
Conclusion
Market is new and underdeveloped, therefore the nature of competition is specific. The products are heterogeneous and protected by patents and the amount of firms-producers is fairly low. The market has noticeable geographical differentiation, because free movement of the products around the globe does not exist due to different local pharmacological and healthcare legislation and different ethical perception.
Major part of products is protected with patents, which last for a long time, usually for 10 years. This fact is very crucial for competitors and potential entrants – these companies cannot easily and instantly entice competitors’ customers.
Therefore severe price competition and price wars barely exist if exist at all. Companies do not have high enough production capacity to maintain the price war long enough to achieve any result.
In the long term the firm producing a particular product loses its unique right to produce it as the patent expires. Due to this fact every competitor acquires the right to produce it – the product changes its nature from heterogeneous to homogeneous. Thus the firm should implement the following strategy:
Keep producing the first product because it still has high market share but the market growth rate for this product decreases.
Conduct R&D in order to form a new product.
Launch the new product.
New product develops
Cash Cows
Question marks
Dogs
Stars
Market Growth Rate (Cash
usage)
High
Low
Low
High
Relative Market Share (Cash
generation)


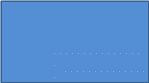









Old product reaches maturity
This BCG matrix shows better the idea of long-term profitability when we lose the unique right to produce the first product (orange circle) and implement another one (red circle).
The alternative strategy is to improve our primary product and take out a patent on a modified product.
Another strategy is to improve the production cycle, e.g. implement new material saving technology.
Sources
The world pharmaceutical industry, James H. Taggart
Cognition Enhancers, Roy Jones, Kelly Morris http://www.bis.gov.uk/assets/bispartners/foresight/docs/brain-science/cognition-enhancers.pdf
Economics of Addiction and Drugs, Jonathan Cave, Christine Godfrey
http://www.bis.gov.uk/assets/bispartners/foresight/docs/brain-science/economics.pdf
Smart drugs 2: next generation, Ward Dean, John Morgenthaler and Steven Fowkes
http://bltc.com/library/library.htm
Cognitive Commodities in the Neuro Marketplace, James Kent
http://hplusmagazine.com/2009/12/23/cognitive-commodities-neuro-marketplace/
Cognition Enhancers: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives, Shubhada R. Ingole, Satyendra K. Rajput and S.S. Sharma
http://www.niper.ac.in/cognition.pdf
Анализ аптечных продаж ноотропных препаратов, Светлана Горелова
http://www.economist.com/node/11402761
Обзор рынка ноотропных препаратов, Леонид Коковин, http://www.rosapteki.ru/arhiv/detail.php?ID=1432
Smart policy: cognitive enhancement and the public interest, Nick Bostrom, Rebecca Roache
http://www.fhi.ox.ac.uk/__data/assets/pdf_file/0008/10241/smart-policy.pdf
Cognition Enhancers: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives, http://www.niper.ac.in/cognition.pdf
Cardiovascular segment, http://www.ipapharma.org/pp/IPA%20April%2010[1].pdf
TARGETING THE CREB PATHWAY FOR MEMORY ENHANCERS, http://pharmacology.ucsd.edu/graduate/courseinfo/Tully-Tullyetal(2003).pdf
Mechanisms of Action of Cognitive Enhancers on Neuroreceptors, http://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/27/11/1701/_pdf
Pharmexpert. Market Research Center, http://www.pharmexpert.ru/en/
