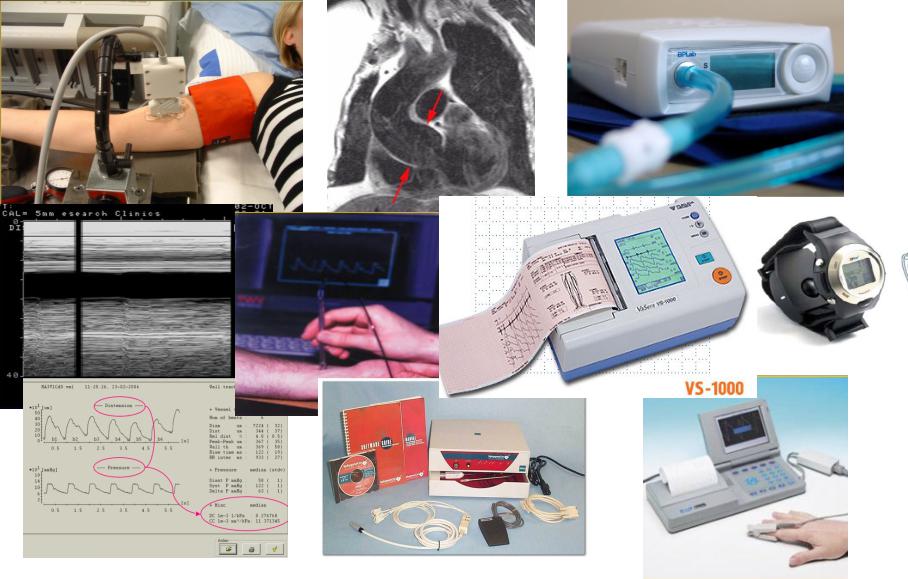
Methods of arterial compliance measurement
Спасибо за внимание
Выберите положение, верное в отношении I тона:
A.возникает в диастолу
B.оценивается на основании сердца
C.совпадает с верхушечным толчком и пульсацией на сонной артерии
D.является добавочным тоном
