
- •DERMATOLOGY 3.001-3.003
- •Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
- •Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
- •Implantation dermoid cysts
- •Amelanotic malignant melanoma
- •Amelanotic malignant melanoma
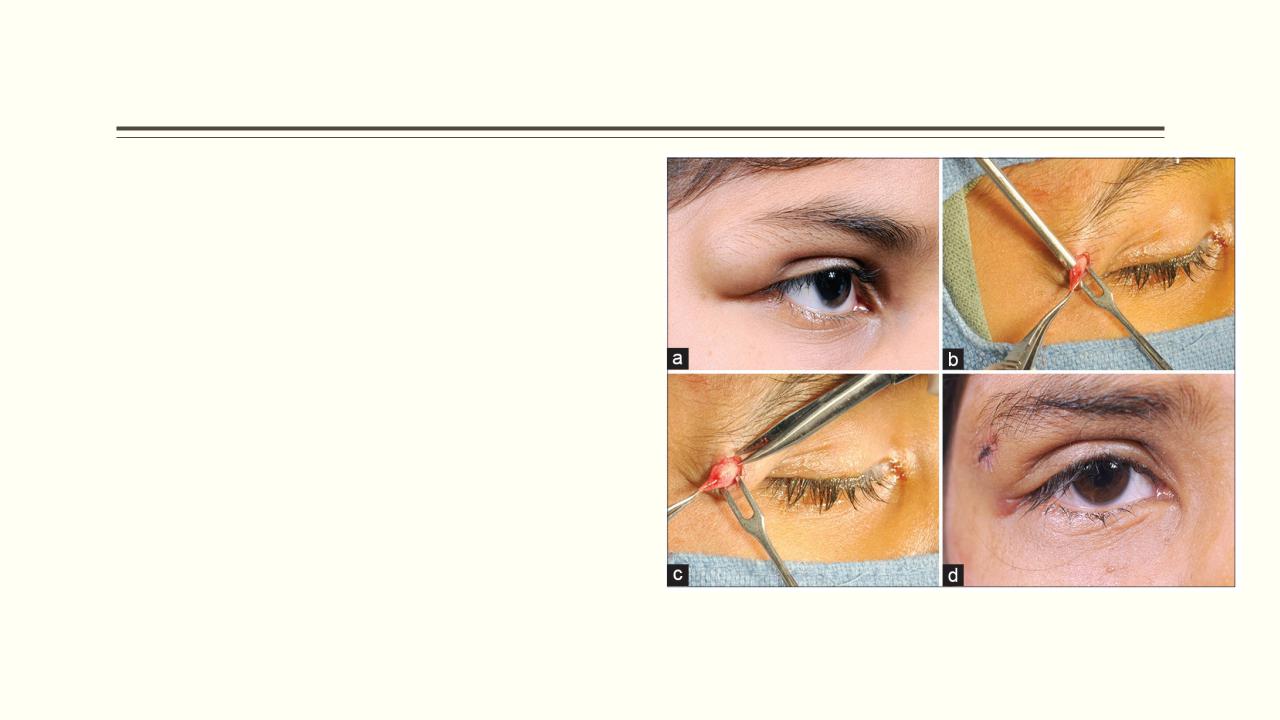
- •External angular dermoids
- •Keratoacanthoma
- •Malignant melanoma
- •Melanoma
- •Melanoma
- •Management points for naevi and melanomas
- •Neuropathic ulcer
- •Diabetic foot ulcer
- •Burkholderia pseudomallei
- •Burkholderia pseudomallei
- •Necrotising fasciitis
- •Erythema ab igne

DERMATOLOGY 3.001-3.003
Handbook

3.001

Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Age: usually >35 yearsMore frequent in males
Mostly on sun-exposed areas: face (mainly), neck, upper trunk, limbs
May ulcerate easily = ‘rodent ulcer’Slow-growing over years
Has various forms: nodular, pigmented, ulcerated, etc.
Does not metastasise via lymph nodes or bloodstream
Management:
Simple elliptical excision (3–4 mm margin) is best.
Photodynamic therapy—response rate is >90% for nodular and superficial BCCs.
Cryotherapy is suitable for well- defined, histologically confirmed, superficial tumours at sites away from head and neck.

Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Pearly edge 

Implantation dermoid cysts
as the result of implantation of epidermal fragments into the dermis by a penetrating injury.
The epidermis continues to grow and forms a cyst lined with stratified squamous epithelium and filled with keratin

Amelanotic malignant melanoma
•Amelanotic melanoma is a form of melanoma
•The malignant cells have little to no pigment
•Risk factors: Increasing age, Sun-exposed skin
Treatment:
wide local excision of the wound with a 10–20 mm margin of normal tissue
Amelanotic melanoma can metastasis. These cases require individualized
treatment that may include surgery,
• May present as an erythematous scaly
macule, plaque, or nodule with irregular radiotherapy, chemotherapy borders

Amelanotic malignant melanoma
External angular dermoids
Looks like subcutaneous lumps at the lateral angle of the eye
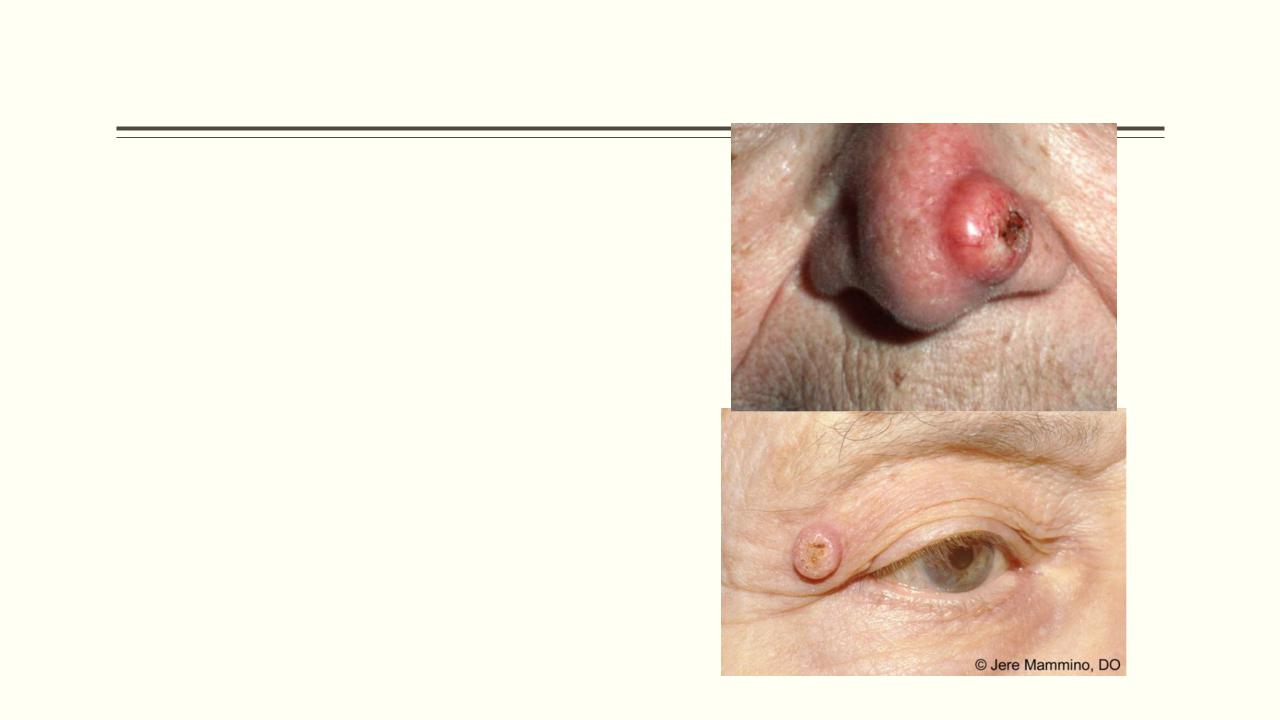
Keratoacanthoma
Tumour of keratinocytes
Occur singly on light-exposed areas
Raised crater with central keratin plug
Grows to 2 cm or more
Can be confused with SCC
Treatment is surgical excision and histological examination. Ensure a 2–3 mm margin for excision.
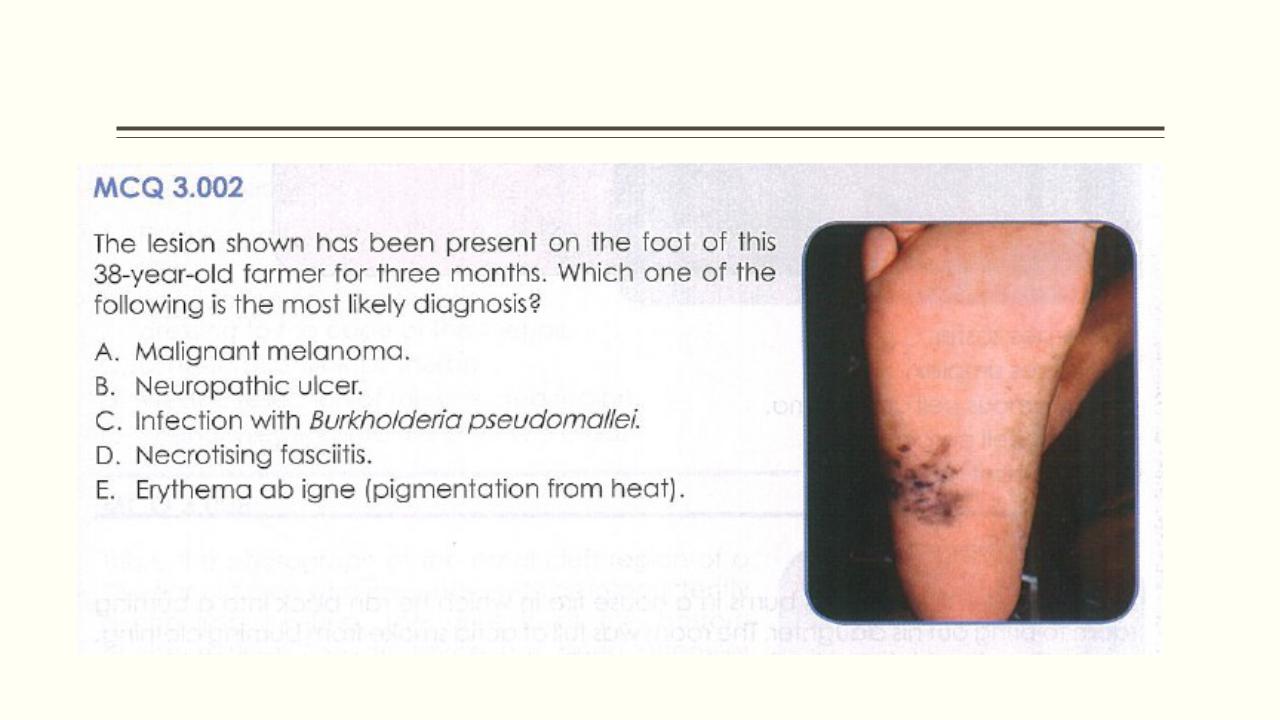
3.002
