
6 курс / Кардиология / И_А_Овсыщер_Ведение_больных_после_РЧИ_УЛВ
.pdf
Ben Gurion University
Ведение больных после немедикаментозного лечения аритмий
Профессор И. Овсыщер
I. Eli Ovsyshcher, MD, PhD,
FESC, FACC, FHRS, FAHA
Professor of Medicine/Cardiology
Faculty of Health Sciences,
Ben Gurion University of the Negev,
Beer-Sheva, Israel
Санкт-Петербург, Май, 2011

LMWH-low molecular weight heparin; OACoral anticoagulant; UFHunfractionated heparin.

Follow-up After AF Ablation
Anticoagulation
Initially post-ablation, LMWHlow molecular weight heparin; or i.v. UFHunfractionated heparin should be used as a bridge to continuation of systemic anticoagulation, which should be continued for a minimum of 3 months, although some centers do not interrupt anticoagulation for the ablation procedure.
Thereafter, the individual stroke risk of the patient should determine whether OAC should be continued.
Discontinuation of warfarin post-ablation is generally not recommended in pts at risk for stroke, as AF is a chronically progressing arrhythmia, especially in pts at risk for stroke.

Follow-up After AF Ablation
Monitoring for AF Recurrences
The clinical assessment 3 months after AF ablation remains unclear.
Symptom-based FU may be sufficient, as symptom relief is the main aim of ablation.
To obtain information regarding real heart rate systematic, ECG monitoring is needed.
Expert consensus recommends an initial FU visit at 3 months, with 6 monthly intervals thereafter for at least 2 years. In this situation the true recurrence rate will be markedly underestimated.
Kirchhof P, et al. Eur Heart J 2007;28:2803–2817.
Calkins H, et al. Europace 2007;9:335–379.

Silent/Asymptomatic AF
There are two clinical manifestations of AF:
Symptomatic AF
Silent/Asymptomatic AF
In pts with PAF, asymptomatic AF far more frequently than symptomatic ones: almost 13 times more frequent1
PAFAC (Prevention of AF after cardioversion)2:
70% asymptomatic
SOPAT (Suppression of paroxysmal atrial tachyarrhythmias)3:
58% asymptomatic
1.Page RL, et al. Circulation 1994; 89:224-7
2.Fetsch T, et al., Eur Heart J 2004; 25: 1385-94
3.Patten M, et al. Eur Heart J 2004; 25:1395-1404

Asymptomatic AF After Ablation
Asymptomatic AF occurs in pts presenting with highly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
symptomatic |
|
AF who qualify for catheter ablation: |
|||||||||||||||||||
AF |
treated |
100 |
|
|
% of pts. with only asymptomatic AF among all pts. with AF recurrences |
||||||||||||||||
documented |
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
% of |
pts. |
with symptomatic AF among all pts. with AF recurrences |
|||||||||||||||
Before80 |
|
ablation, |
>50% of pts showed a mixture of |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
symptomatic and asymptomatic AF, whereas only |
|||||||||||||||||||||
withpatients |
patientsallamong |
60 |
|
|
5% |
22%* |
38%* |
* = < 0.05 |
36%* |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
37%* |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
38% of pts recognized all AF episodes accurately. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95% |
78%* |
|
|
62%* |
|
|
|
63%* |
|
|
|
64%* |
|
|
|
||
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
% of |
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
After catheter ablation, the incidence of asymptomatic AF significantly increased (4-7.6 fold):
From 5% at baseline to 22% after ablation (P=0.027),
To 38% at 3-month follow-up (P=0.021)
To 37% at 6-month follow-up (P=0.021)
To 36% at 12-month follow-up (P=0.05).
Hindricks G, et al. Perception of atrial fibrillation before and after radiofrequency catheter ablation: relevance of asymptomatic arrhythmia recurrence. Circulation. 2005;112:307–313.

Can Be Predicted Silent AF?
There is a lack of correlation between AF symptoms and heart rate variation at the onset of AF, episode duration, and the presence of heart disease and antiarrhythmic treatment (drugs, ablations).
Probably the major determinant of AF symptoms is the subjective perception of each patient as well as perception of pain.
Hindricks G, et al. Circ Arrhythm EP. 2010;3:141
Hindricks G, et al. Circulation 2005; 112:307.
Quarino G, et al. PACE 2009; 32:91.
Senatore G, et al. JACCC 2005; 45:873.

Clinical Implications of Asymptomatic AF

AFFIRM: Adverse Events
|
Rate Control (AF) |
Rhythm Control (SR) |
|
|
|
|
|
Ischemic Stroke |
5.7%* |
7.3%* |
|
|
|
|
|
Symptomatic AF at |
69% (31%) |
36% (64%) |
|
time of event** |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Sinus Rhythm** |
45% |
65% |
|
|
|
|
|
INR > 2.0 |
30% |
22% |
|
|
|
|
|
INR < 2.0 |
35% |
20% |
|
|
|
|
|
Not taking warfarin |
33% |
58% |
|
|
|
|
*Event rates derived from Kaplan-Meier analysis, p = 0.680
**Such equal amount of adverse events in patients with AF and SR can be explained only by silent AF events in patients with SR.
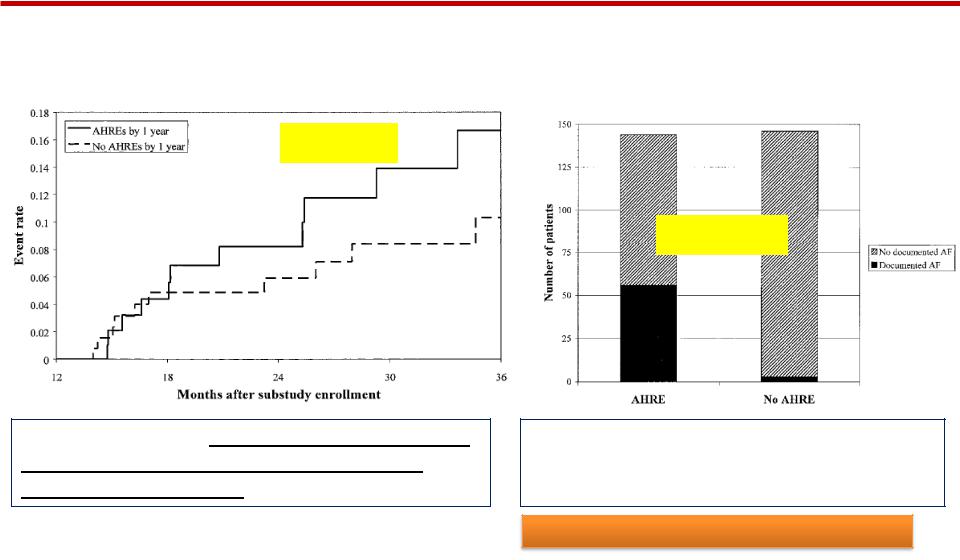
Atrial High Rate Events Detected by Pacemaker Diagnostics Predict Death and Stroke (MOST Trial)
|
Documented AF in pts with AHREs |
Death or nonfatal stroke |
vs pts without AHREs; |
P<0.001
P<0.0001
AF
Kaplan-Meier plot of death or nonfatal stroke after 1 year of FU in pts with atrial high rate events (AHREs) vs those without; P=0.001.
In pts with atrial high rate event (AHRE) AF observed in 40% vs. 3% in those without; P=0.0001.
Glotzer TV et al., Circulation 2003;107:1614
